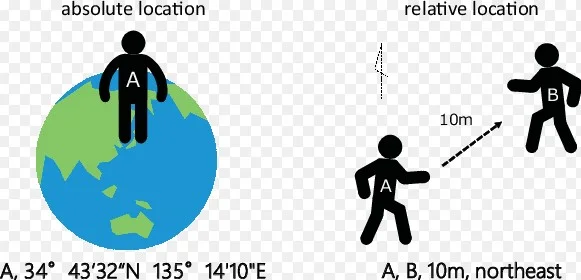
In the vast and intricate world of geography, two concepts stand prominently at the forefront of navigation, mapping, and understanding our environment: absolute and relative location. These foundational elements serve as the core for various fields, from urban planning to global navigation, emphasizing the diverse ways in which we comprehend and describe positions on Earth. The distinction between these two types of location is not just academic; it influences everything from the way we navigate daily routes to how international trade routes are established.
Absolute location defines a fixed point on the Earth’s surface with a specific set of coordinates, usually expressed in latitude and longitude. This precision allows for a universal understanding of exact positions, making it possible to locate any place on the planet with accuracy. Relative location, on the other hand, describes a place’s position in relation to other locations, providing a more context-based understanding that can vary depending on the perspective of the individual or the reference point used.
Grasping the difference between absolute and relative location enriches our understanding of geographical principles, aiding in the comprehension of how places are interconnected. It also enhances our navigation skills, whether we are exploring a new city or understanding global dynamics. These concepts not only assist in practical navigation tasks but also play a significant role in cultural, economic, and environmental studies, highlighting the multifaceted ways we interact with the space around us.
Location Basics
Understanding our world begins with the basics of location. It’s how we describe where things are, plan our journeys, and even define our very existence in the context of the larger world. Let’s dive into the fundamentals of absolute and relative location, their key differences, and practical applications in everyday life.
Absolute Location
Definition and Significance
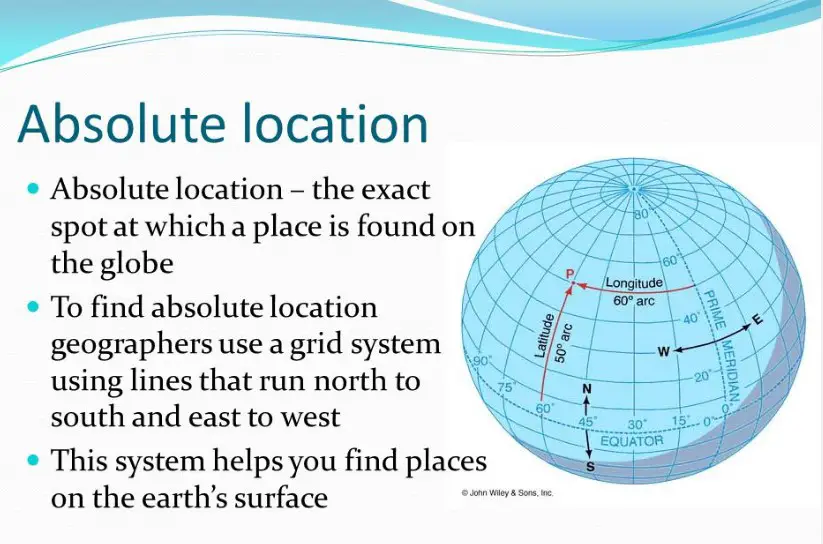
Absolute location refers to the exact, fixed position of a place on the Earth’s surface. It’s a specific point that can be pinpointed through coordinates, typically using latitude and longitude. This concept is crucial for global navigation, precise mapping, and even online services that rely on geolocation. Absolute location provides a universal language for everyone, everywhere, to understand exactly where something is, eliminating confusion and ambiguity.
How It Is Determined
Determining absolute location is a science that has evolved with technology. Today, the most common method involves:
- GPS (Global Positioning System): A network of satellites that provide location information to GPS receivers, allowing us to pinpoint a location with remarkable accuracy.
- Coordinates: Latitude and longitude lines form a grid on the Earth’s surface, offering a way to express location in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
Relative Location
Definition and Context Use
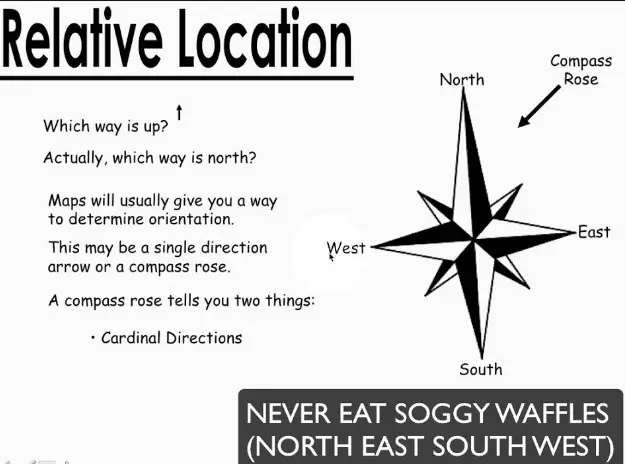
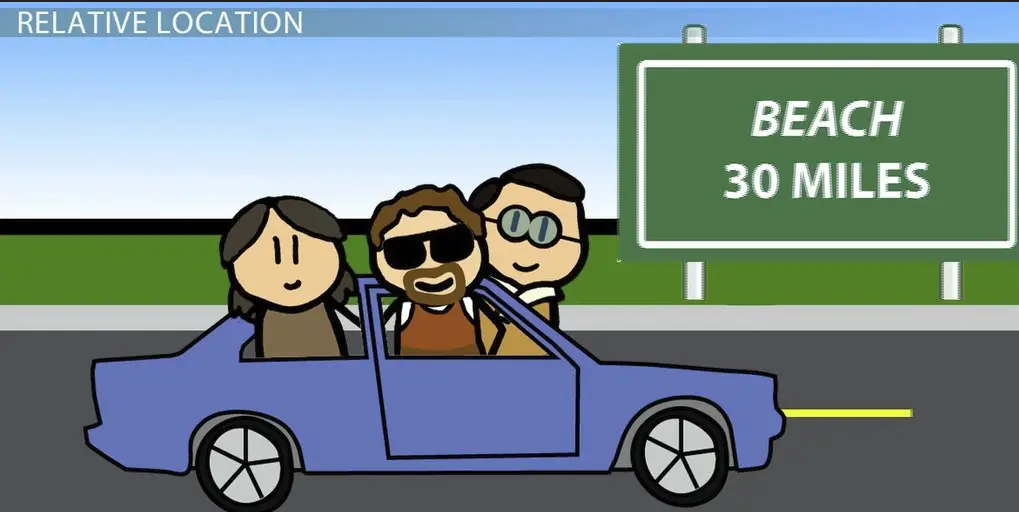
Relative location describes where a place is in relation to other landmarks or places. It’s more about the context and relationship between locations than about precise coordinates. This type of location is often used in everyday conversation, directions, and when the absolute location is not known or necessary.
Examples in Daily Life
- Telling a friend your home is “next to the post office”
- Describing a restaurant as “across the river from the museum”
- Explaining a city’s location as “north of the capital”
These examples show how relative location is about understanding and communicating location in a way that is immediately relevant and useful to the listener, based on familiar landmarks or directions.
Key Differences
When comparing absolute and relative location, several key differences emerge.
Measurement Methods
- Tools and Technologies for Absolute Location: GPS devices, maps with latitude and longitude, and online mapping services.
- Descriptive Methods for Relative Location: Oral descriptions, written directions, and maps highlighting landmarks or other significant features.
Use Cases
- Navigation and Mapping: Absolute location is essential for global positioning and detailed mapping, while relative location is more useful for everyday directions and local area understanding.
- Cultural and Societal Context: Relative location takes on added significance when considering cultural landmarks, historical sites, and societal boundaries, where the meaning of a place is tied to its relationship with other locations.
Accuracy and Precision
- Exactness of Absolute Location: This method provides a precise, unchanging reference point.
- Variability of Relative Location: The description can change based on the observer’s perspective, the chosen landmarks, and even time, as landmarks can change, move, or disappear.
Practical Applications
The concepts of absolute and relative location are not just academic; they have practical applications in various aspects of daily life and industry.
In Navigation
- GPS Technology and Travel: GPS has revolutionized travel, allowing for real-time navigation, route planning, and location tracking, all based on absolute location.
- Wayfinding in Urban Environments: Relative location is key in urban navigation, where detailed knowledge of every street and address is unrealistic. Descriptions based on landmarks and visible features guide us through complex environments.
In Real Estate
- Property Descriptions and Values: Absolute location determines legal boundaries and property lines, critical for deeds and official documents. Relative location, such as proximity to schools, parks, and commercial areas, often influences property values and desirability.
In Cultural Context
- Understanding Local Versus Foreign Perspectives: How a place is described can vary significantly depending on local knowledge and cultural significance. What is a well-known landmark to locals may need to be described in terms of absolute location to outsiders, highlighting the interplay between these two concepts.
Importance in Various Fields
Geography and Cartography
Mapping Techniques and Tools
Geography and cartography heavily rely on both absolute and relative location to create accurate and user-friendly maps. Modern mapping techniques incorporate GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and satellite imagery to pinpoint exact locations on Earth. Tools such as digital maps and mobile apps utilize GPS for real-time location tracking, enhancing navigation and geographical education.
- GIS Technology: Combines data and mapping for spatial analysis.
- Satellite Imagery: Offers detailed Earth views, aiding in precise mapping.
- Digital Maps: Provide interactive exploration of areas with zoom and search features.
Importance in Mapping
The accuracy of absolute location and the context provided by relative location are vital for:
- Disaster Management: Planning evacuation routes and emergency responses.
- Environmental Conservation: Identifying protected areas and monitoring changes.
- Urban Development: Planning city expansions and infrastructure projects.
Urban Planning
City Layout and Infrastructure Planning
Urban planning uses absolute and relative locations to design efficient city layouts and infrastructure. Planners assess land use, transportation networks, and community needs based on location data, focusing on:
- Sustainable Development: Balancing growth with environmental protection.
- Transportation Systems: Designing routes that enhance connectivity and accessibility.
- Public Amenities: Locating parks, schools, and hospitals for community benefit.
Role in Development
Effective urban planning leads to:
- Enhanced Mobility: Reduced traffic congestion and improved public transportation.
- Economic Growth: Strategic placement of commercial areas to boost local economies.
- Quality of Life: Well-planned residential areas with access to amenities and green spaces.
Emergency Services
Response Strategies Based on Location Types
Emergency services depend on accurate location information to respond swiftly to incidents. Understanding the difference between absolute and relative locations is crucial for:
- Rapid Deployment: Ensuring emergency teams can find and reach incidents quickly.
- Effective Communication: Describing incident locations in ways that are clear to responders.
- Strategic Planning: Preparing for disasters based on geographic vulnerabilities.
Importance in Emergency Responses
Location data helps in:
- Saving Lives: Faster response times can be the difference between life and death.
- Resource Allocation: Efficient use of resources based on the severity and location of incidents.
- Community Safety: Planning for evacuations and emergency access in urban planning.
Challenges and Considerations
Technological Limitations
GPS Inaccuracies and Limitations
While GPS is a powerful tool for determining absolute location, it has its limitations. Signal blockage, multipath effects, and atmospheric conditions can lead to inaccuracies. It’s essential to understand these limitations for applications requiring high precision.
- Urban Canyons: Tall buildings can block or reflect signals.
- Remote Areas: Limited coverage in forests, mountains, and deserts.
- Atmospheric Effects: Variability in signal transmission due to weather conditions.
Overcoming Challenges
Strategies include:
- Augmented GPS Systems: Using ground-based stations for enhanced accuracy.
- Multi-System Receivers: Combining signals from different satellite systems.
- Error Correction Techniques: Applying algorithms to minimize inaccuracies.
Cultural Sensitivities
Perception of Location in Different Cultures
The concept of relative location is deeply influenced by cultural perspectives. Terms and references used to describe location can vary significantly, affecting communication and understanding across different cultural contexts.
- Language and Terms: Variations in geographical terms and landmarks.
- Spatial Perception: How different cultures conceptualize space and distance.
- Historical and Social Factors: Influence on place names and descriptions.
Navigating Cultural Differences
To address these sensitivities:
- Cultural Education: Learning about local geographical terminologies and concepts.
- Inclusive Mapping: Incorporating local names and symbols in maps and guides.
- Communication Strategies: Adapting descriptions and references to suit diverse audiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is absolute location?
Absolute location refers to a precise point on the Earth’s surface, identified by specific coordinates, typically latitude and longitude. This method of location offers a universal way to find or describe any place on the planet with exactitude, crucial for navigation, mapping, and global communication.
How is relative location determined?
Relative location is determined by describing a place’s position in relation to other known locations. It uses points of reference, such as landmarks, other cities, or geographic features, to convey where something is. This context-dependent method provides a more nuanced understanding of location that can vary with perspective.
Why is understanding both locations important?
Understanding both absolute and relative locations is crucial for accurate navigation, effective communication, and comprehensive geographical analysis. It allows for precise positioning, while also accommodating contextual and cultural nuances in describing places, enhancing both practical and theoretical approaches to geography.
Can relative location change over time?
Yes, relative location can change over time as the surrounding geography or landmarks change. Urban development, natural disasters, and changes in landmarks can all influence a place’s relative location, highlighting its dynamic nature compared to the static nature of absolute location.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between absolute and relative locations is fundamental to our interaction with the world. These concepts not only serve as the backbone for navigation and mapping but also influence economic strategies, environmental planning, and cultural understandings. By comprehending the precise fixity of absolute location and the contextual fluidity of relative location, we unlock a deeper appreciation for the complexity of our world.
As we navigate through the ever-evolving landscape of our planet, the importance of understanding these geographical principles cannot be overstated. They empower us to traverse the globe with confidence, make informed decisions based on location, and appreciate the intricate web of connections that bind us, regardless of where we stand.