The human skeletal system, a marvel of nature, is comprised of numerous bones that work in harmony to support movement, protect vital organs, and serve various other crucial functions. Among these bones, the tarsal and carpal bones play pivotal roles in the mobility and functionality of the feet and hands, respectively. Despite their small size, these bones are integral to our daily activities, from walking and running to grasping and lifting objects.
The primary difference between tarsal and carpal bones lies in their location and function within the human body. Tarsal bones are located in the foot, comprising the ankle and part of the arch, while carpal bones form the wrist. Each set of bones is uniquely structured to support the specific movements and loads of their respective locations, facilitating efficient and versatile movements.
Tarsal bones are larger, fewer in number, and form the foundation for the weight-bearing part of the body, significantly impacting balance and gait. In contrast, carpal bones, smaller and more numerous, contribute to the wide range of motion and dexterity observed in the hands. Their structural differences underscore the distinct evolutionary adaptations that have enabled humans to develop complex locomotor and manipulative abilities.

Anatomy of Tarsal Bones
Location and Function
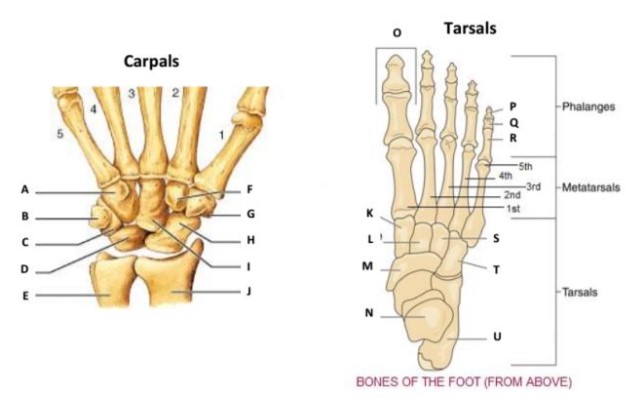
The tarsal bones are a group of seven bones found in the human foot, specifically in the rear part that includes the ankle and part of the arch. Their primary function is to support the body’s weight and enable various movements of the foot, playing a crucial role in maintaining balance and facilitating locomotion.
Number and Names of Tarsal Bones
The foot contains seven tarsal bones, each with a unique name and function:
- Talus – Acts as a bridge between the foot and the leg, allowing for ankle motion.
- Calcaneus – Known as the heel bone, it provides rear foot support and leverage.
- Navicular – Located at the medial side of the foot, it supports the arch.
- Cuboid – Supports the lateral side of the foot and aids in stability.
- Medial Cuneiform
- Intermediate Cuneiform
- Lateral Cuneiform – These three cuneiform bones assist in forming the foot’s arch and aid in stability and movement.
Key Characteristics
Tarsal bones are larger and stronger than many other bones, reflecting their role in supporting the entire body’s weight. They are interconnected with various joints and ligaments, allowing for a complex range of movements essential for walking, running, and balancing.
Anatomy of Carpal Bones
Location and Function
The carpal bones are located in the wrist and consist of eight small bones that form two rows. These bones serve as the connection between the forearm and the hand, facilitating movement and providing the structural foundation for the wrist.
Number and Names of Carpal Bones
The eight carpal bones are:
- Proximal Row: Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform
- Distal Row: Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate
These bones work together to allow the wrist to move and rotate in various directions.
Key Characteristics
Carpal bones are small, compact, and closely packed together, allowing for the intricate and delicate movements required for hand function. They have articulations with both the bones of the forearm and the metacarpal bones of the hand, making the wrist a highly flexible and dynamic part of the human body.
Comparative Analysis
Size and Complexity
Differences in Size
Tarsal bones, being part of the weight-bearing structure of the foot, are significantly larger and less numerous than carpal bones. The latter are smaller but more complex in arrangement, reflecting their different roles in the body.
Structural Complexity
The complexity of tarsal and carpal bones differs notably. Tarsal bones have a simpler structure but are involved in bearing the body’s weight and ensuring stability. In contrast, the carpal bones exhibit a more complex articulation pattern, allowing for a wide range of hand and wrist movements.
Function and Movement
Role in Movement
Tarsal bones provide stability and support for walking and running by bearing the body’s weight. Carpal bones, on the other hand, allow for the fine motor skills and dexterity necessary for hand functions like grasping and manipulating objects.
Types of Joints and Articulations
The joints within the tarsal and carpal regions are key to their functionality. Tarsal bones form hinge and gliding joints, allowing for movements like inversion and eversion. Carpal bones, conversely, are involved in creating condyloid and saddle joints, facilitating a broader range of motion, including flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
Evolutionary Perspective
Evolutionary Development
The development of tarsal and carpal bones represents an evolutionary adaptation to the demands of mobility and manipulation. Tarsal bones have evolved to support upright locomotion, while carpal bones have adapted to enhance manual dexterity.
Adaptations for Different Functions
These adaptations reflect the different ecological and survival strategies adopted by humans, with tarsal bones providing the foundation for bipedalism and carpal bones enabling tool use and complex hand functions.
Impact on Health
Common Injuries and Conditions
Tarsal and carpal bones are susceptible to various injuries, including fractures, sprains, and arthritis. Conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome and plantar fasciitis also highlight the importance of these bones in overall health and mobility.
Importance in Medical Diagnosis
Understanding the anatomy and function of tarsal and carpal bones is crucial for diagnosing and treating related conditions. Medical professionals rely on this knowledge to offer effective treatments and interventions, emphasizing the importance of these bones in health and medicine.
Diagnostic Techniques
Imaging Studies
X-rays and MRI
X-rays are a primary tool for examining bone fractures and joint abnormalities in both the tarsal and carpal bones. They provide clear images of bone structure, helping to identify breaks or displacements. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), on the other hand, offers detailed images of both bones and soft tissues, including ligaments and tendons. This makes MRI particularly useful for diagnosing soft tissue injuries and conditions that may not be visible on X-rays.
Ultrasound and CT Scans
Ultrasound imaging is used to view soft tissues around tarsal and carpal bones, including muscles and ligaments, and is useful for assessing tendon tears or inflammation. CT (Computed Tomography) scans provide a more detailed cross-sectional view of the bones than X-rays, especially useful for complex fractures. They combine several X-ray images from different angles to create a comprehensive picture of the bone structure.
Physical Examination
Mobility Tests
Mobility tests involve moving the affected area to assess the range of motion and identify any limitations or pain. For the wrist and ankle, this may include flexing, extending, rotating, and sideways movements. Reduced mobility can indicate injuries or conditions affecting the tarsal or carpal bones.
Pain Assessment
Pain assessment is a crucial part of the physical examination. It helps to localize the source of pain, understand its severity, and determine how it affects functionality. The doctor may apply gentle pressure to different parts of the foot or hand to identify sensitive areas, correlating them with potential injuries or conditions of the tarsal or carpal bones.
Treatment and Management
Conservative Therapies
Rest and Immobilization
For many injuries involving tarsal and carpal bones, rest is crucial to prevent further damage and promote healing. Immobilization using casts, splints, or braces helps to keep the bones in proper alignment and restricts movement, allowing for recovery without surgery.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a significant role in the recovery process, especially after immobilization. It involves exercises designed to restore movement, strengthen muscles, and reduce stiffness. Rehabilitation focuses on regaining full functionality of the foot or hand, tailored to the specific needs of the patient.
Surgical Interventions
When Surgery is Needed
Surgery may be necessary for severe fractures, misalignments, or when conservative treatments fail to provide relief. It’s also considered for conditions that inherently require surgical correction, such as certain types of arthritis or deformities.
Types of Procedures for Tarsal and Carpal Issues
Surgical procedures vary depending on the specific issue but may include:
- Realigning and fixing fractures using screws, plates, or pins.
- Joint replacement in severe arthritis cases.
- Arthroscopy for repairing soft tissue damage with minimal incisions.
- Fusion surgery to permanently join bones that are not healing correctly.
Each surgical approach is chosen based on the individual’s condition, lifestyle, and overall health.
Preventive Measures
Lifestyle and Activity Modifications
Making changes to daily activities can significantly reduce the risk of tarsal and carpal bone injuries. This includes:
- Avoiding repetitive stress on the hands and feet by taking regular breaks.
- Practicing good posture and ergonomics at work, especially if it involves prolonged typing or standing.
- Wearing supportive footwear to cushion and support the feet.
Protective Gear and Ergonomics
Using protective gear like wrist guards during sports can prevent injuries. Ergonomic tools and accessories, such as keyboard supports, can minimize strain on the wrists and hands during computer work. Additionally, ergonomic assessment of workspaces and daily activities can help identify changes that promote health and prevent strain.
FAQs
What are tarsal bones?
Tarsal bones are a group of seven bones located in the foot’s rear portion, forming the ankle and arch. These bones include the talus, calcaneus, navicular, cuboid, and three cuneiform bones. They play a crucial role in supporting the body’s weight and facilitating foot movement, contributing significantly to balance and locomotion.
How many carpal bones are there, and what are their names?
There are eight carpal bones in the human wrist, arranged in two rows. The proximal row includes the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, and pisiform bones, while the distal row consists of the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones. These bones work together to enable the wrist’s complex range of movements.
Why is it important to understand the difference between tarsal and carpal bones?
Understanding the differences between tarsal and carpal bones is essential for diagnosing and treating injuries or conditions affecting the feet and hands. It aids healthcare professionals in pinpointing the specific bones involved in various ailments, facilitating accurate treatment plans. Moreover, this knowledge is crucial for athletes, dancers, and others who rely heavily on the optimal functioning of their feet and hands.
How do tarsal and carpal bones affect movement?
Tarsal bones, due to their larger size and structure, provide stability and support for the body’s weight, playing a vital role in balance, walking, and running. Carpal bones, however, are smaller and enable the hands’ wide range of precise movements, from gripping to manipulating objects. The functional design of these bones reflects their adaptation to different mechanical demands.
Conclusion
In the exploration of the human body’s complexities, the distinction between tarsal and carpal bones highlights the intricate design and evolutionary sophistication behind our ability to move and interact with the world. These bones, though small, are fundamental to the diverse capabilities that define human mobility and dexterity.
Understanding the nuanced differences and similarities between these bone groups not only enriches our knowledge of human anatomy but also underscores the importance of each bone in our daily lives. From supporting weight and enabling balance to facilitating precise movements, the tarsal and carpal bones play roles that are vital to our well-being and quality of life, reminding us of the marvels of human biology.
