Infections are a common part of human life, manifesting in various forms and requiring different approaches for treatment. Among these, yeast and bacterial infections stand out for their prevalence and the confusion they often cause. Both can affect various parts of the body, leading to discomfort and a range of symptoms that may overlap, yet they stem from entirely different causes and organisms.
The difference between yeast and bacterial infections lies primarily in their causative agents: yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Candida, while bacterial infections are the result of an imbalance or invasion of harmful bacteria. Yeast infections commonly present as itchiness, redness, and discharge, whereas bacterial infections may cause similar symptoms but often include a noticeable odor and varying discharge characteristics.
Understanding the distinctions between these infections is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. While symptoms can be similar, the underlying causes, risk factors, and treatment options for yeast and bacterial infections vary significantly. Recognizing these differences is key to adopting the correct medical approach, ensuring not only the alleviation of immediate discomfort but also the prevention of future recurrences.

What is Yeast Infection?
Definition and Causes
A Yeast Infection is a fungal infection primarily caused by Candida albicans. This yeast is a natural part of the body’s flora, living in balance with bacteria in various parts of the body, such as the mouth, gut, and the vaginal area. Problems arise when this balance is disturbed, leading to an overgrowth of Candida, which can cause infections.
The main causes of yeast infections include:
- Antibiotic use, which can kill off the beneficial bacteria that control Candida growth
- Hormonal imbalances, often related to pregnancy, birth control, or hormone therapy
- Compromised immune system, making it harder for the body to regulate yeast growth
- Diabetes, especially when blood sugar levels are not well controlled
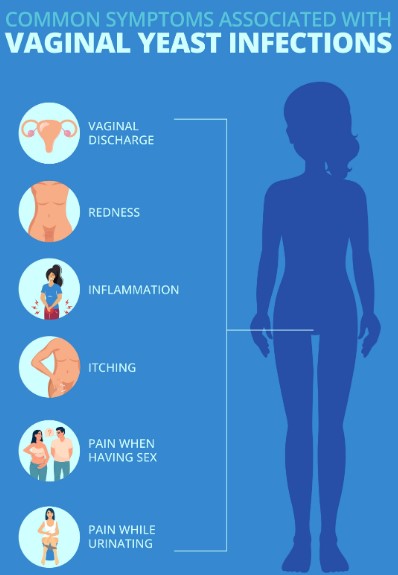
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of a yeast infection may include:
- Itchiness and irritation in the affected area
- Redness and swelling
- Pain during intercourse or when urinating
- Thick, white discharge that can resemble cottage cheese
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of developing a yeast infection include:
- Antibiotic treatment, which disrupts the natural microbial balance
- High estrogen levels from birth control pills or hormone therapy
- Pregnancy
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Poor hygiene, including the use of scented hygiene products that can irritate
What is Bacterial Infection?
Definition and Causes
Bacterial Infections in the context of this article refer specifically to bacterial vaginosis (BV), the most common vaginal infection in women of childbearing age. Unlike yeast infections, BV is caused by an imbalance of bacteria in the vagina. Normally, the vagina contains a balance of various bacteria, including lactobacilli, which are beneficial. When harmful bacteria overtake these good bacteria, it leads to symptoms associated with BV.
The exact cause of this imbalance is not always clear, but several factors can contribute:
- New or multiple sexual partners
- Douching, which can upset the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina
- Lack of lactobacilli bacteria
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of bacterial infections like BV include:
- Thin, gray, or white discharge
- Fishy odor, especially after sex
- Burning sensation when urinating
- Itching around the outside of the vagina
Risk Factors
Risk factors for bacterial infections include:
- Multiple or new sexual partners
- Douching
- Not using condoms during intercourse
Key Differences
Symptoms Comparison
Itchiness and Discomfort
- Yeast infections often cause significant itchiness and discomfort in the affected area.
- Bacterial infections may cause some discomfort, but itchiness is less common.
Discharge Characteristics
- Yeast infections produce a thick, white, clumpy discharge resembling cottage cheese.
- Bacterial infections lead to a thin, gray, or white discharge that’s more uniform in consistency.
Smell
- Yeast infections typically do not have a strong odor.
- Bacterial infections are characterized by a noticeable fishy smell, which can become more pronounced after sexual intercourse.
Causes and Risk Factors
Antibiotics and pH Imbalance
- Antibiotics can trigger yeast infections by killing off beneficial bacteria.
- Bacterial infections can be exacerbated by practices like douching, which disrupts the vagina’s natural pH.
Humidity and Personal Hygiene
- Humidity and moisture-trapping clothing can create an environment conducive to yeast growth.
- Poor hygiene or the use of irritating products can increase the risk of both infections.
Underlying Health Conditions
- Conditions like diabetes can predispose individuals to yeast infections due to higher sugar levels.
- Bacterial infections may not be directly linked to such conditions but can be influenced by sexual behavior and hygiene practices.
Diagnosis Methods
Physical Examination
A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, noting any visible symptoms that might indicate either a yeast or bacterial infection.
Laboratory Tests
- Yeast infections can often be diagnosed with a simple microscopic examination of vaginal discharge.
- Bacterial infections may require more specific testing, such as a bacterial culture or pH testing, to identify the imbalance of bacteria.
Treatment Options
Yeast Infection Treatment
Over-the-counter medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments are widely used for managing yeast infections. They come in various forms, such as creams, tablets, and suppositories. These medications typically contain antifungal agents like miconazole, clotrimazole, and tioconazole that help reduce the fungal overgrowth causing the infection.
- Apply the cream as directed, usually once a day at bedtime.
- Insert tablets or suppositories into the vagina using the applicator provided.
- Continue treatment for the duration recommended, even if symptoms improve earlier.
Prescription drugs
When OTC medications are not effective, a doctor may prescribe stronger antifungal drugs. Fluconazole is a common prescription medication taken orally to treat yeast infections. It’s particularly useful for severe or recurrent infections.
- Take the prescribed dose of medication.
- Follow up with your doctor if symptoms persist or recur.
Home remedies and lifestyle changes
Some home remedies and lifestyle adjustments can support treatment and prevent future yeast infections.
- Wear loose, breathable cotton underwear.
- Avoid prolonged wet clothing.
- Limit sugar intake as it can promote yeast growth.
- Consider natural remedies like yogurt with live cultures or probiotics supplements to restore the natural vaginal flora.
Bacterial Infection Treatment
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for bacterial infections. The type of antibiotic prescribed depends on the specific bacteria involved.
- Complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you feel better before it’s finished.
- Avoid skipping doses to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Probiotics
Probiotics, beneficial bacteria, can help restore the natural balance of bacteria in the body and are often recommended alongside antibiotics to reduce side effects like diarrhea or yeast infections.
- Include probiotic-rich foods like yogurt or kefir in your diet.
- Consider probiotic supplements, especially those containing Lactobacillus strains.
Preventive measures
Preventing bacterial infections involves maintaining a healthy immune system and practicing good hygiene.
- Wash hands regularly with soap and water.
- Avoid unnecessary use of antibiotics to prevent resistance.
- Stay up to date with vaccinations that prevent bacterial infections.
Prevention Strategies
Maintaining proper hygiene
Good hygiene practices are essential in preventing both yeast and bacterial infections.
- Bathe regularly and dry the body thoroughly afterward.
- Change out of wet swimwear and workout clothes promptly.
Dietary considerations
Diet plays a role in maintaining the balance of microbes in the body.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Reduce intake of sugars and refined carbs that can feed harmful microbes.
Avoiding irritants
Certain products can irritate the vagina, disrupting its natural environment and making it more susceptible to infections.
- Avoid scented hygiene products like douches and sprays.
- Choose fragrance-free soaps and laundry detergents.
When to See a Doctor
Persistence of symptoms
If symptoms persist despite treatment, it may indicate a more serious issue or an incorrect diagnosis.
- Consult a doctor if symptoms do not improve within a week of treatment.
Recurring infections
Frequent infections can be a sign of an underlying health issue.
- Seek medical advice if you experience four or more infections in a year.
Preventing complications
Untreated infections can lead to more serious health problems.
- Visit a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment to avoid complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes yeast infections to recur?
Recurrent yeast infections can result from several factors, including hormonal imbalances, uncontrolled diabetes, and the use of antibiotics that disrupt the natural flora of the body. Maintaining a balanced diet, proper hygiene, and consulting a healthcare provider for tailored advice can help manage and prevent recurrences.
Can bacterial infections clear up on their own?
Some mild bacterial infections may resolve without treatment as the body’s immune system fights off the invaders. However, more serious infections require antibiotics to prevent complications. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
How can I tell the difference between a yeast infection and a bacterial infection?
While some symptoms overlap, yeast infections typically present with itchiness and a thick, white discharge without a strong odor. Bacterial infections, on the other hand, often produce a fishy odor and a thinner, grayish discharge. A medical examination and tests can provide a definitive diagnosis.
Are over-the-counter treatments effective for both yeast and bacterial infections?
Over-the-counter treatments are available for yeast infections and can be quite effective. However, bacterial infections usually require prescription antibiotics. It’s crucial to diagnose the type of infection accurately before starting any treatment.
Conclusion
Recognizing the differences between yeast and bacterial infections is fundamental to effective treatment and overall well-being. Both conditions are common, yet their management requires distinct approaches tailored to the specific causative agents. Misdiagnosis or incorrect treatment can lead to complications or recurrent episodes, underscoring the importance of professional medical advice.
Armed with the knowledge of these differences and the treatments available, individuals can take proactive steps towards prevention and seek appropriate care when symptoms arise. Awareness and understanding are key to navigating the complexities of these infections, ensuring health and comfort in the face of such challenges.