The relationship between wages and employee productivity is a critical aspect of organizational success and economic theory. It embodies the connection between the financial remuneration employees receive for their labor and the quantity and quality of work they produce. This dynamic not only influences individual worker satisfaction and motivation but also impacts the overall performance and competitiveness of businesses.
The relation between wages and employee productivity suggests that fair and competitive wages are essential for maximizing employee output and enhancing job satisfaction. When employees feel adequately compensated, their motivation, loyalty, and productivity tend to increase, leading to improved business outcomes. Conversely, insufficient wages can result in decreased motivation, higher turnover rates, and lower productivity levels.
This topic encompasses various dimensions, including economic theories, psychological perspectives, and real-world applications. It reveals how wage policies can significantly affect workplace dynamics, employee well-being, and ultimately, the bottom line of organizations. Through examining this relationship, businesses can develop strategies that not only boost productivity but also foster a motivated and committed workforce.

Wage Fundamentals
Definition and Types
Wages are the financial compensation paid to employees for their labor. They come in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and benefits. The primary types of wages include:
- Hourly Wages: Employees receive a fixed amount for each hour worked. This model is common in industries requiring flexible work schedules.
- Salary: A fixed annual amount, divided into regular payments, typically monthly or bi-weekly. Salaries are common in professional and managerial roles.
- Commission-Based: Compensation based on performance, often a percentage of sales made by the employee. This is prevalent in sales roles, incentivizing higher performance.
- Bonuses: Additional financial rewards given for meeting or exceeding specific targets or as part of profit-sharing schemes.
Importance of Wages
Wages play a crucial role in several aspects of employment and personal life:
- Motivation: Adequate compensation is a key motivator for employees, encouraging higher productivity and engagement.
- Retention: Competitive wages help retain top talent, reducing turnover and associated costs.
- Lifestyle: Wages directly impact an employee’s quality of life, affecting their ability to meet living expenses and invest in personal and family well-being.
Productivity Insights
Defining Productivity
Productivity in the workplace refers to the efficiency with which inputs (like labor and capital) are converted into outputs (goods and services). Measuring productivity involves comparing the amount of work produced to the resources used.
Factors Influencing Productivity
Several factors influence productivity beyond wages, including:
- Work Environment: A positive, safe, and supportive workplace enhances productivity.
- Technology and Tools: Access to modern tools and technology can significantly boost the efficiency of work.
- Skills and Training: Continuous learning and skill development contribute to higher productivity.
- Management Practices: Effective leadership and management practices, including clear communication and goal-setting, motivate employees to perform better.
Theoretical Perspectives
Economic Theories
Economic theories on wages and productivity have evolved over time, with each offering insights into how wages influence economic outcomes.
- Classical Economics: Suggests that wages are determined by the laws of supply and demand. Higher wages could lead to higher productivity as workers are motivated to keep their jobs.
- Modern Theories: Include concepts like efficiency wage theory, which argues that employers pay above the market rate to increase productivity and reduce turnover.
Psychological Views
Psychological perspectives focus on how wages impact an employee’s motivation and satisfaction. Theories such as Maslow’s hierarchy of needs suggest that financial security (provided by wages) is a fundamental need that must be satisfied for employees to engage in higher levels of productivity.
Real-world Evidence
Case Studies
Real-world examples highlight the impact of wage adjustments on productivity:
- A technology firm increased its minimum wage and observed a reduction in employee turnover and an increase in productivity, attributed to higher employee satisfaction and loyalty.
- A manufacturing company introduced performance-based bonuses, leading to a significant increase in output as employees were motivated to exceed production targets.
Statistical Data
Data and research findings support the relationship between wages and productivity:
- Studies show that a 10% increase in wages can lead to a 1-2% increase in productivity, indicating a positive but diminishing return on investment in wage increases.
- Research also highlights the role of non-financial factors, suggesting that while wages are important, they are part of a broader set of influences on productivity.
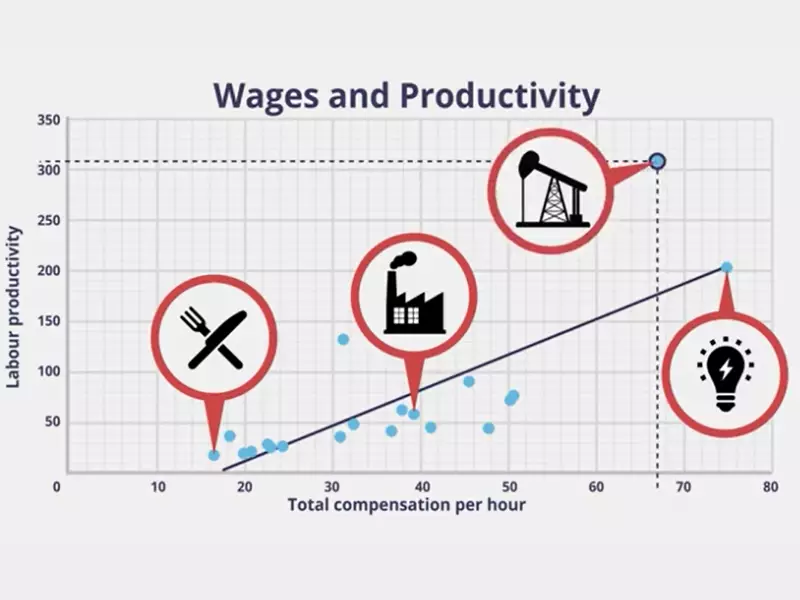
Wage-Productivity Dynamics
Direct Effects
Increases in wages can directly enhance productivity in several ways. Higher wages improve the living standard of employees, leading to better health, morale, and thus, higher productivity. When workers recognize that their efforts are rewarded with fair pay, their motivation to work efficiently increases. Moreover, competitive wages can attract skilled workers, elevating the overall productivity of the workforce.
Indirect Influences
Wages also have significant indirect effects on workplace dynamics. Higher wages can improve morale, making employees feel valued and reducing workplace stress. This improvement in morale can lead to lower employee turnover, as employees are less likely to leave for better-paying opportunities. Additionally, offering competitive wages can make a company more attractive in the job market, aiding in the recruitment of top talent.
Industry-Specific Analysis
Service vs. Manufacturing Sectors
The impact of wages on productivity can vary between the service and manufacturing sectors. In service industries, where customer interaction and service quality are crucial, higher wages can lead to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty, as employees are more motivated to provide exceptional service. In manufacturing, where productivity is often measured by output, wage increases can incentivize employees to meet or exceed production targets.
High-skilled vs. Low-skilled Jobs
The relationship between wages and productivity also differs across job types. In positions requiring high skills and expertise, competitive wages are critical to attracting and retaining talent, and the impact on productivity is more pronounced. For low-skilled jobs, where the labor market is more saturated, wage increases may not have the same direct impact on productivity, although they can still improve morale and reduce turnover.
Challenges and Considerations
Diminishing Returns
The concept of diminishing returns suggests that after a certain point, increases in wages lead to progressively smaller increases in productivity. It’s important for employers to recognize that throwing more money at employees will not infinitely increase productivity. There’s a balance to be struck where wages are fair and competitive but also sustainable for the business.
Wage Inflation
Another challenge is the potential for wage increases to contribute to inflation. If wages rise across the board, the increased purchasing power can lead to higher demand for goods and services, pushing prices up. This inflation can negate the real value of wage increases, leading to a cycle of wage and price increases that can be difficult to manage.
Global Perspectives
The wage-productivity relationship varies globally due to differing economic conditions, cultures, and labor laws. In countries with strong social safety nets and high living standards, the impact of wage increases on productivity might be less pronounced compared to developing countries, where even small wage increases can significantly affect employee well-being and productivity.
Strategies for Employers
Effective Wage Policies
To foster a productive workforce, employers should develop effective wage policies. These policies can include regular wage reviews to ensure competitiveness, performance-based bonuses to reward high achievers, and transparent communication about wage determinations. Here are some recommendations:
- Conduct regular market comparisons to ensure wages remain competitive.
- Implement performance-based incentives to reward productivity.
- Ensure wage transparency to build trust and motivation among employees.
Non-financial Motivators
Employers should also consider non-financial motivators to enhance productivity. These can include:
- Career development opportunities, such as training and progression paths.
- Recognition programs to acknowledge outstanding work.
- Positive work environment, ensuring a safe and supportive space for employees.
- Work-life balance, with flexible working options and support for personal commitments.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do wages affect employee productivity?
Wages have a direct impact on employee productivity by influencing motivation and satisfaction levels. Competitive salaries encourage workers to perform better, foster loyalty, and reduce turnover. Conversely, inadequate wages can demotivate staff, leading to reduced output and higher attrition rates.
Can increasing wages always improve productivity?
Increasing wages can improve productivity up to a point, following the principle of diminishing returns. Beyond a certain wage level, further increases may not yield proportionate gains in productivity. It’s crucial for businesses to find a balanced approach, considering both financial and non-financial factors that influence employee motivation.
What are non-financial motivators that can enhance productivity?
Non-financial motivators include recognition for hard work, opportunities for career advancement, a positive work environment, and work-life balance. These factors can significantly enhance employee satisfaction and productivity, often complementing the effects of financial incentives.
How does the wage-productivity relationship vary across industries?
The wage-productivity relationship can vary significantly across industries due to differences in job nature, skills required, and market dynamics. For example, in sectors where creativity and innovation are crucial, non-financial motivators might play a more significant role than in industries where output is more directly measurable and linked to financial incentives.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuanced relationship between wages and employee productivity is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their workforce’s output while ensuring job satisfaction and loyalty. This balance is not solely about the financial compensation but also involves creating an engaging and supportive work environment where employees feel valued and motivated.
As businesses navigate the complexities of this relationship, the key lies in adopting a holistic approach that considers both financial rewards and the intrinsic motivations that drive human behavior. By doing so, organizations can foster a high-performing culture that not only boosts productivity but also contributes to long-term success and sustainability.
