When it comes to testing for certain proteins in the body, two of the most common methods used are serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation. Both tests are used to measure the amount of proteins present in a sample, but the major difference between them lies in their ability to differentiate between different types of proteins. In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between these two tests, and how they can be used to diagnose various medical conditions.
In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between these two tests, and how they can be used to diagnose various medical conditions.
Why perform serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation
Serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation are two common laboratory tests used to diagnose many diseases and conditions. Both tests measure the amount and types of proteins in the blood.
Serum protein electrophoresis is useful for detecting an overall imbalance in proteins, while immunofixation can be used to detect specific antibodies and identify the cause of an imbalance. Ultimately, these two tests work together to provide a comprehensive picture of a patient’s protein levels and any possible underlying issues.
How serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation tests are performed

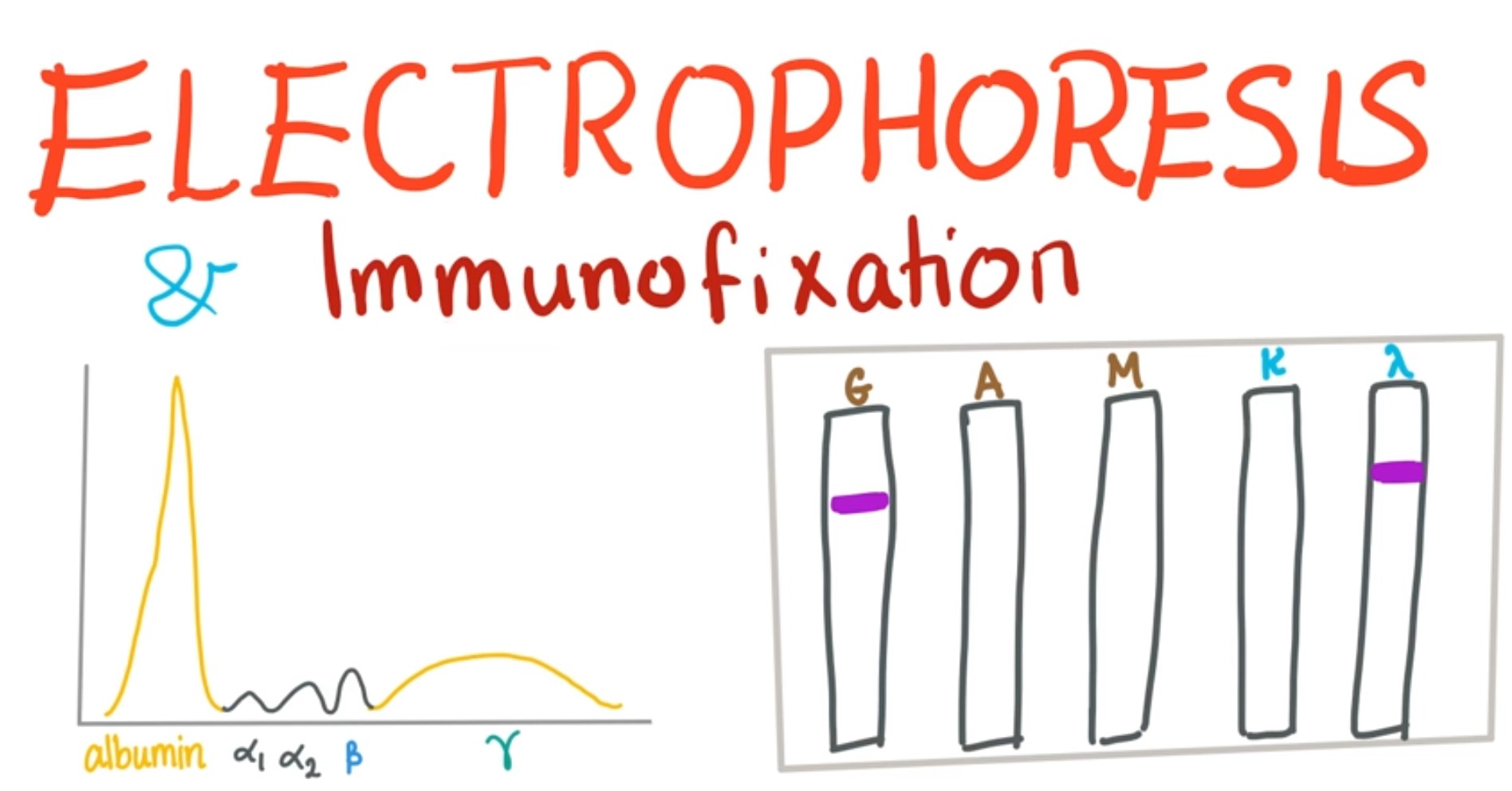
Serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation tests are two commonly used laboratory tests for analyzing proteins in the blood. Both tests involve separating proteins from a sample of blood serum, but the two tests differ in the process used to detect and identify the proteins.
Immunofixation is a method that involves combining the sample of serum with antibodies that recognize specific proteins, allowing for the detection and identification of those proteins. Both tests provide important information about the proteins present in the serum and can be used to diagnose and monitor a variety of health conditions.
The results of serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation tests
Serum protein electrophoresis (SPE) and immunofixation (IF) are two different tests that measure levels of proteins in the blood. Both tests are used to diagnose and monitor diseases, such as multiple myeloma, that affect the production of proteins. While both tests measure proteins, there are significant differences between them.
SPE is the more comprehensive test, measuring all the proteins in the blood, while IF measures specific proteins that are associated with certain diseases. Additionally, SPE can detect subtle changes in proteins that may indicate a potential problem, while IF is more reliable for detecting certain proteins that are associated with certain diseases.
Ultimately, both tests are important for diagnosing and monitoring certain diseases, but it is important to understand the differences between them.
Advantages and disadvantages of serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation
Serum protein electrophoresis (SPE) and immunofixation (IF) are two commonly used laboratory tests that are used to diagnose diseases related to proteins in the body. SPE is a test that separates proteins in the serum by size, charge and shape.
Immunofixation, on the other hand, is used to identify and characterize monoclonal proteins. It involves the use of antibodies to bind to the monoclonal proteins, providing information about the type of protein present.
Both tests can be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, including multiple myeloma, amyloidosis, and Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. The main difference between serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation is the way in which they identify monoclonal proteins. SPE is used to determine the presence of monoclonal proteins, while immunofixation is used to identify the type of protein present.
Additionally, SPE is a more comprehensive test, as it can also detect polyclonal proteins and other abnormalities in the serum. Immunofixation, on the other hand, is more specific and only identifies monoclonal proteins.
Both tests have their advantages and disadvantages. SPE is more sensitive and can detect protein abnormalities at lower concentrations than immunofixation. However, it can be more time consuming and expensive than immunofixation. Immunofixation is faster and more cost-effective, but it is less sensitive than SPE and may miss some abnormalities. Overall, serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation are two important tests that are used to diagnose diseases related to proteins in the body. While both tests have their advantages and disadvantages, they can provide important information about a patient’s condition and help guide treatment decisions.
Further resources for learning about serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation

Serum protein electrophoresis (SPE) and immunofixation (IF) are both laboratory tests that are used to analyze proteins in the blood. While SPE is a technique used to measure the amount of each protein present in a sample, IF is a method that is used to identify and identify the specific proteins in a sample.
The main difference between SPE and IF is that SPE looks for the amount of protein in a sample, while IF looks for the identity of those proteins. SPE is a more general approach to analyzing proteins, while IF is a more specific approach. Both tests are important tools in diagnosing and treating various diseases.
For further information on serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation, please consult with a healthcare professional or refer to online resources.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, the difference between serum protein electrophoresis and immunofixation is that serum protein electrophoresis is a process used to separate proteins into bands based on their electrical charge, whereas immunofixation is an immunoassay used to specifically identify a single protein. Serum protein electrophoresis is useful for measuring the levels of various proteins in the blood and identifying any changes, while immunofixation can be used to identify and quantify a specific protein.