Hydrolysis is a fundamental chemical process that plays a pivotal role in the degradation of complex molecules into simpler forms. It is essential for numerous industrial applications, from biofuel production to waste management, and is equally critical in biological systems, where it breaks down nutrients and macromolecules. The process involves the reaction of water with another compound, leading to the disintegration of chemical bonds in the latter.
The core difference between acid hydrolysis and enzymatic hydrolysis lies in their respective catalysts and mechanisms. Acid hydrolysis uses inorganic acids to accelerate the breakdown of complex molecules, making it faster and more aggressive. In contrast, enzymatic hydrolysis employs specific enzymes to target bonds within a molecule, offering a more selective and less environmentally damaging approach.
Both methods have their distinct advantages, applications, and limitations. Acid hydrolysis, known for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, is widely used in industries that require the rapid processing of materials. Enzymatic hydrolysis, however, shines in applications where precision and environmental sustainability are paramount, despite its higher operational costs. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate hydrolysis method for a given application, balancing efficiency, cost, and ecological impact.

Basics of Hydrolysis
Definition and Process
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction where water splits molecules into smaller parts. This fundamental process plays a crucial role in breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones. Hydrolysis occurs naturally in our bodies, helping to digest food, and is also a critical process in many industrial applications.
Role in Breaking Down Complex Molecules
Hydrolysis enables the transformation of large, complex substances into more manageable and useful forms. For example, in our digestive system, hydrolysis breaks down proteins into amino acids, making them accessible for our bodies to use. Similarly, in industries, hydrolysis is used to convert cellulose from plants into glucose for biofuel production.
Types of Hydrolysis
There are several methods of hydrolysis, each with its specific applications and benefits. The two main types we’ll focus on are acid hydrolysis and enzymatic hydrolysis. These methods differ mainly in the catalysts used to initiate the reaction: acids or enzymes.
Introduction to Acid and Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Acid hydrolysis uses acids as catalysts to accelerate the breaking down of molecules. This method is known for its efficiency and is widely used in various industries. On the other hand, enzymatic hydrolysis employs enzymes—proteins that act as biological catalysts—to selectively break bonds within molecules. This method is celebrated for its specificity and reduced environmental impact.
Acid Hydrolysis
Overview
Acid hydrolysis is a process where inorganic acids (such as sulfuric acid) are used to catalyze the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones. It’s a robust method, often employed to process materials that are resistant to other types of degradation.
Definition and Mechanism
In acid hydrolysis, the acid not only provides H+ ions that facilitate the breaking of molecular bonds but also accelerates the reaction, making it much faster than it would be in neutral conditions. The choice of acid and concentration can significantly affect the efficiency and outcome of the reaction.
Common Uses in Industry
This method is extensively used in the paper and textile industries for the hydrolysis of cellulose, in biofuel production to break down biomass into fermentable sugars, and in the food industry for various processes, including hydrolyzing proteins to produce soy sauce and other flavorings.
Advantages
Cost-effectiveness
Acid hydrolysis is generally less expensive than enzymatic methods, making it an attractive option for industries that process large volumes of material.
Efficiency for Certain Materials
It is particularly efficient for breaking down cellulose and other tough materials that might not be easily processed by other means.
Disadvantages
Environmental Impact
The use of strong acids can lead to environmental concerns, including acid runoff and the need for neutralization steps post-reaction.
Lack of Specificity
Acid hydrolysis is not as selective as enzymatic hydrolysis, which can lead to the breakdown of desired molecules along with the target molecules.
Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Overview
Enzymatic hydrolysis uses specific enzymes to catalyze the hydrolysis of complex molecules. This method is highly selective, allowing for the targeted breakdown of specific bonds without affecting the rest of the molecule.
Definition and How It Works
Enzymes are natural catalysts that increase the rate of reactions by lowering the activation energy. In enzymatic hydrolysis, specific enzymes target and cleave specific bonds within a molecule, leading to its breakdown into desired products.
Biotechnological Applications
Enzymatic hydrolysis has a wide range of applications in biotechnology, including the production of biofuels, where enzymes are used to convert biomass into sugars, and in the pharmaceutical industry, for the synthesis of certain drugs.
Advantages
Specificity and Selectivity
Enzymatic hydrolysis is highly specific, allowing for the precise targeting of certain bonds, which is invaluable in applications requiring precision.
Lower Environmental Footprint
This method produces fewer byproducts and requires less energy, contributing to a lower environmental impact compared to acid hydrolysis.
Disadvantages
Higher Costs
The production and purification of enzymes can be expensive, making enzymatic hydrolysis more costly than acid-based methods.
Sensitivity to Conditions
Enzymes are sensitive to their environment, including pH and temperature, which can limit the conditions under which enzymatic hydrolysis can occur effectively.
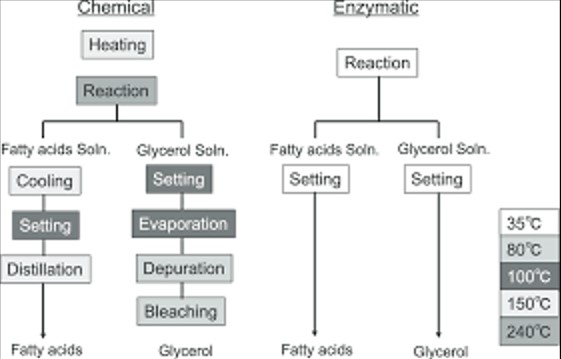
Comparative Analysis
Efficiency and Selectivity
When comparing acid hydrolysis and enzymatic hydrolysis, two key factors stand out: efficiency and selectivity. Acid hydrolysis is known for its robust efficiency, capable of breaking down a wide range of materials quickly. This method excels in processing materials resistant to other forms of degradation, making it invaluable in settings where time is of the essence. However, its broad reactivity spectrum means it lacks the finesse and selectivity of enzymatic hydrolysis.
Enzymatic hydrolysis, in contrast, shines in its selectivity. Specific enzymes can target precise bonds within a molecule, leaving the surrounding structures intact. This selectivity is crucial in industries where the integrity of the final product must be maintained, such as in the pharmaceutical and food industries. While enzymatic hydrolysis may operate at a slower pace compared to acid hydrolysis, its precision ensures that the right bonds are broken, optimizing product yield and quality.
Environmental Impact
The ecological footprints of acid and enzymatic hydrolysis vary significantly. Acid hydrolysis can have a notable environmental impact due to the use of strong acids, which can lead to hazardous waste that must be carefully neutralized and disposed of. The process also carries the risk of acid runoff, potentially harming aquatic ecosystems and soil health.
Conversely, enzymatic hydrolysis boasts a lower environmental footprint. Since enzymes are biodegradable and typically operate under milder conditions, they generate fewer harmful byproducts. This method aligns well with sustainable practices, reducing the need for harsh chemicals and minimizing waste production.
Application Scope
The choice between acid and enzymatic hydrolysis depends largely on the material being processed and the specific application. Acid hydrolysis is prevalent in the paper and textile industries for cellulose processing and is also a cornerstone of biofuel production, where its efficiency at breaking down biomass into fermentable sugars is unmatched.
Enzymatic hydrolysis, with its precise targeting capabilities, is favored in the production of pharmaceuticals, where specific molecular structures must be altered without damaging other parts of the molecule. It’s also used in the food industry to modify proteins and carbohydrates to enhance flavor, texture, or nutritional content.
Cost Considerations
The financial implications of implementing acid or enzymatic hydrolysis are a critical consideration for industries. Acid hydrolysis, while generally cheaper in terms of raw materials (acids are relatively inexpensive), can entail additional costs for neutralization and waste management.
Enzymatic hydrolysis, though more expensive upfront due to the cost of enzymes, can be cost-effective in the long run for processes that benefit from its selectivity. The reduced need for waste treatment and the ability to operate under milder conditions can offset the higher initial investment.
Case Studies
Industrial Application
Real-world applications offer a glimpse into the practical differences between acid and enzymatic hydrolysis. In the textile industry, acid hydrolysis is used to modify cellulose fibers, improving their properties for fabric production. Similarly, in biofuel production, acid hydrolysis plays a pivotal role in converting lignocellulosic biomass into sugars that can be fermented into ethanol.
Enzymatic hydrolysis has made significant inroads in the brewing industry, where enzymes break down starches into sugars, and in the dairy industry, where lactose is hydrolyzed into glucose and galactose to produce lactose-free milk products. These applications underscore the method’s versatility and ability to maintain product integrity.
Research and Development
Recent advancements in hydrolysis techniques focus on enhancing the efficiency, selectivity, and sustainability of these processes. Innovations include the development of more robust enzymes capable of operating under a wider range of conditions and the engineering of microorganisms for biohydrolysis, offering a greener alternative to chemical methods.
Future Perspectives
Innovations in Hydrolysis
The future of hydrolysis lies in the ongoing search for methods that combine the best of both worlds: the efficiency of acid hydrolysis and the selectivity of enzymatic hydrolysis. Research is directed towards emerging trends and technologies, such as immobilized enzymes for repeated use and novel acid catalysts that are less harmful to the environment.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is a driving force in the evolution of hydrolysis methods. The industry is moving towards practices that minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and utilize renewable resources. Enzymatic hydrolysis, with its inherent eco-friendliness, is at the forefront of this shift, offering a model for future developments in hydrolysis technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is hydrolysis?
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction where water is used to break down the bonds of a molecule. This process is integral to many biological and chemical systems, allowing for the decomposition of complex substances into simpler, more usable forms. It’s a key reaction in digestion, biodegradation, and numerous industrial processes, facilitating the transformation and recycling of organic and inorganic matter.
Why is acid hydrolysis used?
Acid hydrolysis is employed primarily for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness in breaking down complex molecules. It uses strong inorganic acids to cleave chemical bonds, making it suitable for processing materials that require rapid decomposition. This method is extensively used in industries such as paper manufacturing and biofuel production, where the swift breakdown of cellulose or other polymers is essential.
How does enzymatic hydrolysis differ from acid hydrolysis?
Enzymatic hydrolysis differs from acid hydrolysis in its mechanism and specificity. It uses enzymes as catalysts to selectively break down molecules, resulting in less environmental impact and a higher degree of precision. This method is favored in applications where the selective degradation of compounds is necessary, such as in the pharmaceutical and food industries, due to its ability to target specific bonds without damaging surrounding materials.
What are the environmental impacts of hydrolysis methods?
The environmental impacts of hydrolysis methods vary significantly between acid and enzymatic hydrolysis. Acid hydrolysis can lead to the release of harmful acids and byproducts into the environment, posing risks to ecosystems and water sources. Enzymatic hydrolysis, on the other hand, is considered more environmentally friendly, as it produces fewer harmful byproducts and requires less energy, reducing its overall ecological footprint.
Conclusion
Choosing between acid hydrolysis and enzymatic hydrolysis involves weighing the benefits and limitations of each method against the specific requirements of an application. Acid hydrolysis offers a robust and cost-effective solution for the rapid decomposition of materials, making it indispensable in certain industrial processes. Enzymatic hydrolysis, with its specificity and reduced environmental impact, represents a sustainable alternative for applications where precision and ecological considerations are paramount.
The evolution of hydrolysis techniques continues to advance, driven by the need for more efficient, selective, and environmentally friendly methods. As research progresses, the development of novel enzymes and more sustainable acid catalysts is expected to further refine these processes, enhancing their applicability and efficiency. Understanding the differences and capabilities of each method ensures the optimal application of hydrolysis in various industrial, environmental, and biological contexts, contributing to technological advancement and environmental sustainability.