Fitness, an essential aspect of well-being, encompasses various dimensions that cater to our overall health and abilities. While the concept broadly implies a state of being fit and healthy, it intricately divides into health-related and skill-related components, each serving distinct purposes and outcomes. This differentiation not only highlights the diverse nature of fitness but also underlines the tailored approaches required to achieve specific fitness goals.
The primary difference between health-related and skill-related fitness lies in their core objectives: health-related fitness focuses on improving overall health and preventing diseases, including cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, and flexibility. Skill-related fitness, however, aims to enhance one’s performance in athletic or physical activities through agility, balance, and coordination. Understanding this distinction is crucial for individuals looking to tailor their fitness regimen according to personal health goals or performance aspirations.
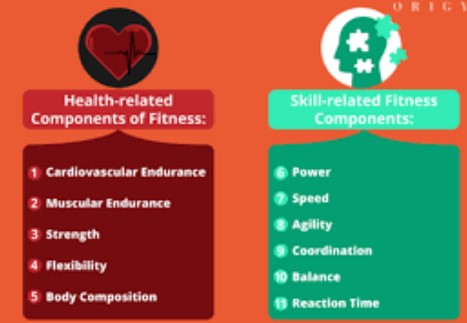
Health-related fitness components are vital for everyone, irrespective of age or lifestyle, as they contribute to a person’s overall health, longevity, and quality of life. In contrast, skill-related fitness components are often more relevant to athletes and those engaging in physical activities requiring specific skills. Both types, however, play significant roles in fostering a well-rounded and functional fitness level that can enhance daily life and improve performance in various tasks and sports.
Health-Related Fitness
Definition
Health-related fitness refers to the aspect of fitness that encompasses components leading to good health and a lower risk of chronic diseases. This concept is fundamental to anyone’s exercise regimen, aiming to improve overall wellness rather than skills specific to sports or activities.
Components
Cardiovascular Endurance
Cardiovascular endurance is the ability of your heart and lungs to work together to fuel your body with oxygen during extended periods of exercise. It’s crucial for activities like running, swimming, and cycling. To improve this component, regular aerobic exercises are recommended, which have significant benefits for heart health and stamina.
Muscular Strength
Muscular strength is about how much force your muscles can exert in a single effort. This component is vital for daily tasks such as lifting groceries or pushing a heavy door. Strength training, involving weights or resistance bands, can enhance muscular strength, impacting positively on metabolism and bone density.
Muscular Endurance
Muscular endurance differs from muscular strength by focusing on a muscle’s ability to continue exerting force without tiring. Exercises that improve this component include cycling, plank exercises, and swimming, leading to better overall endurance and less fatigue in daily activities.
Flexibility
Flexibility is the range of motion available at a joint. Yoga and stretching exercises can improve flexibility, which is key to preventing injuries, reducing muscle soreness, and improving posture and functional movements.
Body Composition
Body composition refers to the ratio of fat to lean mass in your body. Achieving a healthy body composition is a balance between adequate physical activity and nutrition, crucial for reducing the risk of obesity-related diseases.
Importance
Benefits for General Health
Engaging in regular physical activity that targets these health-related components can lead to numerous health benefits, including improved heart health, stronger muscles, better joint mobility, and improved mental health. These activities help manage weight, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and enhance immune function.
Impact on Longevity and Quality of Life
By focusing on health-related fitness, individuals can significantly impact their longevity and quality of life. Regular exercise is linked to a longer lifespan, reduced risk of many health conditions, and an enhanced sense of well-being, enabling people to enjoy a more active and fulfilling life.
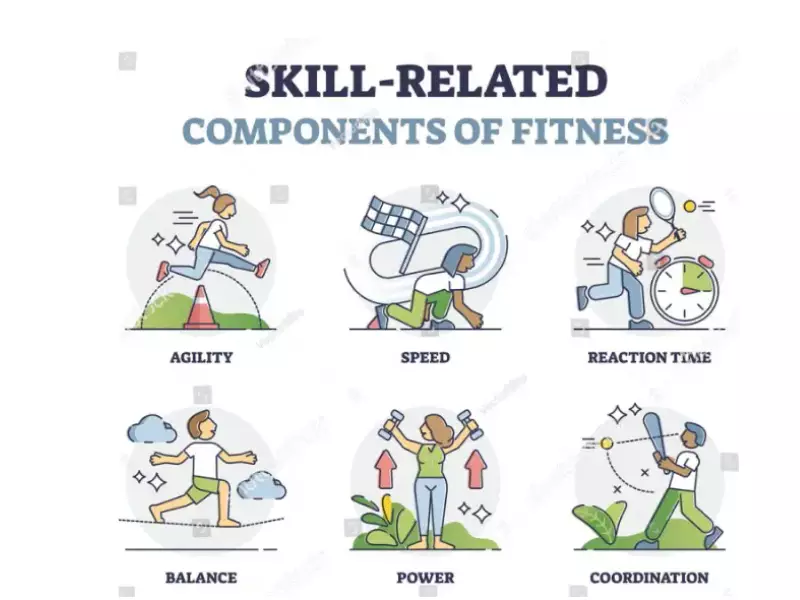
Skill-Related Fitness
Definition
Skill-related fitness concentrates on improving physical abilities specific to sports or activities requiring particular skills. This form of fitness is about enhancing performance and efficiency in movements that are often complex and require precision.
Components
Agility
Agility is the ability to move quickly and change direction with ease. It’s essential for sports like soccer, basketball, and tennis. Drills that improve agility include ladder drills and cone drills, beneficial for anyone looking to enhance their quickness and responsiveness.
Balance
Balance involves maintaining body position, whether moving or stationary. Yoga and tai chi improve balance, crucial for everyday activities and reducing the risk of falls, especially as one ages.
Coordination
Coordination is the ability to use different parts of the body together smoothly and efficiently. Activities like juggling or playing catch can enhance coordination, important for tasks requiring fine motor skills.
Power
Power is the ability to exert maximum force in short intervals of time. Jumping exercises and Olympic lifting can increase power, essential for sports that require explosive movements, like sprinting or weightlifting.
Reaction Time
Reaction time is how quickly an individual can respond to stimuli. Fast-paced sports, video games, and specific drills can improve reaction time, crucial for driving, playing sports, and avoiding everyday hazards.
Speed
Speed is the ability to move quickly over a distance. Sprinting and speed drills are effective for improving speed, necessary for almost all sports and helpful in emergency situations.
Importance
Benefits in Sports and Activities
Skill-related fitness components are vital for athletes and sports enthusiasts aiming to improve their performance. Enhancing these skills can lead to better outcomes in competitive sports, more enjoyment of recreational activities, and a higher level of athletic achievement.
Enhancing Daily Functional Movements
Even for non-athletes, skill-related fitness can improve the quality of daily life by making everyday tasks easier and reducing the risk of injury. Improved balance, coordination, and agility can help in navigating complex environments, while power and speed enhance one’s ability to perform quick movements, like catching a falling object or sprinting to catch a bus.
Focus and Goals
Health-related vs. Skill-related Objectives
The focus of health-related fitness is on enhancing overall health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and promoting a long and quality life. Its goals are universally applicable, aimed at improving fundamental physical attributes such as cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, and flexibility. These components are essential for everyone, from children to the elderly, emphasizing the importance of a healthy lifestyle.
In contrast, skill-related fitness focuses on optimizing specific physical abilities that contribute to sports performance or activities requiring particular skill sets. The objectives here are to improve agility, balance, coordination, power, reaction time, and speed. While these attributes can benefit anyone, they are particularly targeted towards athletes or individuals engaged in physical activities that demand high levels of physical skill and performance.
Population and Application
General Public vs. Athletes
Health-related fitness is relevant to the general public, as it encompasses the basic elements necessary for maintaining overall health and functional ability. It applies to everyday life activities, such as walking, lifting objects, and performing household chores, making it essential for all age groups and fitness levels.
Skill-related fitness, however, is more specifically tailored to athletes and individuals who actively participate in sports or activities that require a high degree of physical skill. While these components can enhance the general population’s ability to perform daily tasks more efficiently and safely, they are crucial for those looking to excel in competitive environments or improve in specific physical disciplines.
Training and Development
Variations in Training Approaches
The training methodologies for health-related and skill-related fitness components differ significantly. Training for health-related fitness often involves aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility workouts. These activities are designed to improve the body’s efficiency and functionality in a broad sense, accessible to everyone regardless of their fitness level or athletic ambition.
Skill-related fitness training, on the other hand, incorporates more specialized and targeted exercises. These might include plyometrics, balance training, coordination drills, and speed workouts, often requiring more sophisticated techniques and equipment. This form of training is highly specific and tailored to the individual’s sport or activity, emphasizing the development of precise skills that enhance performance.
Assessment and Evaluation
Measuring Success in Both Areas
Success in health-related fitness is measured by improvements in physical health indicators such as reduced body fat percentage, enhanced cardiovascular efficiency, increased muscular strength and endurance, and improved flexibility. These achievements can be evaluated through various means, including medical assessments, fitness tests, and personal health tracking devices.
For skill-related fitness, success is typically assessed through performance metrics relevant to the specific skill or sport. This could include time improvements in sprinting, increased jump height, enhanced agility through obstacle courses, or improved accuracy in sport-specific drills. The evaluation criteria are more performance-oriented, focusing on the tangible advancements in the individual’s ability to execute specific physical tasks.
Integrating Both Fitness Types
Balanced Approach
Integrating both health-related and skill-related fitness into a training regimen is crucial for achieving a holistic fitness level. A balanced approach ensures that individuals not only maintain good health and reduce the risk of diseases but also enhance their physical abilities, making daily activities easier and improving sports performance. This comprehensive strategy to fitness acknowledges the interconnectedness of various physical components, promoting a well-rounded and functional physique.
Examples and Strategies
Activities that Combine Both Types of Fitness
Many activities seamlessly blend both health-related and skill-related components, offering a comprehensive workout that benefits the body and mind. Examples include:
- Swimming: Improves cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, and coordination.
- Cycling: Enhances cardiovascular health, leg strength, and balance.
- Yoga: Boosts flexibility, balance, and muscular endurance.
- Team sports (like soccer and basketball): Develop cardiovascular health, agility, coordination, and power.
Tailoring a Fitness Plan to Individual Needs
Creating a fitness plan that incorporates both fitness types involves understanding an individual’s health goals, performance objectives, and current fitness level. Steps include:
- Assessment: Evaluate current health status and physical abilities.
- Goal Setting: Define clear, achievable goals for both health-related and skill-related fitness.
- Activity Selection: Choose activities that address both types of fitness components relevant to the goals.
- Scheduling: Plan a balanced routine that allows for variety, rest, and progressive difficulty adjustments.
- Monitoring: Track progress and adjust the plan as needed to ensure continued improvement and motivation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is health-related fitness?
Health-related fitness refers to physical capacities directly impacting one’s health, including cardiovascular endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and body composition. This type of fitness is crucial for maintaining and improving overall health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, and enhancing the quality of life.
How does skill-related fitness differ from health-related fitness?
Skill-related fitness focuses on abilities that enhance one’s performance in sports and physical activities, such as agility, balance, coordination, power, reaction time, and speed. Unlike health-related fitness, which benefits everyone by improving health and functionality, skill-related fitness is particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals engaged in activities requiring specific physical skills.
Can someone focus on both health-related and skill-related fitness?
Absolutely, focusing on both health-related and skill-related fitness components is not only possible but recommended for a well-balanced fitness regimen. Integrating both types into your fitness plan can lead to comprehensive health benefits, improved physical abilities, and enhanced performance in various activities and sports.
Why is flexibility considered a health-related fitness component?
Flexibility is classified as a health-related fitness component because it plays a crucial role in the overall health and functionality of the body. Improved flexibility contributes to a range of motion in the joints, reduces the risk of injuries, aids in muscle recovery, and can improve performance in physical activities, thereby supporting general well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the primary difference between health-related and skill-related fitness allows individuals to tailor their exercise routines to meet specific health goals or performance objectives. Health-related fitness, focusing on overall health and disease prevention, is essential for everyone, contributing significantly to a better quality of life and longevity. Skill-related fitness, on the other hand, is key for those looking to excel in physical activities and sports, requiring specific abilities like agility and balance.
By recognizing the distinct roles both types of fitness play, individuals can create more effective, comprehensive fitness plans that not only aim at achieving personal health and performance goals but also ensure a balanced approach to physical well-being. Embracing both aspects of fitness, therefore, paves the way for a holistic approach to health and performance, enriching our lives in multiple dimensions.
