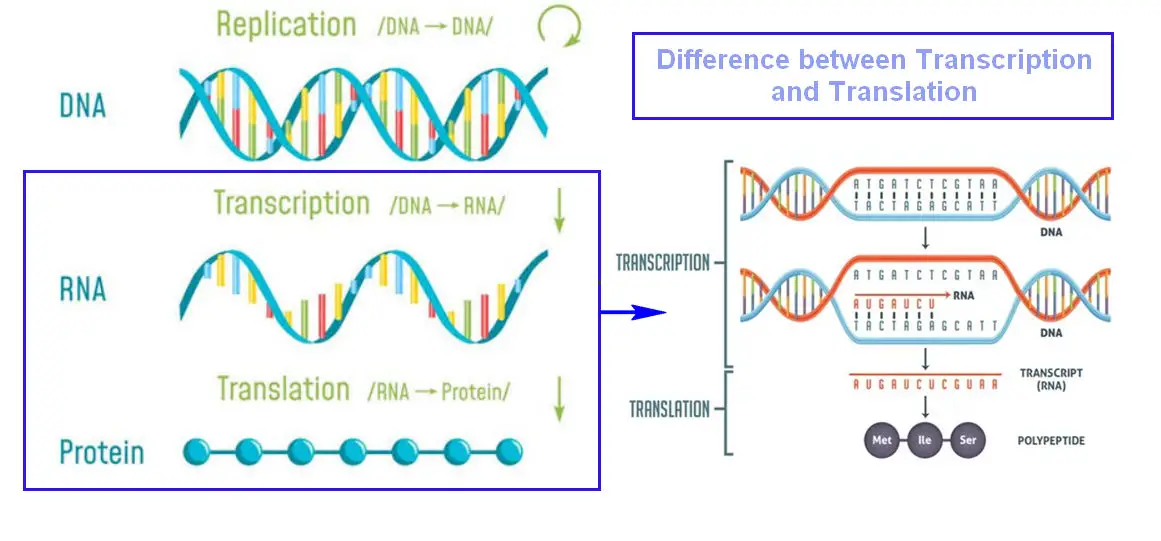
DNA is the basic building block of life, and understanding how it works is essential to understanding the structure and function of our bodies. Transcription and translation are two processes that occur within the cells of living organisms, and understanding the difference between these two processes is key to understanding how DNA works. In this blog, we will discuss the differences between transcription and translation in DNA, and how they work together to create proteins and other molecules essential for life.
How transcription and translation differ
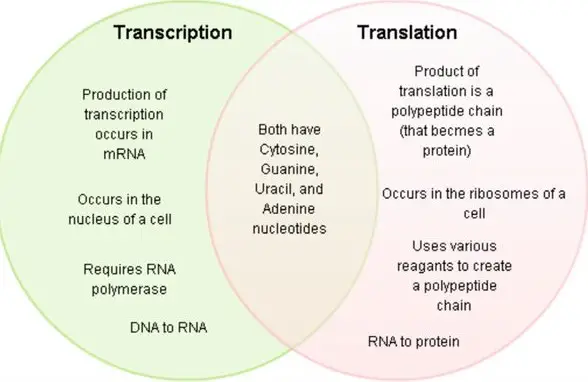
Transcription and translation are two of the most essential processes in the life of a cell. Transcription is the process whereby genetic information in DNA is converted into a complementary RNA molecule.
While both are important in the formation of proteins, there are distinct differences between them. Transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell, while translation takes place in the cytoplasm.
During transcription, the information from the DNA is copied into messenger RNA. During translation, the messenger RNA is decoded into a sequence of amino acids, which then form a protein. Transcription involves the use of DNA-specific enzymes to copy the genetic information from the DNA into a messenger RNA molecule, while translation involves the use of ribosomes and transfer RNA to decode the information contained in the RNA molecule and form a protein.
In summary, transcription is the process of copying genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, while translation is the process of decoding the messenger RNA to form a protein.
Steps of transcription
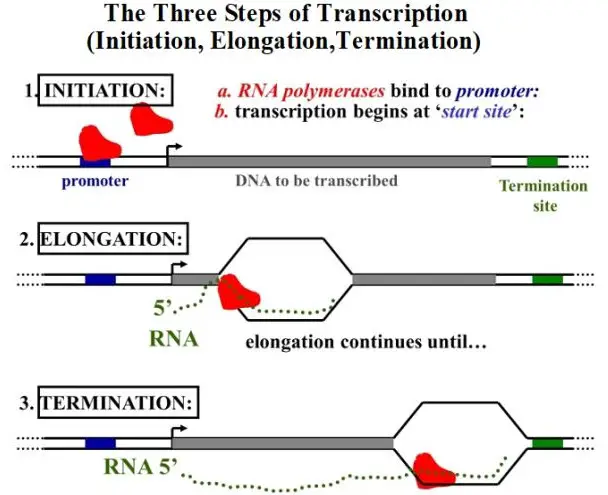
Transcription and translation are two of the most important processes in DNA. They both work together to create proteins, which are essential to life.
To understand the difference between transcription and translation, it’s important to understand the steps that each process involves. Transcription begins when a strand of DNA unwinds and a specific enzyme, called RNA polymerase, binds to a specific sequence of the DNA.
The enzyme then begins to copy the code from the DNA into mRNA. Once the process is complete, the mRNA is released and the DNA strand reforms. Translation then begins when the mRNA strand is read by ribosomes, which convert the code into a functional protein.
This process involves the addition of amino acids to the mRNA strand, creating the protein. Once the ribosomes have finished, the mRNA strand is released and the newly formed protein is free to do its job.
In summary, transcription is the process of copying the DNA code into mRNA, while translation is the process of creating a protein from the mRNA code. Understanding the difference between these two processes is essential to understanding how genetic information is expressed in the body.
Steps of translation
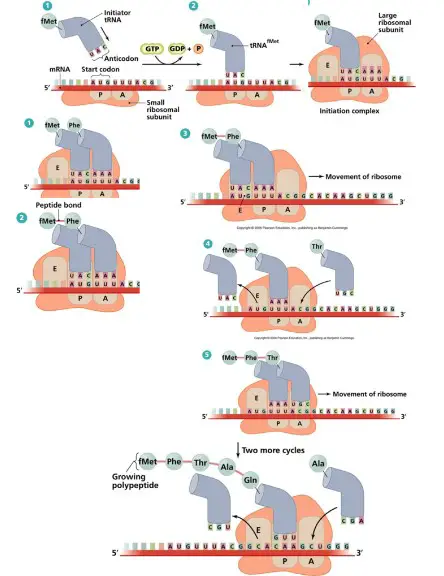
The difference between transcription and translation in DNA is an important concept to understand in biology. Transcription is the process of creating an RNA molecule from a DNA template.
During this process, the information from the DNA is copied into the RNA molecule. Translation is the process of decoding the RNA molecule and turning it into a functional protein. This is done through the ribosomes which read the information on the RNA and translate it into a sequence of amino acids, which then build the protein.
Transcription and translation are two distinct steps that must occur for a gene to be expressed. While transcription is the process of copying the DNA sequence into an RNA molecule, translation is the process of using the information on the RNA molecule to produce a functional protein. Through these two steps, the genetic code of the DNA is able to be expressed and ultimately create the proteins necessary for life.
Examples of transcription and translation in dna
DNA is the essential building block of life, and understanding the difference between transcription and translation is key to understanding how genetic information is stored and expressed. Transcription occurs when the information in a gene is copied from DNA into an intermediary molecule called mRNA.
This mRNA molecule then travels to a ribosome, where it is used as a template to “translate” the information into a protein. In this way, transcription and translation are complementary processes, and together they form the basis of gene expression. Transcription is the first step in gene expression and is the process of copying the information from DNA into mRNA.
Translation is the second step and is the process of translating the information from mRNA into a protein. While both processes are essential for gene expression, they differ in several key ways. Transcription is carried out by DNA-dependent RNA polymerase while translation is carried out by a complex of proteins and ribosomes.
Transcription is carried out by DNA-dependent RNA polymerase while translation is carried out by a complex of proteins and ribosomes. Furthermore, transcription involves the synthesis of a single-stranded molecule of mRNA while translation involves the synthesis of a polypeptide. Finally, transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell while translation occurs in the cytoplasm.
Benefits of understanding the difference between transcription and translation
Understanding the difference between transcription and translation is essential in understanding how DNA works. Transcription is the process of copying a gene’s DNA sequence into a complementary RNA molecule. Translation is the process of translating the information encoded in an mRNA molecule into a functional protein.
Translation is the process of translating the information encoded in an mRNA molecule into a functional protein. Together, these processes are responsible for the production of the proteins necessary for the body to function. By understanding the difference between transcription and translation, we can better understand how cells use genetic information to create proteins, and how mutations in DNA can have serious consequences.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, the difference between transcription and translation in DNA is that transcription is the process of creating an mRNA molecule from the DNA template, while translation is the process of using the mRNA sequence to create a functional protein. Transcription occurs in the nucleus of a cell, while translation occurs in the cytoplasm.
Both processes are essential for the production of proteins and the functioning of all living organisms.