Proteins play a pivotal role in numerous biological processes, and among them, troponin and calmodulin stand out due to their critical functions in muscle contraction and cellular signaling, respectively. These proteins, though similar in being calcium-binding, have distinct structures and roles within the cell, influencing various physiological and pathological processes. The comparison between troponin and calmodulin reveals fascinating aspects of cellular mechanics and regulatory systems.
Troponin and calmodulin are essential proteins that differ primarily in their structure and function. Troponin is a complex protein integral to muscle contraction in cardiac and skeletal muscles, acting as a regulatory protein in the thin filaments of muscle tissue. Calmodulin, on the other hand, functions as a multifunctional intermediary protein that modulates numerous enzymes and other proteins by binding calcium ions, influencing many cellular processes including metabolism, apoptosis, and muscle contraction.
These proteins not only facilitate vital cellular functions but also have significant implications in medical diagnostics and treatments, particularly in cardiac health for troponin and in signaling pathways for calmodulin. Understanding their differences is crucial for advancements in medical science and therapeutic interventions.
Protein Basics
Definition and Function
Proteins are large, complex molecules essential to all living organisms. They are composed of amino acids, the building blocks that play critical roles in cell structure and function. Proteins serve a vast array of functions within biological systems, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another.
Importance in Cellular Activities
Proteins are indispensable for the survival and proper functioning of cells. They are involved in virtually every cellular process, from muscle contraction and immune response to signal transduction and cell adhesion. Their ability to perform a wide variety of functions derives from their unique three-dimensional structures, which are precisely folded according to instructions encoded within genes.
What is Troponin?
Structure Details
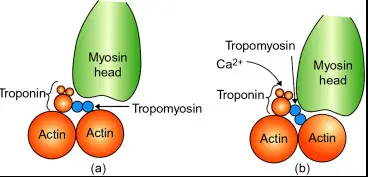
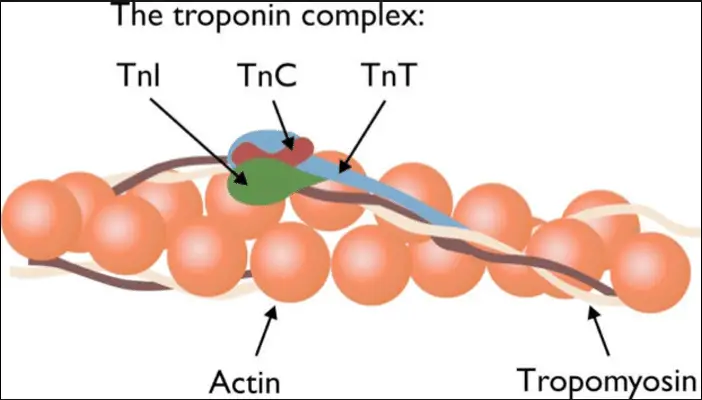
Troponin is a complex of three regulatory proteins (troponin C, I, and T) that is integral to muscle contraction in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Each component has a specific role: troponin C binds calcium ions, troponin I inhibits actin-myosin interactions, and troponin T binds to tropomyosin, positioning the troponin complex on the muscle fiber.
Role in Muscle Contraction
Troponin plays a pivotal role in regulating muscle contraction. It is located on the thin filament of muscle fibers and acts as a sensor and mediator of calcium ion concentrations. When calcium binds to troponin C, it causes a conformational change in the troponin complex, leading to the removal of troponin I from the actin binding site. This action allows actin and myosin to interact, resulting in muscle contraction.
Types and Functions
There are three main types of troponin (C, I, and T), each essential for the contraction of different muscle types. Troponin T anchors the complex to the muscle fiber, troponin I inhibits muscle contraction until calcium binds to troponin C, and troponin C triggers the contraction process. This division of labor is crucial for precise muscle function and regulation.
What is Calmodulin?
Structure Insights
Calmodulin is a small, highly conserved protein that can bind and respond to calcium ions. It is composed of two roughly symmetrical globular domains connected by a flexible linker. Each domain can bind two calcium ions, allowing calmodulin to function effectively as a calcium sensor and signal transducer in various cellular processes.
Mechanism of Action
Calmodulin mediates many crucial cellular functions through its ability to bind calcium and interact with various target proteins. Upon binding calcium, calmodulin undergoes a change in its structure that allows it to activate or inhibit a wide range of target proteins, including kinases, phosphatases, and ion channels, thereby influencing cellular activities such as metabolism, cell cycle progression, and gene expression.
Cellular Roles
Calmodulin plays a central role in cellular signaling pathways. It affects processes such as muscle contraction, neurotransmitter release, and memory formation in the brain. Its ability to regulate different proteins makes it a key player in cellular response mechanisms, adapting to and influencing cellular conditions and signals.
Key Differences
Structural Comparisons
While both troponin and calmodulin bind calcium, their structures are fundamentally different. Troponin is a complex protein specific to muscle fibers, whereas calmodulin is smaller and more versatile, involved in numerous cellular processes across different cell types.
Functional Divergences
Troponin’s primary function is muscle contraction regulation, specifically in cardiac and skeletal muscles. In contrast, calmodulin serves as a multifunctional intermediary that affects various enzymes and proteins, influencing numerous cellular processes.
Interaction Varieties
The interactions of troponin are mainly with muscle-related proteins, directly affecting muscle contraction mechanics. Calmodulin, however, interacts with a broader array of proteins, regulating activities from metabolism to memory in the brain, showcasing its versatility and widespread influence in cellular signaling.
Troponin and Health
Cardiac Health Indicators
Troponin is a key biomarker for cardiac health, particularly in diagnosing heart attacks. The presence of troponin in the blood is a significant indicator of heart muscle damage because it is released into the bloodstream when the heart muscle suffers injury. Elevated levels of troponin are thus used by healthcare professionals to quickly and accurately diagnose myocardial infarctions (heart attacks).
Diagnostic Uses
The diagnostic applications of troponin testing are crucial in emergency medicine. Tests for troponin levels are typically performed on patients who exhibit symptoms of a heart attack, such as chest pain and shortness of breath. The test’s results help in:
- Determining the presence of cardiac events.
- Guiding treatment decisions, including the urgency of need for interventions like angioplasty.
- Monitoring cardiac patients over time to assess recovery or progression of disease.
Calmodulin in Signaling
Role in Cellular Signaling
Calmodulin’s role in cellular signaling is broad and impactful, acting as a mediator for various cellular responses to calcium changes in the environment. This protein participates in processes such as:
- Activation of calcium-dependent protein kinases, which are vital for cell cycle control and gene expression.
- Regulation of ion channels that control muscle contractions, neuronal activity, and other physiological functions.
Impact on Health
The function of calmodulin in health is profound, particularly concerning its role in neuromuscular activities and mental health. Disruptions in calmodulin function have been associated with a variety of health issues, including heart arrhythmias and certain forms of intellectual disability, highlighting its critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and function.
Research and Innovations
Recent Studies on Troponin
Recent advancements in the study of troponin have focused on improving the sensitivity and specificity of troponin tests. Innovations include:
- High-sensitivity troponin tests that can detect very low levels of troponin, enabling earlier diagnosis of cardiac events.
- Studies exploring genetic variants of troponin that might influence heart disease risk and treatment outcomes.
Advances in Calmodulin Research
Research into calmodulin has revealed its involvement in a broader range of diseases than previously understood, including neurological disorders. Recent studies highlight:
- New therapeutic targets for drugs that can modulate calmodulin activity.
- Genetic studies linking calmodulin to specific diseases, offering potential for personalized medicine approaches.
Practical Applications
Clinical Implications
The clinical implications of understanding troponin and calmodulin are significant. For troponin, its role in cardiac diagnostics helps in:
- Rapid risk assessment in emergency settings.
- Tailoring patient management strategies based on risk.
For calmodulin, its ubiquitous presence across cell types makes it a potential target for treating a wide array of conditions, influencing treatments in:
- Neurological disorders, where modulation of calmodulin activity could alter disease progression.
- Cardiac therapies, where calmodulin inhibitors could potentially treat arrhythmias.
Therapeutic Potentials
The therapeutic potential of targeting these proteins is vast. With troponin, therapies that could specifically influence its expression or function might improve outcomes in heart disease. For calmodulin, potential therapies could include:
- Small molecules that can inhibit or enhance calmodulin activity.
- Biologicals that modulate the signaling pathways influenced by calmodulin, offering new avenues for disease modification in complex conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and bipolar disorder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Troponin?
Troponin is a regulatory protein found in skeletal and cardiac muscle fibers that controls the calcium-dependent interaction between actin and myosin, facilitating muscle contraction. It is critically used in medical diagnostics as a marker for heart muscle damage.
How does Calmodulin function?
Calmodulin acts as a versatile calcium sensor and mediator in cells, influencing various enzymes, ion channels, and other proteins. It binds calcium ions and undergoes a conformational change that allows it to regulate different cellular mechanisms and responses.
Why compare Troponin and Calmodulin?
Comparing troponin and calmodulin helps clarify their distinct roles in muscle contraction and cellular signaling, respectively. Understanding these differences is vital for biomedical research and therapeutic applications, especially in cardiovascular and neurological disorders.
Are Troponin and Calmodulin related?
While both troponin and calmodulin bind calcium, they are functionally and structurally distinct, with troponin primarily involved in muscle contraction and calmodulin in regulating a wide array of cellular processes.
How are Troponin and Calmodulin used in healthcare?
Troponin is widely used as a biomarker for diagnosing heart attacks, indicating cardiac muscle stress or damage. Calmodulin, through its role in cellular signaling pathways, has implications in understanding and treating neurological and metabolic diseases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, troponin and calmodulin serve as fascinating examples of how proteins can have specialized yet crucial roles in the human body. Their study not only enriches our understanding of cellular functions but also enhances our capabilities in diagnosing and treating diseases. As research continues, the depth of our knowledge about these proteins will likely unlock new therapeutic avenues and improve our approach to healthcare.
Future explorations into troponin and calmodulin will undoubtedly reveal more about their potential in medical science. As our understanding deepens, so will our ability to craft targeted treatments that address the specific mechanisms these proteins influence, offering hope for better management of cardiac and cellular functions.