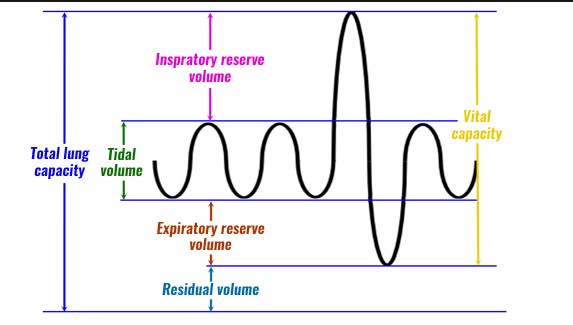
Lung capacity plays a critical role in our overall health and well-being, significantly impacting everything from daily activities to athletic performance. The terms “tidal volume” and “vital capacity” are central to understanding how our lungs function, representing key measurements in the field of respiratory physiology. Despite their importance, these concepts are often surrounded by confusion, with many unsure of their distinct meanings and implications.
Tidal volume refers to the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing, while vital capacity is the maximum amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after a maximum inhalation. Essentially, tidal volume measures everyday breathing, and vital capacity assesses lung capacity at its maximum effort, highlighting their roles in evaluating respiratory health.
These measurements not only provide insights into an individual’s respiratory health but also indicate potential medical concerns. By accurately assessing tidal volume and vital capacity, healthcare professionals can detect, diagnose, and monitor respiratory conditions, tailor treatments, and guide patients towards healthier lifestyles. As such, understanding the difference between these two metrics is crucial for anyone looking to maintain or improve their respiratory well-being.
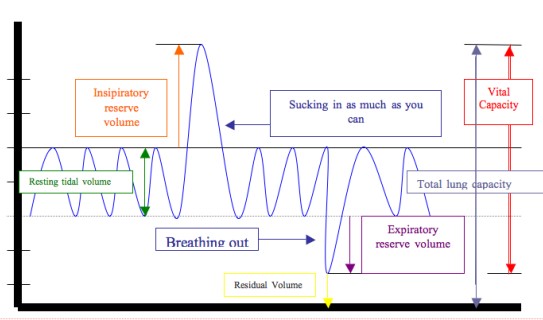
Tidal Volume Explained
Definition and Importance
Tidal volume is the amount of air inhaled or exhaled with each breath under resting conditions. It’s a foundational concept in respiratory physiology, essential for understanding how our lungs function during everyday breathing. Tidal volume plays a pivotal role in maintaining oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the bloodstream, crucial for homeostasis.
Measurement Process
The measurement of tidal volume is typically done using a device called a spirometer. This process involves:
- Breathing normally into a mouthpiece connected to the spirometer.
- The device records the amount of air inhaled and exhaled.
- The data is analyzed to determine the average tidal volume.
Accurate measurement of tidal volume is vital for assessing lung function and detecting potential respiratory issues early.
Vital Capacity Uncovered
Definition and Significance
Vital capacity represents the maximum amount of air a person can expel from their lungs after a maximal inhalation. It is a key measure of lung capacity and health, reflecting the total volume of air that can be utilized during physical exertion. Understanding vital capacity is crucial for identifying respiratory health status and potential lung diseases.
Measurement Techniques
Vital capacity is measured using a spirometer in a slightly different manner than tidal volume:
- The individual takes a deep breath in, filling the lungs to maximum capacity.
- They then exhale as much air as possible into the spirometer.
- The measurement reflects the person’s maximal expiratory effort.
Factors influencing vital capacity include age, gender, body composition, and physical conditioning.
Key Differences
Tidal Volume vs. Vital Capacity
While both tidal volume and vital capacity are measures of lung function, they represent different aspects. Tidal volume is the air moved during normal breathing, whereas vital capacity measures the maximum effort of the lungs. Understanding these differences is crucial for assessing lung function and health.
Measurement Contrasts
- Tidal volume is measured under resting conditions, reflecting everyday lung function.
- Vital capacity requires maximal inhalation followed by maximal exhalation, showing the lungs’ total capacity.
These differences in measurement highlight the distinct roles each plays in respiratory health assessment.
Health Implications
Variations in tidal volume and vital capacity can indicate respiratory or general health issues. Lower than average measurements may signal obstructive or restrictive lung diseases, while higher values are generally seen in well-conditioned individuals. Monitoring these metrics helps in early detection and management of potential health concerns.
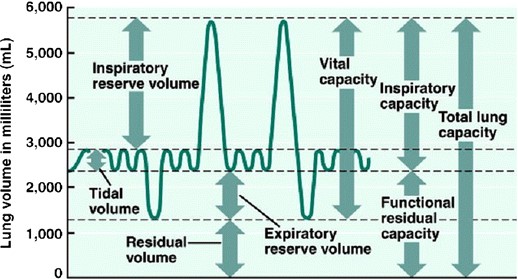
Factors Influencing Measurements
Age and Gender
Age and gender are significant factors affecting tidal volume and vital capacity. As we age, our lung capacity tends to decrease, which can be seen in the reduction of both tidal volume and vital capacity. This decline begins after peak lung function is reached, typically in the mid-20s for most people. Gender differences are also evident, with males generally having higher lung volumes than females, attributed to differences in body size and lung size.
Physical Fitness
Physical fitness plays a crucial role in enhancing lung capacity. Regular exercise can increase vital capacity and improve tidal volume efficiency. Well-conditioned athletes often exhibit larger vital capacities due to their enhanced ability to utilize oxygen efficiently. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to decreased lung function, emphasizing the importance of physical activity for respiratory health.
Medical Conditions
Several medical conditions can significantly impact tidal volume and vital capacity:
- Asthma and COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) can reduce airflow, affecting tidal volume and reducing vital capacity.
- Pulmonary fibrosis restricts lung expansion, decreasing vital capacity.
- Neuromuscular diseases can weaken the muscles involved in breathing, impacting both measurements.
Practical Applications
In Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, tidal volume and vital capacity measurements are critical for:
- Diagnosing respiratory conditions like asthma, COPD, and restrictive lung disease.
- Treatment planning, including ventilator settings for patients with respiratory failure.
- Monitoring disease progression and response to treatment.
For Athletes
Athletes rely on optimal lung function for peak performance. Monitoring tidal volume and vital capacity helps in:
- Assessing the effectiveness of training programs.
- Identifying potential respiratory issues before they affect performance.
- Tailoring breathing techniques to enhance oxygen efficiency.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle changes can significantly impact lung health. Suggestions include:
- Quitting smoking to improve overall lung capacity.
- Avoiding pollutants where possible to reduce the risk of lung damage.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to decrease the workload on the lungs.
Enhancing Respiratory Health
Breathing Exercises
Breathing exercises can help increase tidal volume and vital capacity:
- Diaphragmatic breathing focuses on engaging the diaphragm, promoting efficient oxygen exchange.
- Pursed-lip breathing helps increase tidal volume by slowing down the exhalation rate, improving oxygen saturation.
- Deep breathing exercises can enhance vital capacity by stretching the lungs and strengthening respiratory muscles.
Physical Activities
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining and improving lung function. Recommended activities include:
- Aerobic exercises like walking, running, and cycling to increase heart rate and lung function.
- Strength training to improve chest and abdominal muscles, supporting better breathing.
- Yoga and Pilates, which often focus on breath control and lung capacity.
Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of lung capacity can lead to early detection of potential issues and help maintain respiratory health:
- Use of home spirometry to track changes in tidal volume and vital capacity.
- Regular medical check-ups for professional assessment and advice.
- Self-monitoring of breathing patterns and symptoms to identify changes early.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Tidal Volume?
Tidal volume is the volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during a normal breath. It’s a critical component of respiratory health, reflecting the efficiency of the lungs in performing the most basic function—breathing. For an average adult, this typically ranges from about 500 mL per breath.
How is Vital Capacity Measured?
Vital capacity is measured using a spirometer, which evaluates the amount of air a person can exhale after a deep inhalation. This measurement reflects the total capacity of the lungs and can vary based on factors such as age, gender, fitness level, and underlying health conditions.
Why are Tidal Volume and Vital Capacity Important?
These measurements are vital for assessing lung health, diagnosing respiratory disorders, and tracking the progress of treatment. Tidal volume gives insights into everyday lung function, while vital capacity provides a broader view of the lungs’ potential, helping to identify issues like restrictive or obstructive lung diseases.
How Do Age and Gender Affect Lung Capacity?
Age and gender significantly influence lung capacity; typically, lung capacity increases with physical growth until the mid-20s and then gradually decreases with age. Men generally have higher lung capacity than women, owing to differences in lung size and muscle strength.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between tidal volume and vital capacity is essential for anyone interested in their respiratory health. These measures not only offer a window into the body’s basic functioning but also serve as critical tools in diagnosing and managing lung conditions. By keeping track of these parameters, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining lung health, optimizing breathing, and enhancing overall well-being.
The insights gained from tidal volume and vital capacity measurements empower us to make informed decisions about our health. Whether you’re a healthcare professional, an athlete, or simply someone invested in your health, appreciating the nuances of these respiratory metrics can guide you towards better respiratory practices and, ultimately, a healthier life.