Adsorption and desorption are two fundamental phenomena that occur at the interface of two phases, typically solid and liquid or solid and gas. These processes are pivotal in the fields of chemistry, physics, and various industries, playing a crucial role in operations ranging from water treatment to gas storage. At their core, they involve the adhesion of atoms, ions, or molecules from a gas, liquid, or dissolved solid to a surface.
The difference between adsorption and desorption lies primarily in the direction of the process. Adsorption is the accumulation of particles on a surface, leading to a higher concentration on the surface than in the bulk material. In contrast, desorption involves the release of adsorbed particles from a surface, decreasing their concentration on the surface relative to the bulk material.
Adsorption and desorption are not just isolated processes but are interconnected in a dynamic equilibrium. This balance is essential for various applications, such as catalysis, sensor technology, and environmental cleanup. Understanding the factors that influence these processes, including surface area, pressure, and temperature, is crucial for optimizing their use in industrial and environmental applications.
Adsorption Explained
Basics of Adsorption
Definition and how it works
Adsorption is a surface phenomenon where molecules from a gas, liquid, or dissolved solid (adsorbate) adhere to the surface of a solid or liquid (adsorbent). This process results in a higher concentration of the adsorbate on the surface than in the bulk phase. Adsorption occurs due to the attractive forces between the adsorbate and the adsorbent. These forces can be physical, such as van der Waals forces in physical adsorption, or chemical, involving the formation of covalent bonds in chemical adsorption.
Types of adsorption
- Physical adsorption (Physisorption): Characterized by weak van der Waals forces, reversible, and occurs at lower temperatures.
- Chemical adsorption (Chemisorption): Involves stronger chemical bonds, is usually irreversible, and occurs at higher temperatures.
Factors Influencing Adsorption
Surface area
- The surface area of the adsorbent is crucial. A larger surface area provides more sites for adsorption, enhancing the process.
Pressure
- Pressure increases the concentration of adsorbate molecules around the adsorbent, promoting adsorption. The relationship is described by the adsorption isotherms.
Temperature
- Generally, an increase in temperature reduces physical adsorption due to increased molecular kinetic energy but may increase chemisorption up to a point.
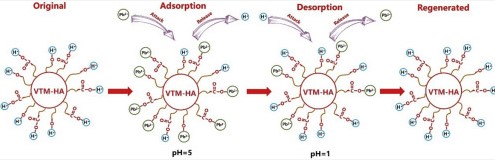
Desorption Explained
Basics of Desorption
Definition and mechanism
Desorption is the process by which adsorbed molecules leave the surface and return to the bulk phase. This can be seen as the reverse of adsorption, driven by changes in conditions like temperature or pressure that reduce the attractive forces between the adsorbate and adsorbent.
Desorption types
- Thermal desorption: Triggered by heating the system.
- Pressure swing desorption: Utilizes pressure changes to induce desorption.
- Chemical desorption: Involves chemical reactions that release adsorbed species.
Factors Influencing Desorption
Binding strength
- The strength of the bond between the adsorbate and adsorbent impacts the ease of desorption. Weaker bonds facilitate easier desorption.
Heat application
- Applying heat can provide adsorbed molecules with enough energy to overcome adsorption forces, leading to desorption.
Pressure changes
- Reducing the pressure can shift the equilibrium towards desorption, especially in processes like pressure swing adsorption.
Key Differences
Process Comparison
Direction of the phenomenon
- Adsorption involves the accumulation of particles on a surface, while desorption involves their release.
Energy changes
- Adsorption releases energy as heat, typically exothermic. Desorption requires energy input to break the interactions between adsorbate and adsorbent.
Application Variance
Industrial uses of adsorption
- Water treatment: Removing contaminants.
- Air purification: Adsorbing pollutants and odors.
- Gas storage: Hydrogen storage in fuel cells.
Industrial uses of desorption
- Regeneration of adsorbents: Reusing materials in adsorption processes.
- Analytical chemistry: In techniques like thermal desorption gas chromatography.
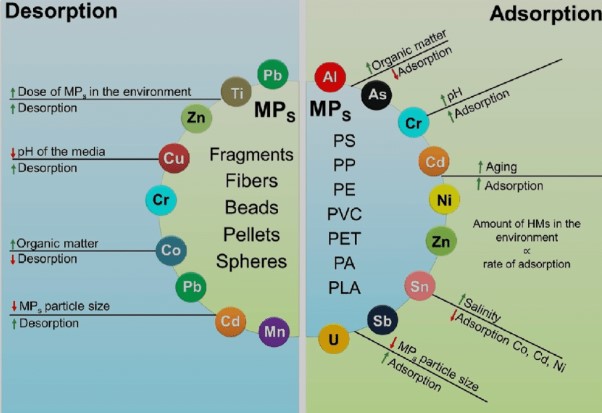
Similarities and Connections
Underlying Principles
Surface interaction
Both adsorption and desorption rely heavily on surface interactions. These interactions dictate how molecules attach to or detach from a surface, influenced by the characteristics of both the adsorbate and adsorbent. The nature of these interactions, whether physical or chemical, sets the foundation for how these processes are utilized across various applications.
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a key player in both adsorption and desorption, with energy changes guiding the direction and efficiency of these processes. The principles of thermodynamics explain why adsorption usually releases heat (exothermic) and desorption requires energy input. Understanding these energy dynamics is crucial for designing systems that efficiently utilize these phenomena.
Role in Industry
Cleaning processes
In industries like water treatment and air purification, adsorption serves as a primary method for removing contaminants. The efficiency of adsorption in trapping pollutants makes it indispensable in maintaining environmental health and safety.
Separation techniques
Both adsorption and desorption are fundamental to separation techniques in chemical processing. Adsorption allows for the selective capture of specific compounds, while desorption enables their recovery from the adsorbent, facilitating the separation of mixtures into their constituent components.
Practical Applications
Adsorption Applications
Water treatment
In water treatment, adsorption is used to remove pollutants, including organic compounds and heavy metals, from water, making it safe for consumption and release into the environment. Activated carbon is a widely used adsorbent because of its high surface area and strong affinity for various contaminants.
Gas storage
Adsorption is key in gas storage applications, especially for gases like hydrogen and methane. Materials with high surface areas, such as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), allow for the storage of large volumes of gas under relatively low pressure, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Desorption Applications
Material regeneration
Desorption enables the regeneration of adsorbent materials, allowing them to be reused in processes like water treatment. This not only extends the life of the adsorbent but also reduces waste and operational costs.
Analytical chemistry
In analytical chemistry, desorption techniques, such as thermal desorption, are used to release adsorbed substances from a sample. This is crucial in gas chromatography and mass spectrometry, where it aids in the identification and quantification of various compounds.
Technological Advances
Innovations in Adsorption
New materials
Recent advancements have introduced new materials like MOFs and graphene-based adsorbents. These materials offer higher surface areas and specificity, improving the efficiency and selectivity of adsorption processes.
Efficiency improvements
Technological innovations have focused on improving the energy efficiency of adsorption processes. Developments include better heat management systems and the design of adsorbents that operate effectively at lower temperatures or pressures.
Innovations in Desorption
Enhanced techniques
Enhancements in desorption techniques, such as microwave-assisted desorption, have been developed. These methods aim to reduce the energy required for desorption, speeding up the process and lowering operational costs.
Energy reduction strategies
Strategies to reduce energy consumption in desorption include the use of alternative energy sources, like solar thermal energy, and the optimization of process parameters to minimize energy requirements.
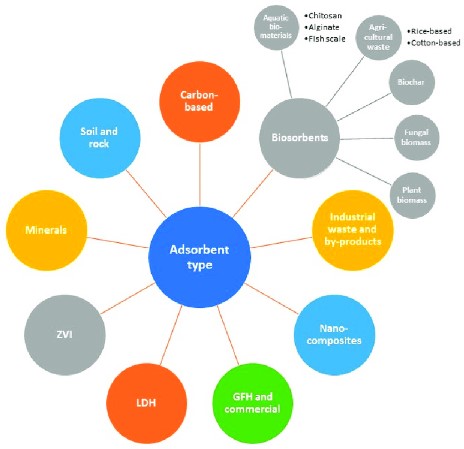
Environmental Impact
Adsorption’s Role
Pollution control
Adsorption plays a critical role in controlling pollution by capturing contaminants from air and water. This not only helps in maintaining environmental health but also aids in achieving regulatory compliance in industries.
Resource recovery
Through adsorption, valuable resources, such as precious metals from industrial wastewater, can be recovered. This contributes to resource efficiency and sustainability by enabling the recycling of materials.
Desorption’s Role
Waste treatment
Desorption is vital in waste treatment processes, where it allows for the detoxification and recovery of pollutants adsorbed onto materials. This process helps in the sustainable management of waste, turning pollutants into recoverable resources.
Energy consumption
While desorption is an energy-intensive process, ongoing research and technological advancements aim to reduce its energy footprint. This is crucial for making both adsorption and desorption more environmentally friendly and economically viable in large-scale applications.
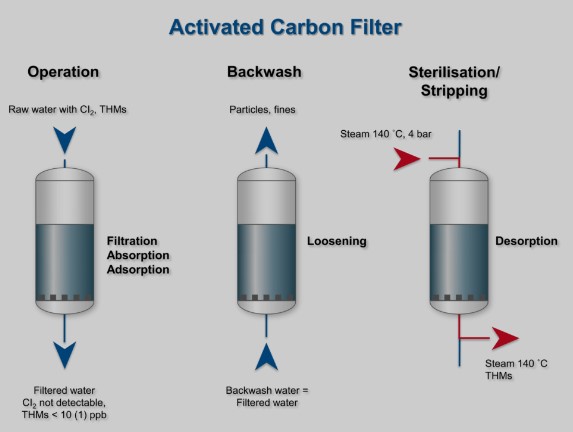
Frequently Asked Questions
What is adsorption?
Adsorption is a surface phenomenon where atoms, ions, or molecules from a gas, liquid, or dissolved solid adhere to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent, occurring due to various forces, including ionic, covalent, and van der Waals forces.
How does temperature affect adsorption?
Temperature plays a significant role in adsorption; generally, as temperature increases, adsorption decreases. This is because higher temperatures provide the adsorbate molecules with more kinetic energy, overcoming the attractive forces of the adsorbent surface. However, the effect can vary based on the type of adsorption process (physical or chemical adsorption).
Can adsorption be reversed?
Yes, adsorption can be reversed through a process known as desorption. Desorption occurs when the adsorbed molecules on the surface gain enough energy to overcome the attractive forces holding them to the surface, allowing them to return to the bulk phase. This can be achieved by changing conditions such as temperature, pressure, or chemical composition.
What is the significance of desorption in environmental applications?
Desorption is significant in environmental applications for processes like pollutant removal and regeneration of adsorbents. For instance, desorption allows for the recovery and recycling of adsorbed chemicals from water treatment processes, reducing waste and making the process more sustainable.
Conclusion
The intricate balance between adsorption and desorption underpins many of the technologies and processes that are fundamental to modern industry and environmental management. Understanding these phenomena is not just an academic exercise but a practical necessity to innovate and improve applications ranging from catalysis to pollution control. The future advancements in material science and process engineering will undoubtedly reveal even more efficient ways to harness these processes for technological and environmental benefits.
As we continue to explore and refine the applications of adsorption and desorption, their significance across various industries cannot be overstated. The ongoing research and development efforts aim to enhance efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and mitigate environmental impacts, ensuring that these processes remain at the forefront of sustainable technology.