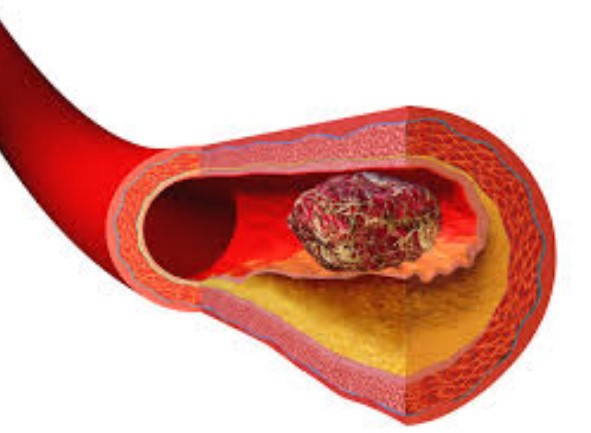
Thrombosis and embolism are two distinct cardiovascular events that can occur in the body, and understanding the difference between the two can be important in determining the best treatment. In this blog, we will explore the differences between thrombosis and embolism, how they are related, and the potential treatments for each.
What is thrombosis
Thrombosis and embolism are two terms that are commonly used to describe conditions related to blood clots. Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel and embolism is the transfer of a blood clot from one part of the body to another. While the two terms are related, there are some key differences between them.
Thrombosis is a localised clot that is usually caused by a decrease in the flow of blood and can be treated with anticoagulants. Embolism, on the other hand, is a more serious condition as the clot can travel through the bloodstream and cause damage to other parts of the body.
Treatment for embolism may involve surgery, drugs or other interventions.
What is embolism
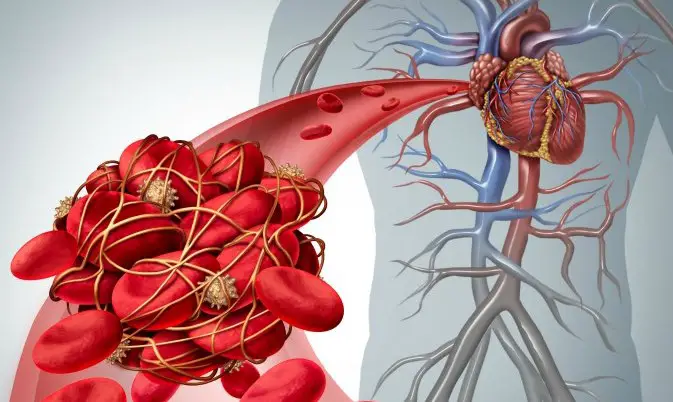
Embolism and thrombosis are two conditions that affect the circulatory system. While they both involve the formation of a clot, the difference lies in where the clot forms and where it travels.
Embolism is more serious and can be life-threatening, as the blockage of the vessel can lead to tissue damage or even organ failure.
Causes of thrombosis and embolism
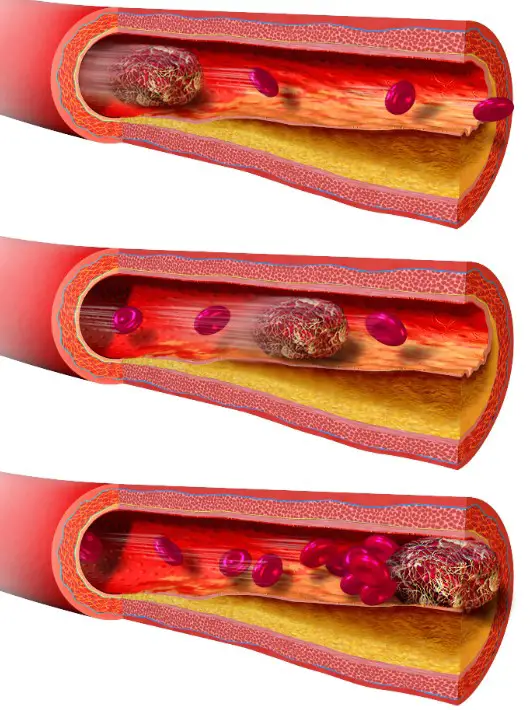
Thrombosis and embolism are two related medical conditions that are often confused. Both involve the formation of a mass of blood cells, but the key difference is the location and consequences of the mass. Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein or artery, potentially blocking the flow of blood and leading to serious health complications.
Embolism occurs when a clot, fat, or other material travels through the bloodstream, eventually lodging in a blood vessel and blocking the flow of blood. In both cases, immediate medical attention is necessary to prevent serious health consequences.
Symptoms of thrombosis and embolism
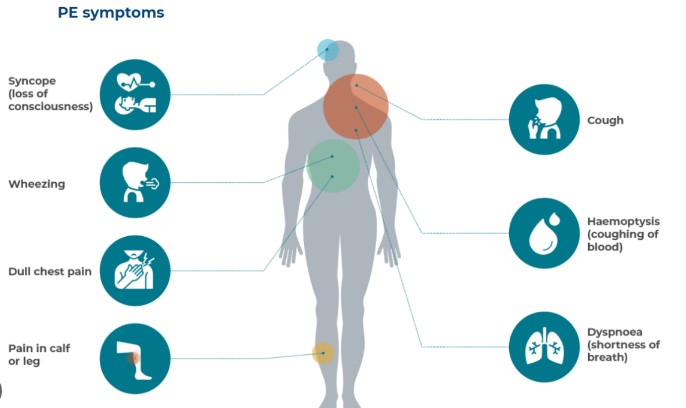
Thrombosis and embolism are both medical conditions involving the disruption of blood flow. The main difference between thrombosis and embolism is the cause of the disruption. Thrombosis is caused by the formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel, while embolism is caused by a substance, such as a blood clot, traveling through the bloodstream and lodging inside a blood vessel.
Thrombosis is caused by the formation of a blood clot within a blood vessel, while embolism is caused by a substance, such as a blood clot, traveling through the bloodstream and lodging inside a blood vessel. Symptoms of thrombosis and embolism can include pain or swelling in the affected area, discoloration of the skin, and a feeling of warmth or coldness in the affected area. Prompt medical attention is essential in cases of thrombosis or embolism, as these conditions can be life-threatening.
Complications of thrombosis and embolism
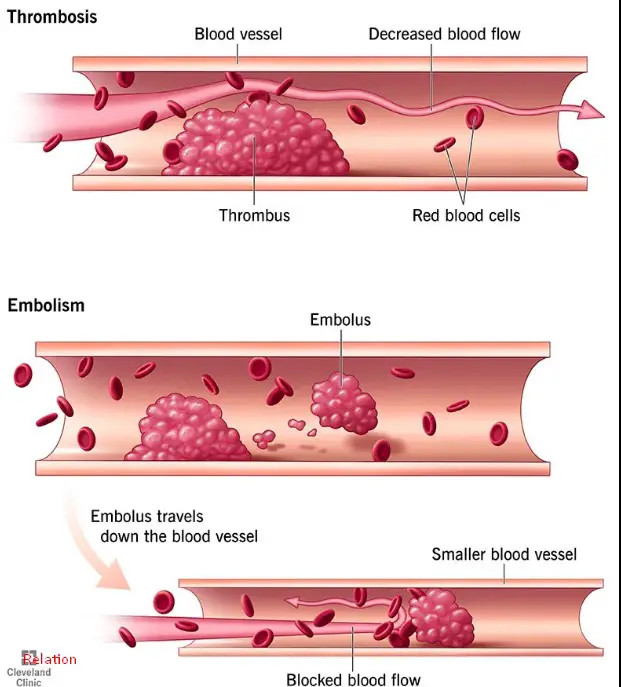
Thrombosis and embolism are both complications of vascular disease – conditions that involve the blood vessels. While the terms are often used interchangeably, there is an important difference between thrombosis and embolism. Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms inside a blood vessel, restricting or blocking the flow of blood.
An embolism, on the other hand, is a clot of material (such as a fat or air bubble) that travels through the bloodstream, blocking a blood vessel. While both conditions can be serious, the treatment for each can differ.
Therefore, it is important to understand the difference between thrombosis and embolism in order to ensure that you receive the correct treatment.
Treatments and prevention of thrombosis and embolism
Thrombosis and embolism are two medical terms that are often used interchangeably, but their meanings are actually quite different. Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, whereas embolism refers to the movement of a clot or other object from one part of the body to another.
For instance, anticoagulant medications are typically used to treat thrombosis, while surgeries to remove the clot may be required in some cases of embolism. Furthermore, preventive measures such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking can help to reduce the risk of developing either thrombosis or embolism.
Final Touch
The key difference between thrombosis and embolism is that thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in a blood vessel, while embolism is the blockage of a blood vessel by a substance that has moved from another part of the body. A thrombus can become an embolus when it breaks free from its original location and travels through the bloodstream to get stuck somewhere else.
It is important for people to be aware of the risk factors and symptoms related to both conditions and to seek medical help if necessary.