The quest to understand the age of the Earth and the artifacts within it has long fascinated scientists and historians alike. Dating methods, such as relative dating and radioactive dating, serve as the cornerstone of this quest, providing insights into the timeline of geological formations and the chronology of archaeological finds. These techniques, grounded in different scientific principles, offer a glimpse into the past, revealing the sequence and time frame of historical and prehistorical events.
Relative dating and radioactive dating are two distinct methods used to determine the age of rocks, fossils, and artifacts. Relative dating places events or objects in sequence relative to one another but does not provide specific numerical ages. In contrast, radioactive dating, which includes techniques such as carbon-14 and uranium-lead dating, measures the decay of radioactive isotopes to estimate the absolute age of an object, giving a more precise time frame.
The significance of these dating methods extends beyond academic curiosity. They play a crucial role in reconstructing the history of the Earth and human civilization, aiding in the understanding of geological processes and the evolution of life. By analyzing the position of rock layers or the decay of radioactive elements, scientists can piece together the jigsaw puzzle of our planet’s past, offering valuable insights into the forces that have shaped the world we live in today.

Dating Methods Overview
Dating the age of rocks, fossils, and artifacts is crucial for understanding Earth’s history and human civilization. There are two main categories of dating methods used by scientists: relative dating and radioactive dating. These techniques provide the foundation for determining the timeline of geological formations and archaeological sites.
Relative Dating
Definition and Basic Concept
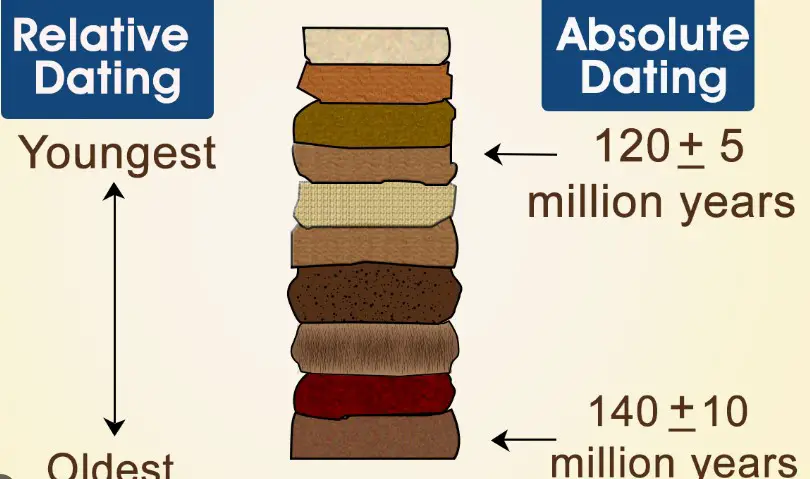
Relative dating helps determine the sequence of events or objects, one in relation to another, without specifying their absolute age. This method is essential for placing geological events and the objects found within those layers in a chronological sequence. The primary goal is to establish a relative time scale where one can say that an object or event is older or younger than another, without stating the exact time in years.
Examples of Relative Dating Techniques
Several techniques fall under the umbrella of relative dating, each based on the observation of different geological or archaeological features:
- Stratigraphy: Observing the layers of rock or sediment to determine the sequence of events.
- Typology: In archaeology, comparing objects, such as tools or pottery, to place them in a sequence by form and design.
- Biostratigraphy: Using fossil remains to date rock layers and the objects within them.
Radioactive Dating
Definition and Explanation
Radioactive dating, also known as radiometric dating, measures the decay of radioactive isotopes within materials to determine their absolute age. This method is based on the principle that certain isotopes decay at a predictable rate, known as their half-life. By measuring the ratio of the original radioactive isotope to the products of its decay in a sample, scientists can calculate the time elapsed since the rock or object was formed.
Introduction to Isotopes and Radioactive Decay
Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which have the same number of protons in their nucleus but different numbers of neutrons. Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive, meaning they decay over time into other elements. This process of decay is what underpins radioactive dating.
Principles of Relative Dating
Law of Superposition
The law of superposition is a fundamental principle of stratigraphy that states in any undisturbed sequence of rocks deposited in layers, the youngest layer is on top, and the layers get progressively older as you go deeper. This law is significant for understanding the relative ages of geological and archaeological layers.
Cross-Cutting Relationships
This principle asserts that if a geological feature cuts across another, the feature that has been cut is older. For example, if an igneous intrusion goes through a series of sedimentary rocks, the rocks must be older than the intrusion. This helps in establishing the relative ages of rock layers and the features within them.
Fossil Succession
Fossil succession refers to the identification and dating of rock layers by the fossils found within them. The presence of certain fossils in a rock layer can indicate its relative age, as some species are known to have lived during specific periods of Earth’s history.
Basics of Radioactive Dating
Isotopes and Radioactive Decay
Understanding isotopes and their decay is fundamental to radioactive dating. Each radioactive isotope has a characteristic half-life, the time it takes for half of the isotope in a sample to decay. This predictable decay allows scientists to measure the age of materials based on the remaining amount of the original isotope and its decay products.
Common Radioactive Dating Methods
- Carbon-14 Dating: Used for dating organic materials up to about 50,000 years old. It measures the decay of carbon-14, which is continuously replenished in living organisms until their death.
- Uranium-Lead Dating: Applied to date rocks older than 1 million years. This method relies on the decay of uranium isotopes into lead and is used for dating the Earth’s oldest rocks.
Comparing the Methods
Accuracy and Precision
When evaluating relative dating and radioactive dating, it’s essential to distinguish between accuracy and precision. Accuracy refers to how close the estimated age is to the actual age, while precision indicates the consistency of repeated measurements.
Relative Dating
Relative dating’s accuracy is inherently limited. Since it provides a sequence of events rather than exact dates, its precision can vary significantly based on the context and the methods used. Relative dating excels in establishing a chronological order but falls short in pinpointing the precise age of an object or event.
Radioactive Dating
Radioactive dating, on the other hand, offers a higher degree of accuracy and precision, thanks to the quantifiable nature of radioactive decay. Methods like carbon-14 and uranium-lead dating can provide exact ages within a relatively small margin of error, especially when performed with modern equipment and techniques.
Applicable Materials
Different dating methods are suitable for different types of materials, affecting their applicability across various scientific fields.
Relative Dating
Relative dating is versatile, applicable to a wide range of materials. It’s particularly useful for sedimentary rock layers and archaeological sites. However, it requires well-defined stratigraphic sequences to be effective and is less useful where such sequences have been disturbed or are not present.
Radioactive Dating
Radioactive dating is best applied to igneous rocks and can also be used on some sedimentary rocks and carbon-containing materials. Its applicability is limited by the presence of suitable isotopes for dating and the condition of the sample being dated.
Time Range
The effective time range of each dating method varies, influenced by the materials being dated and the specific techniques used.
Relative Dating
Relative dating can be applied to materials of almost any age, from thousands to billions of years old. Its effectiveness, however, diminishes when it comes to pinpointing the exact timing of events within the geological time scale.
Radioactive Dating
Radioactive dating covers a wide time range but is particularly effective for dates ranging from a few thousand to billions of years, depending on the half-life of the isotopes used. For example, carbon-14 dating is most effective for materials less than 50,000 years old, while uranium-lead dating can date rocks billions of years old.
Advantages and Limitations
Relative Dating
Advantages:
- Provides a broad overview of geological and archaeological sequences.
- Can be applied without the need for high-tech equipment.
Limitations:
- Lacks the precision to provide exact ages.
- Its effectiveness is contingent on undisturbed stratigraphic sequences.
Radioactive Dating
Advantages:
- Offers precise age estimates.
- Wide applicability to a variety of rock types and organic materials.
Limitations:
- Requires sophisticated equipment and expertise.
- The accuracy can be affected by external factors, such as contamination or environmental changes.
Real-World Applications
Geology
In geology, dating methods are crucial for understanding the Earth’s history and the timing of geological events. For example, relative dating techniques have been instrumental in mapping the geological time scale, while radioactive dating has refined these time scales, providing precise ages for various strata and the events they represent. One notable case study involves the dating of the Earth itself, with uranium-lead dating providing an age of approximately 4.5 billion years.
Archaeology
Archaeological dating benefits immensely from both relative and radioactive dating methods. Relative dating helps archaeologists determine the chronological sequence of artifacts in a site, while radioactive dating, especially carbon-14 dating, offers a method to accurately date organic materials, such as wood, bones, and charcoal, from archaeological sites. This dual approach has been pivotal in dating key historical sites and understanding the timelines of human civilizations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is relative dating?
Relative dating is a method used to determine the order of events or objects, one in relation to another, without necessarily determining their absolute age. By observing the layering of rocks and other geological features, scientists can infer the sequence of geological events in a specific location.
How does radioactive dating work?
Radioactive dating measures the decay of radioactive isotopes within fossils and rocks to determine their absolute age. This method relies on the known rates of decay of these isotopes, using their half-lives to calculate the time since the rock or fossil was formed.
What is the principle of superposition?
The principle of superposition is a core concept in relative dating, stating that in an undisturbed sequence of rocks or sediments, layers on the bottom are older than those on the top. This principle helps scientists establish a relative time scale for geological strata.
How accurate is radioactive dating?
Radioactive dating is considered highly accurate when the appropriate method is used for specific materials and the samples are properly collected and preserved. Its precision is often complemented by cross-referencing results from different dating methods.
Conclusion
The exploration of Earth’s history and the quest to date archaeological finds have greatly benefited from the development and refinement of relative and radioactive dating methods. These techniques, each with its unique approach and scope of application, offer a window into the past, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of the timeline and evolution of our planet and its inhabitants.
The integration of relative and radioactive dating continues to be a vital aspect of geological and archaeological research, shedding light on questions that have puzzled humanity for centuries. As we refine these methods and apply new technologies, our grasp of the temporal dimensions of the Earth and human history becomes ever more precise, opening new avenues for discovery and understanding.