When it comes to encrypting data, there are two main types of ciphers commonly used: stream ciphers and block ciphers. In this blog, we’ll discuss the key differences between the two and explore which one may better suit your needs. We’ll cover topics such as the encryption process, the types of data each is best suited for, and the advantages and disadvantages of each.
So if you’re looking to learn more about the differences between stream ciphers and block ciphers, you’ve come to the right place.
How stream and block ciphers differ
Stream ciphers and block ciphers are two of the most commonly used encryption methods. While both are used to secure data, they have distinct differences.
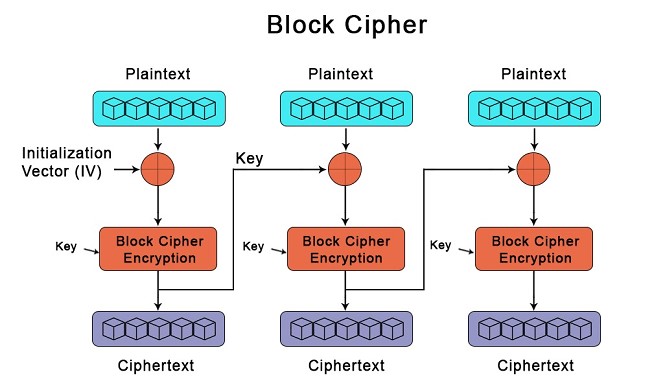
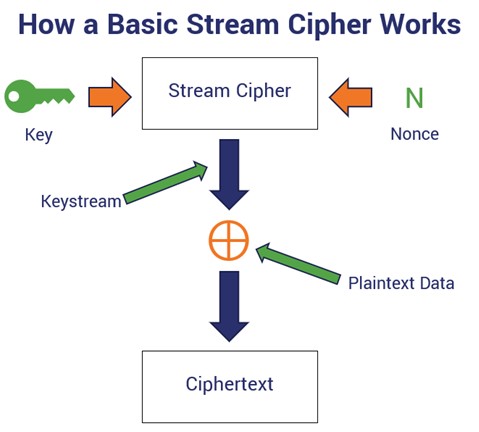
Stream ciphers are encryption algorithms that encrypt data one bit or one byte at a time. This method is used to encrypt data as it is being sent over a network, making it an ideal choice for real-time, secure communications. Block ciphers, on the other hand, encrypt data in chunks of bits or bytes.
This makes them a better choice for encrypting large amounts of data, since the entire message can be encrypted at once. The main difference between the two is that stream ciphers are faster and more efficient for real-time communications, while block ciphers are better suited for encrypting large amounts of data.
Advantages and disadvantages of stream ciphers
Stream ciphers and block ciphers are two of the most common types of encryption algorithms used to protect data. While both types of ciphers provide a secure way to encrypt data, there are some key differences between the two that should be considered when making a decision on which type of encryption to use. Stream ciphers, as the name implies, operate on a stream of data, encrypting individual bits or bytes one at a time.
Block ciphers, on the other hand, operate on blocks of data, encrypting each block separately. The main advantage of a stream cipher is that it can encrypt data quickly and efficiently.
Since stream ciphers operate on individual bits or bytes of data, they require less processing power than block ciphers, which have to process entire blocks of data at a time. This makes stream ciphers ideal for applications that require real-time encryption, such as online banking and streaming media.
The main disadvantage of stream ciphers is that they are susceptible to certain attacks, such as replay attacks and known-plaintext attacks. While these attacks can be mitigated with the use of authentication protocols, the additional complexity can sometimes outweigh the potential security benefits. In comparison, block ciphers are more secure than stream ciphers, as they are not vulnerable to the same types of attacks.
Block ciphers also provide better security when encrypting large amounts of data, as they can process the entire block of data at once, thus reducing the possibility of data leakage. However, block ciphers require more processing power than stream ciphers, and thus may not be the best choice for applications that require real-time encryption. In conclusion, stream ciphers and block ciphers each have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice for a particular application will depend on the security requirements and processing power available.
Advantages and disadvantages of block ciphers
Block ciphers and stream ciphers are two distinct types of cryptographic algorithms used to protect data. Block ciphers are used to encrypt data in fixed-size blocks while stream ciphers encrypt data one bit or byte at a time.
Block ciphers work by taking a plaintext input and breaking it up into blocks of a fixed size. Each block is then encrypted with the same key using a series of algorithms to produce a unique ciphertext output.
Block ciphers are more secure, as they are better at resisting brute-force attacks and ciphertext manipulation. On the other hand, stream ciphers encrypt data one bit or byte at a time, using a keystream generated from a key.
Stream ciphers are simpler to implement, but they are more susceptible to attack because of the use of the same key for encryption and decryption. In conclusion, block ciphers and stream ciphers are two distinct types of cryptographic algorithms used to protect data.
Block ciphers are more secure, but also more complex, while stream ciphers are easier to implement but may be less secure.
Examples of stream ciphers
Stream ciphers and block ciphers are two of the most commonly used cryptographic methods out there. While both of these ciphers are designed to keep data secure, they work in very different ways.
Stream ciphers encrypt data one bit at a time, while block ciphers encrypt data in larger chunks or blocks. This difference in approach can be seen in the way each cipher is used. Stream ciphers are often used for applications such as real-time streaming, while block ciphers are more suitable for bulk encryption tasks.
Examples of stream ciphers include RC4, E0 and Salsa20, while AES and 3DES are two of the most popular block ciphers.
Examples of block ciphers
Block ciphers are cryptographic algorithms that encrypt data in fixed size blocks. They are used to protect data in transit and at rest, and are typically used for things like encrypting files, encrypting email, and password protection. Stream ciphers, on the other hand, are designed to encrypt data one bit or byte at a time.
The main difference between a block cipher and a stream cipher is the size of the data being encrypted. With a block cipher, the data is broken into fixed-length blocks, while with a stream cipher, the data is encrypted one bit or byte at a time.
Block ciphers are generally considered to be more secure than stream ciphers, as they offer more protection against attacks. Additionally, block ciphers are more efficient at encrypting larger amounts of data, making them better for applications where data security is paramount.
Final Touch
In conclusion, the main difference between stream ciphers and block ciphers is the size of the data being encrypted. Stream ciphers encrypt data one bit at a time, while block ciphers encrypt data in chunks of fixed size, usually 64 or 128 bits. Stream ciphers are more efficient when encrypting small amounts of data, while block ciphers are better suited for larger amounts of data.
Both types of ciphers are important components of modern cryptography and are used to protect sensitive data in various applications.