The male reproductive system, complex yet fascinating, comprises various components, each playing a crucial role in reproduction. Among these, the Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia stand out due to their essential functions in the transport and maturation of sperm, respectively. While they may seem similar at a glance due to their roles in sperm handling, significant differences between them are pivotal for the fertility process.
The Vas Deferens is a long, muscular tube that transports mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra, readying it for ejaculation. In contrast, the Vasa Efferentia are a series of small ducts that carry sperm from the testis to the epididymis, where sperm undergo maturation and storage. These structures, though distinct in their anatomy and function, work in concert within the male reproductive system to ensure the efficient transfer and maturation of sperm.
Anatomy, function, and the implications of these reproductive components are critical not just for understanding male fertility but also for medical practices like vasectomy and assisted reproductive technologies. Recognizing the differences between the Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia sheds light on their unique roles and how they contribute to the complex journey of sperm from production to ejaculation, a journey that is fundamental to reproduction.
Anatomy and Location
Vas Deferens
Description and Structure
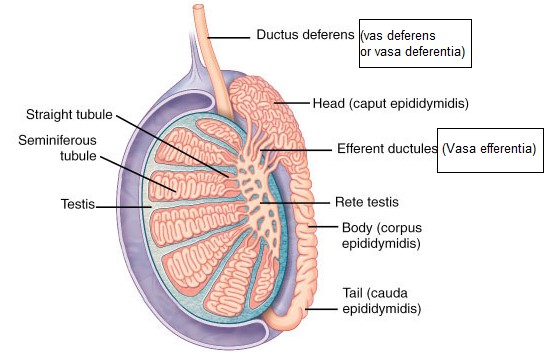
The Vas Deferens, also known as the ductus deferens, is a vital component of the male reproductive system. It is a muscular tube, approximately 45 centimeters long, responsible for the transport of sperm from the epididymis, where sperm are stored and mature, to the ejaculatory ducts. The wall of the Vas Deferens is made up of three layers: an inner lining (mucosa), a middle muscular layer, and an outer fibrous layer. This structure allows it to contract rhythmically, propelling sperm forward during ejaculation.
Anatomical Location
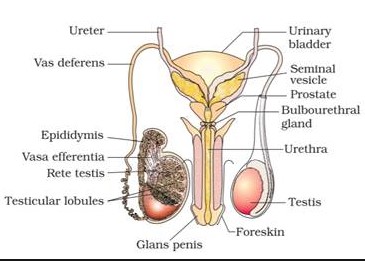
The Vas Deferens begins at the tail of the epididymis, ascending into the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal as part of the spermatic cord. It then traverses down the posterior border of the bladder, where it joins with the seminal vesicle to form the ejaculatory duct. This positioning is crucial for its role in sperm transport, placing it strategically within the male reproductive anatomy.
Vasa Efferentia
Description and Structure
The Vasa Efferentia are a series of small ducts connecting the rete testis, a network of tubules in the testis, to the head of the epididymis. Typically, there are about 10 to 20 of these efferent ductules. Each ductule is lined with ciliated epithelial cells to help move the immature sperm from the testis to the epididymis for maturation. Their ciliated nature is key to their function, gently propelling the sperm along their journey.
Anatomical Location
Located within the testicular substance, the Vasa Efferentia begin at the rete testis. From there, they extend to the upper portion of the epididymis, specifically to its head, where they coalesce. This proximal positioning to the testes and epididymis highlights their role in the initial phase of sperm transport and maturation.
Function and Role
Vas Deferens
Role in Sperm Transport
The primary role of the Vas Deferens is to transport mature sperm from the epididymis to the urethra, the final pathway for ejaculation. During sexual arousal, rhythmic contractions of the muscular layer of the Vas Deferens propel the sperm forward, mixing with seminal fluid to form semen.
Interaction with Other Reproductive Organs
The Vas Deferens interacts closely with several reproductive organs:
- It receives sperm from the epididymis.
- It connects with the seminal vesicles to form the ejaculatory ducts, where seminal fluid is added to the sperm.
- Finally, it empties into the urethra, where sperm is expelled during ejaculation.
Vasa Efferentia
Role in Sperm Maturation
The Vasa Efferentia play a critical role in the initial stage of sperm maturation. By transporting sperm from the testes to the epididymis, they facilitate the environment necessary for sperm to gain motility and the ability to fertilize an egg.
Connection to the Epididymis
The close anatomical and functional relationship between the Vasa Efferentia and the epididymis is essential. The epididymis is where sperm undergo further maturation, acquiring motility and the capability for fertilization. This process is vital for ensuring sperm are prepared for their role in reproduction.
Physiological Differences
Sperm Maturation Process
The journey of sperm from production to ejaculation involves several critical stages:
- Production: Sperm are produced in the testes.
- Initial Transport: Via the Vasa Efferentia, immature sperm are moved to the epididymis.
- Maturation: In the epididymis, sperm undergo maturation, acquiring motility and fertilization ability.
- Final Transport: Mature sperm are then moved through the Vas Deferens for ejaculation.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones play a pivotal role in the functioning of both the Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia. Testosterone, in particular, is crucial for the regulation of sperm production and maturation. Hormonal signals also coordinate the timing of sperm transport and ejaculation.
Timing and Sequence of Function in Reproduction
The timing and sequence of each component’s function are meticulously orchestrated:
- Vasa Efferentia act first, moving sperm from the testes to the epididymis.
- Following maturation in the epididymis, the Vas Deferens then transports the sperm towards the urethra, culminating in ejaculation.
Pathological Conditions
Vas Deferens
Common Disorders and Abnormalities
- Congenital Absence: Some men are born without a Vas Deferens, a condition often associated with cystic fibrosis.
- Obstruction: Blockages can occur, preventing the transport of sperm and affecting fertility.
Impact on Fertility
The absence or obstruction of the Vas Deferens directly impacts a man’s fertility by hindering or stopping the transport of sperm, crucial for natural conception.
Vasa Efferentia
Common Disorders and Abnormalities
- Blockage: Obstructions in the Vasa Efferentia can prevent sperm from reaching the epididymis, impacting their maturation process.
- Inflammation: Infections or inflammation can damage these ducts, affecting sperm quality.
Impact on Sperm Quality and Fertility
Disorders of the Vasa Efferentia can lead to reduced sperm quality by interfering with the early stages of sperm transport and maturation, ultimately affecting male fertility.
Surgical and Medical Relevance
Vasectomy and Vas Deferens
Procedure and its Implications on Reproduction
A vasectomy is a surgical procedure that involves cutting and sealing the Vas Deferens to prevent sperm from entering the seminal stream, effectively resulting in sterility. This procedure is highly effective as a method of contraception, with a success rate surpassing 99%. Despite its effectiveness, a vasectomy is still considered a reversible procedure through a subsequent operation known as a vasovasostomy, where the Vas Deferens is reconnected. However, the success of reversal varies, and fertility may not be fully restored.
Surgical Interventions Involving Vasa Efferentia
Surgical intervention on the Vasa Efferentia is less common and more complex due to their delicate and small structure. In certain cases of male infertility, microsurgical repair of the Vasa Efferentia might be considered if obstruction is identified as the primary cause of impaired sperm maturation or transport. The impact of such procedures on fertility is highly variable and depends on the underlying condition and the success of the surgery in restoring normal sperm flow.
Comparative Analysis
Key Differences Summarized
- Location: Vas Deferens runs from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts, while Vasa Efferentia connect the rete testis to the epididymis.
- Function: Vas Deferens transports mature sperm to the urethra, and Vasa Efferentia are involved in the early transport of immature sperm to the epididymis for maturation.
- Surgical Relevance: Vasectomy involves the Vas Deferens and is a common procedure for contraception, whereas surgical intervention on the Vasa Efferentia is rare and typically aimed at resolving specific fertility issues.
Evolutionary Perspective
Evolution of Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia
The Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia have evolved as critical components of the male reproductive system, optimizing the transport and maturation of sperm. This evolution reflects the necessity of efficient reproductive strategies in mammals. Comparative anatomy studies suggest that while the basic functions of these structures have been conserved, there are variations across species that reflect different reproductive strategies, such as internal versus external fertilization, and the need for sperm storage.
Comparative Anatomy Across Species
In most mammals, the Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia perform similar roles as in humans. However, in species like birds and fish, analogous structures have evolved to meet the demands of their specific reproductive methods. For example, many birds lack a Vas Deferens, having evolved different mechanisms for sperm transport and storage, demonstrating the adaptability and diversity of reproductive systems in the animal kingdom.
Importance in Fertility Treatments
Role in Assisted Reproductive Technologies
The Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia play significant roles in the success of assisted reproductive technologies (ART). For instance, in cases where the Vas Deferens is blocked or absent, sperm can be directly extracted from the epididymis or testis for use in procedures like IntraCytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), part of In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) treatments. Understanding the functional health of the Vasa Efferentia is also crucial for diagnosing certain infertility issues and tailoring the appropriate ART approach.
Implications of Abnormalities in Fertility Planning
Abnormalities in the Vas Deferens or Vasa Efferentia can significantly impact fertility planning. For couples facing such challenges, a thorough understanding of these conditions is essential for making informed decisions about their reproductive options. This might include considering surgical repair, using donor sperm, or exploring ART possibilities. The development of new technologies and surgical techniques continues to provide hope and options for individuals and couples navigating the complexities of infertility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Vas Deferens?
The Vas Deferens is a crucial part of the male reproductive system, acting as a muscular conduit for mature sperm to travel from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts. This tube is integral in the final stages of sperm transport, ensuring that sperm are delivered into the urethra for potential ejaculation. It plays a pivotal role in male fertility, making its functionality vital for successful reproduction.
How does the Vasa Efferentia differ from the Vas Deferens?
The Vasa Efferentia, unlike the Vas Deferens, are small ducts connecting the testicles to the epididymis. Their primary role is in the initial stage of sperm transport, facilitating the movement of sperm from the testes, where they are produced, to the epididymis, where they undergo maturation and storage. This initial step is crucial for the quality and functionality of the sperm, distinguishing the Vasa Efferentia’s role from that of the Vas Deferens.
Why are the Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia important for fertility?
Both the Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia are integral to male fertility. The Vas Deferens ensures the transport of mature sperm to the urethra for ejaculation, while the Vasa Efferentia are responsible for the initial transfer and subsequent maturation of sperm within the epididymis. Their coordinated functions ensure that sperm are both mature and properly transported for fertilization, highlighting their importance in the reproductive process.
Conclusion
The distinction between the Vas Deferens and Vasa Efferentia is more than an anatomical curiosity; it is a testament to the complexity and precision of the male reproductive system. Each structure’s unique role, from the maturation and storage of sperm to their final transport for ejaculation, underscores the intricacies involved in human reproduction. Understanding these differences not only enriches our knowledge of biology but also informs medical practices that can aid those facing fertility challenges.
Furthermore, this awareness facilitates a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance maintained within the body, necessary for the continuation of life. As science advances, the significance of these structures in fertility treatments continues to evolve, offering hope and solutions to individuals and couples navigating the path to parenthood.