Breast cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening illness, and is one of the most common forms of cancer in women. Understanding the different types of breast cancer and their associated treatments is important in order to make an informed decision about your health. In this blog, we will discuss the differences between two common types of breast cancer, DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma In Situ) and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC).
In this blog, we will discuss the differences between two common types of breast cancer, DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma In Situ) and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC). We will discuss the differences between the two, including the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Risk factors for dcis and invasive ductal carcinoma

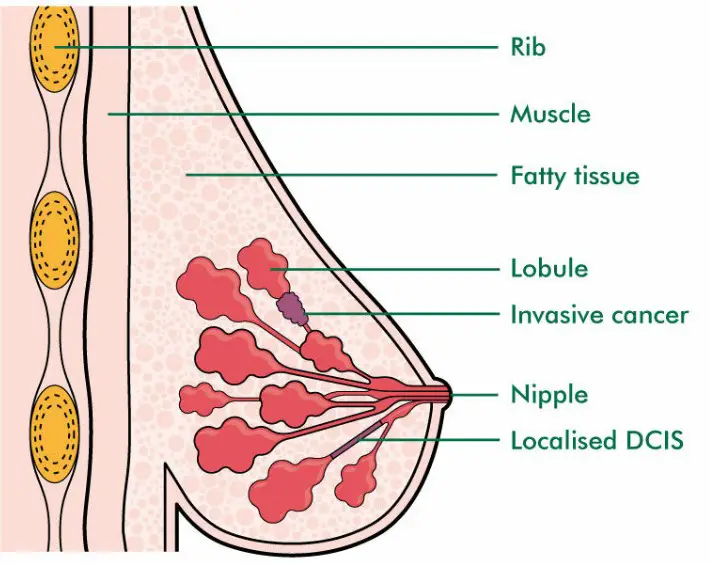
When it comes to breast cancer, there are two main types: DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma In Situ) and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC). The two types of cancer may sound similar, but they have some very distinct differences.
DCIS is the earliest form of breast cancer. It is considered a non-invasive cancer, meaning that the abnormal cells have not spread to other parts of the body. It is usually detected through mammograms and other imaging tests.
DCIS is often treated with lumpectomy or breast-conserving surgery, followed by radiation therapy. Invasive Ductal Carcinoma, on the other hand, is an invasive form of breast cancer. This type of cancer has spread to the nearby tissues and organs, and can even metastasize to other parts of the body.
IDC is usually treated with a mastectomy, radiation, and chemotherapy. Risk factors for DCIS and IDC are similar, and include age, gender, family history, and prior radiation exposure.
It’s important to be aware of the differences between the two types of cancer and to talk to your doctor if you have any concerns.
Symptoms of dcis and invasive ductal carcinoma
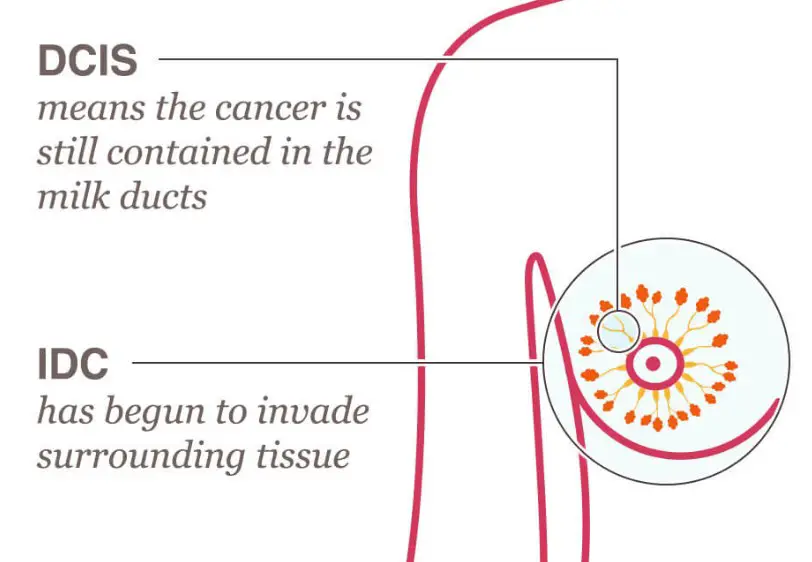
DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma In Situ) and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) are two types of breast cancer. DCIS is a non-invasive form of cancer, which means that it is confined to the milk ducts and has not spread outside of the ducts.
IDC is an invasive form of cancer which means that the cancer cells have spread beyond the milk ducts and can invade other tissues in the breast. The main difference between DCIS and IDC is that DCIS is non-invasive and has not spread, while IDC has spread beyond the milk ducts and can invade other tissues in the breast. DCIS typically presents with no symptoms, while IDC may present with a lump in the breast, skin changes in the breast, or nipple discharge.
It is important to note that both DCIS and IDC require medical treatment, so it is important to consult your doctor if you have any concerns or symptoms.
Diagnosis and treatment of dcis and invasive ductal carcinoma
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) are both forms of breast cancer, but they are very different in terms of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. DCIS is a non-invasive form of breast cancer, meaning it has not spread beyond the milk ducts in the breast. IDC, on the other hand, is an invasive form of breast cancer, meaning it has spread beyond the milk ducts in the breast and may have spread to other parts of the body.
IDC, on the other hand, is an invasive form of breast cancer, meaning it has spread beyond the milk ducts in the breast and may have spread to other parts of the body. Diagnosis of DCIS involves a mammogram, a physical exam, and a biopsy. Treatment can include lumpectomy, mastectomy, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy.
Prognosis for DCIS is generally good, as it has not spread to other parts of the body. IDC is diagnosed with a mammogram, physical exam, and biopsy, and treatment may include lumpectomy, mastectomy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy.
Prognosis for IDC is variable and depends on the stage of the cancer.
Prognosis and prevention of dcis and invasive ductal carcinoma
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) are both types of breast cancer, but they differ in a few important ways. DCIS is an early stage of breast cancer and is generally considered non-invasive, meaning it has not spread from the milk ducts and into other parts of the breast. IDC, on the other hand, is an advanced form of breast cancer and is considered invasive, meaning it has spread beyond the milk ducts and into other areas of the breast.
Prognosis and prevention of DCIS and IDC vary depending on the stage of the cancer and the patient’s individual condition and risk factors. Generally speaking, the earlier the breast cancer is caught and treated, the better the prognosis.
Regular screening and mammograms are key in detecting breast cancer in its early stages, making preventive measures and timely treatment possible.
Common questions about dcis and invasive ductal carcinoma
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC) are two different types of breast cancer that affect women. DCIS is a non-invasive cancer, meaning the cancer cells remain in the milk ducts and have not spread beyond the ducts into the surrounding breast tissue.
IDC, on the other hand, is an invasive cancer that has spread beyond the milk ducts into the surrounding tissue of the breast. DCIS is usually detected early, before it becomes invasive, while IDC is usually found after it has already spread outside of the milk ducts. Both types of cancer require treatment, but the type of treatment will depend on the extent of the cancer.
DCIS is usually treated with a lumpectomy, radiation therapy, or a mastectomy, while IDC may require a mastectomy and other treatments depending on the stage of the cancer.
Final Touch
The main difference between DCIS and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma is that DCIS is a non-invasive form of breast cancer, while Invasive Ductal Carcinoma is an invasive form of breast cancer. DCIS is not considered life-threatening and can often be treated with surgery and radiation, while Invasive Ductal Carcinoma is more serious and may require more aggressive treatments, such as chemotherapy and/or hormone therapy. Generally, early detection and treatment are the best ways to increase the chances of successful treatment.