The human body requires a certain amount of glucose for energy, and two important proteins are involved in the process of maintaining glucose levels – GLUT2 and GLUT In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between GLUT2 and GLUT4, and discuss how they work together to keep our bodies functioning properly. We’ll also look at the role each plays in the human body and in diabetes, and how they may be affected by different types of treatments.
We’ll also look at the role each plays in the human body and in diabetes, and how they may be affected by different types of treatments.
The role of glut2 in the body

Glut2 and Glut4 are two different types of glucose transporters in the body. Glut2 is responsible for transporting glucose from the bloodstream into cells, while Glut4 is responsible for transporting glucose out of cells and into the bloodstream.
This difference is important to understand, as it can help to explain why certain diseases, such as diabetes, can have a greater impact on our bodies. Glut2 helps to maintain optimal glucose levels in the body, while Glut4 helps to ensure that cells are receiving the necessary nutrients to remain healthy.
The role of glut4 in the body
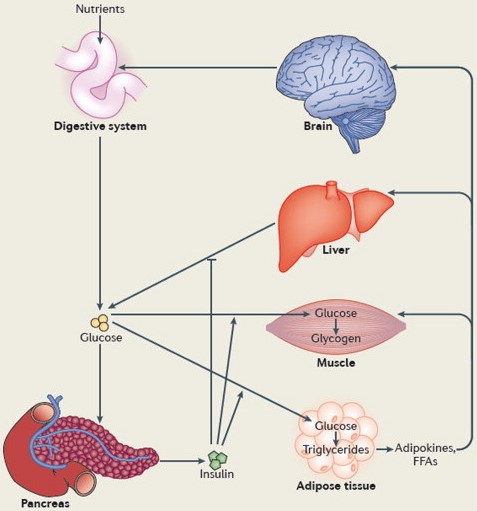
Glut4 is an important protein found in our bodies, and it plays a critical role in regulating the way our bodies process glucose. It is one of the two main types of glucose transporters, the other being Glut
The difference between these two proteins lies in the way they operate. Glut4 is primarily responsible for transporting glucose from the bloodstream into our cells, while Glut2 transports glucose out of the cells. This allows us to maintain a healthy glucose balance in our bodies.
Glut4 also plays a role in controlling the amount of glucose that is stored in our cells, making it an essential part of our metabolic processes.
How glut2 and glut4 differ
Glut2 and Glut4 are both types of transporters that are responsible for the movement of glucose across the cell membrane. The main difference between the two is the rate at which they can transport glucose.
Glut2 is a low-affinity transporter, which means it can move glucose at a slow pace, while Glut4 is a high-affinity transporter, which means it can move glucose quickly. Glut2 is primarily found in the liver and pancreas, while Glut4 is found primarily in muscle and fat cells. Glut2 is responsible for the regulation of blood glucose levels, while Glut4 is responsible for the uptake of glucose during exercise.
In short, Glut2 is the slower, but more precise transporter, while Glut4 is the faster, but less precise transporter.
Benefits of understanding the difference between glut2 and glut4
Understanding the difference between Glut2 and Glut4 can have a major impact on your health. Glut2 and Glut4 are two types of glucose transporters that help regulate glucose levels in the body. Glut2 is a transporter located in the liver and pancreas, whereas Glut4 is found in skeletal muscles, fat tissue, and the heart.
Glut2 is responsible for the uptake of glucose from the blood, while Glut4 is responsible for the uptake of glucose from the muscle and fat tissues. Knowing the difference between these two transporters can help you better understand how to maintain healthy glucose levels in the body.
For example, regular exercise can help increase the activity of Glut4, which can help maintain healthy glucose levels. Additionally, understanding the differences between these two transporters can help inform your diet, as foods that are high in glucose can help increase the activity of Glut
Resources for further reading
Do you ever find yourself wondering what the difference between Glut2 and Glut4 is? It can be a confusing concept to understand, but we have the answer for you. Glut2 is a particular type of glucose transporter, which is responsible for transporting glucose from the blood and into cells.
Glut2 is a particular type of glucose transporter, which is responsible for transporting glucose from the blood and into cells. Glut4, on the other hand, is a type of glucose transporter that is responsible for transporting glucose from the cell to the muscles and other tissues. In order to understand this, it is important to understand the role of glucose in the body.
Glucose is the primary energy source for our cells, and it is essential for normal metabolic processes. Glut2 helps to bring glucose into the cells, while Glut4 helps to carry glucose away from the cells.
Final Touch
In conclusion, the main difference between Glut2 and Glut4 is their subcellular location and their activity in response to hormones like insulin. Glut2 is found in the liver, pancreas and small intestine, where it is involved in the uptake of glucose.
Glut4 is found primarily in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue, where it is activated in response to insulin, allowing glucose to be taken up from the bloodstream. Both transporters are instrumental in the maintenance of glucose homeostasis.

