Temperature measurement plays a pivotal role in both daily activities and scientific research, serving as a fundamental parameter for describing the state of matter, from the simplest household tasks to complex industrial processes. The two most commonly used temperature scales globally are Celsius and Fahrenheit. Each scale has its unique history, application, and significance, marking its presence in diverse fields such as meteorology, cooking, and scientific research.
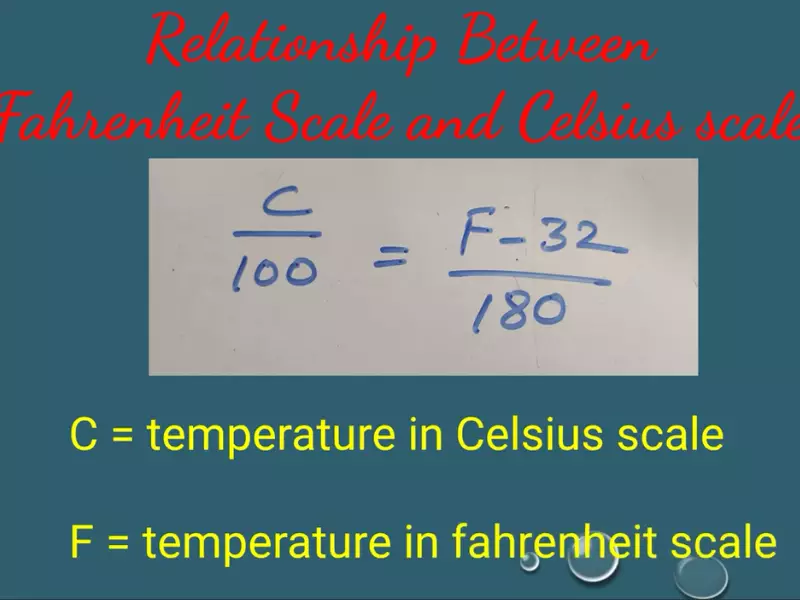
The relation between Celsius and Fahrenheit is established through a conversion formula, making it possible to translate temperatures from one scale to the other seamlessly. Celsius (°C) is preferred in most countries and is used for weather reports, scientific studies, and everyday use. Fahrenheit (°F), on the other hand, is primarily used in the United States for daily weather forecasts, cooking, and describing room temperature. The formula for converting between these scales is straightforward: °�=(°�×95)+32°F=(°C×59)+32 for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit, and °�=(°�−32)×59°C=(°F−32)×95 for converting Fahrenheit to Celsius.
Understanding the conversion and relation between these two scales is more than an academic endeavor; it is a practical necessity in a globalized world. Whether it’s preparing a recipe that uses Fahrenheit while living in a Celsius-dominated region or interpreting weather forecasts during travel, a clear grasp of both scales ensures effective communication and understanding across different regions and cultures.
Temperature Basics
Definition
Temperature is a quantitative measure of how hot or cold something is. It’s a fundamental aspect of our daily lives, influencing everything from the weather to the way we cook our food. At its core, temperature measures the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. This means it tells us how fast the particles in a material are moving. The faster they move, the higher the temperature.
Importance
Why does measuring temperature matter? Temperature measurement is crucial for several reasons:
- Safety: Ensuring food is cooked properly to avoid foodborne illnesses.
- Health: Monitoring body temperature can indicate health conditions.
- Environment: Tracking weather patterns and climate change.
- Industrial: Controlling processes like manufacturing and engineering for quality and safety.
Celsius Scale
Origin
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, was developed in the 18th century by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius. He proposed a scale where 0 represented the boiling point of water, and 100 the freezing point. However, this was later reversed to the scale we use today, where 0°C is the freezing point of water, and 100°C is its boiling point at sea level.
Usage
The Celsius scale is widely adopted around the world for most temperature measurements. It’s used in:
- Scientific research: For its ease of use in calculations involving the Kelvin scale.
- Meteorology: For weather forecasts outside the United States.
- Daily life: In most countries for cooking, weather reports, and medical temperatures.
Fahrenheit Scale
Origin
The Fahrenheit scale was created by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German physicist, in the early 18th century. He developed this scale by setting 32°F as the freezing point of water and 212°F as its boiling point, creating a 180-degree interval between these two points. The choice of these specific values was based on Fahrenheit’s desire to avoid negative temperatures for most practical applications.
Usage
The Fahrenheit scale is predominantly used in:
- The United States: For weather forecasts, body temperature measurements, and cooking.
- Some Caribbean countries: For various local applications.
Conversion Formula
From Celsius to Fahrenheit
Converting temperatures from Celsius to Fahrenheit is straightforward with the following formula:
- Multiply the Celsius temperature by 9/5.
- Add 32 to this result.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Take the Celsius temperature (e.g., 20°C).
- Multiply by 9/5 (20 × 9/5 = 36).
- Add 32 (36 + 32 = 68°F).
This conversion is essential for anyone traveling between countries that use different temperature scales or when following recipes from another country.
From Fahrenheit to Celsius
The process to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius is just the reverse:
- Subtract 32 from the Fahrenheit temperature.
- Multiply this result by 5/9.
Here are the steps:
- Take the Fahrenheit temperature (e.g., 68°F).
- Subtract 32 (68 – 32 = 36).
- Multiply by 5/9 (36 × 5/9 ≈ 20°C).
Practical Applications
Daily Life
Weather Forecasting
In our daily lives, the temperature plays a crucial role in how we plan our activities, what we wear, and how we prepare our homes for the coming days. Weather forecasts provided in Celsius or Fahrenheit inform us of the expected weather conditions, helping us make informed decisions. For instance, knowing it will be 30°C (86°F) outside encourages us to dress lightly, while a forecast of -10°C (14°F) suggests bundling up.
Cooking
Cooking is another area where temperature measurement is vital. Recipes often specify a certain temperature for baking or cooking, which can vary significantly between regions using Celsius or Fahrenheit. Understanding how to convert and apply these temperatures ensures that meals are prepared correctly, achieving the desired taste and texture.
Science and Industry
Scientific Research
In scientific research, precise temperature measurement is fundamental. Whether in chemistry, where reactions occur at specific temperatures, or in physics, where the properties of materials change with temperature, the accurate measurement and understanding of temperature scales are crucial. Researchers often use Celsius due to its scientific basis, but understanding Fahrenheit is also necessary for collaboration with industries and researchers in countries using this scale.
Industrial Processes
Temperature control is essential in various industrial processes, from manufacturing to energy production. For example, the production of steel requires the furnace to reach a specific temperature, often measured in Celsius for precision. However, in the U.S., where Fahrenheit is more common, industries adjust their processes accordingly, demonstrating the importance of understanding both scales.
Comparative Analysis
Advantages
Benefits of Each Scale
Celsius is intuitive for scientific work and daily life in most countries, as its scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, making it easy to grasp for educational purposes and practical applications. Fahrenheit, with its finer scale, offers more detailed temperature readings without resorting to decimals, which can be advantageous in specific fields like meteorology and medical applications where subtle temperature differences matter.
Limitations
Challenges and Criticisms
The Celsius scale is sometimes critiqued for its less detailed readings in everyday scenarios, such as weather forecasts, where the difference of a few degrees can significantly affect comfort. On the other hand, Fahrenheit faces criticism for its complexity in scientific applications and its limited use globally, which can hinder international collaboration and understanding.
Real-World Examples
Weather Reports
The impact of temperature scales becomes evident when comparing weather reports from different countries. For instance, a day forecasted to be 75°F in the United States might be reported as 24°C elsewhere. This variance illustrates the need for both residents and travelers to understand and convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit for practical daily planning.
Cooking Temperatures
Cooking presents a common scenario where temperature conversion is often necessary. A recipe calling for an oven to be preheated to 350°F would require conversion to 177°C for those using ovens calibrated in Celsius. This understanding ensures that food is cooked properly, highlighting the practical importance of mastering both temperature scales.
Tools and Resources
Conversion Tools
Online Calculators and Apps
Numerous online tools and mobile apps are available to effortlessly convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit. These resources eliminate the need for manual calculations, providing instant conversions with the input of a temperature value. This accessibility supports individuals in quickly adapting recipes, understanding weather reports, or engaging in scientific and industrial work across different temperature scales.
Educational Materials
Books and Websites for Further Reading
For those interested in deepening their understanding of temperature measurement and conversion, a wealth of educational materials is available. Books on meteorology, cooking, and science often include sections on temperature scales, while websites dedicated to educational resources in STEM fields provide interactive tools and explanations to enhance learning. These materials not only clarify the practical aspects of temperature conversion but also enrich the reader’s appreciation for the scientific principles underlying these measurements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Celsius and Fahrenheit?
Celsius and Fahrenheit are two different temperature scales. Celsius, part of the metric system, sets the freezing point of water at 0°C and the boiling point at 100°C. Fahrenheit, used primarily in the United States, sets these points at 32°F and 212°F, respectively. The main difference lies in their origins, usage, and the intervals between the freezing and boiling points of water.
How do you convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit?
To convert a temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit, use the formula °�=(°�×95)+32°F=(°C×59)+32. Conversely, to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, apply °�=(°�−32)×59°C=(°F−32)×95. These formulas allow for straightforward conversions between the two scales, facilitating understanding and communication across regions with different temperature scale preferences.
Why is Fahrenheit still used?
Fahrenheit remains in use primarily due to historical and cultural reasons, especially in the United States. It was the first widely adopted temperature scale for precision measurement and has been ingrained in American society through its consistent use in weather forecasts, cooking, and industry. Transitioning to Celsius involves significant changes in daily life, education, and infrastructure, which is a major undertaking.
Is Celsius more accurate than Fahrenheit?
Celsius and Fahrenheit both can be equally accurate for measuring temperature. The difference in perceived accuracy often comes from the scale’s degree division. Fahrenheit has a finer scale than Celsius, allowing for more detailed temperature descriptions without decimals. However, scientific accuracy is not inherently better in one scale over the other; it depends on the precision of measurement instruments and context of use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a testament to the diverse approaches humanity has taken to measure our environment. While each scale has its origins and areas of predominance, the ability to convert between them remains an essential skill in our interconnected world. Whether for personal knowledge, travel, or global communication, understanding both Celsius and Fahrenheit enhances our ability to navigate a wide range of tasks and discussions concerning temperature.
Moreover, as we continue to advance technologically and culturally, the conversation around these two temperature scales underscores the importance of flexibility and adaptation. While certain regions may favor one scale over the other, the global community benefits from a comprehensive understanding of both, ensuring that no matter where we are, the temperature—a universal aspect of our lives—is something we can all speak about with confidence and clarity.
