Distillation is a fundamental process used across various industries to separate and purify compounds. This technique, particularly pivotal in the extraction of essential oils, leverages differences in the boiling points of components within a mixture. By converting liquids into vapor and then condensing this vapor back into a liquid form, distillation enables the extraction of valuable substances in a highly refined form.
The core distinction between steam distillation and hydrodistillation lies in their operational approach and the nature of their output. Steam distillation passes steam through the plant material, vaporizing the volatile compound without direct contact with water. In contrast, hydrodistillation involves boiling the plant material directly in water, where the essence of the plant is extracted along with the steam produced from the boiling water.
These methods, while similar in their aim to extract essential oils, differ markedly in their application and the quality of oil they produce. Factors such as the type of botanicals used, the desired purity of the oils, and specific industry requirements can dictate the choice of distillation method. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate distillation technique for specific applications in industries like perfumery, food processing, and pharmaceuticals.
Distillation Basics
What is Distillation?
Distillation is a separation process used to purify or concentrate materials, typically liquids. This method is fundamental in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to beverage production. At its core, distillation involves heating a liquid to create vapor and then condensing that vapor back into liquid form. It’s particularly effective for separating substances with different boiling points.
Core Principles
The basic principles of distillation revolve around heat, volatility, and condensation. When a mixture is heated, the component with the lower boiling point vaporizes first. This vapor then passes through a cooler environment where it condenses back into a liquid. This process can be repeated to increase purity or separation efficiency.
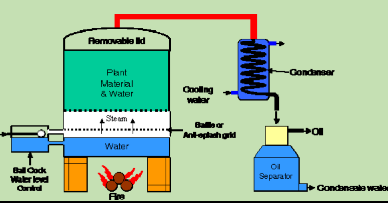
Steam Distillation
Process Overview
Steam distillation is a specialized distillation process used primarily for temperature-sensitive materials like essential oils and aromatic compounds. It involves:
- Introducing steam into a distillation chamber containing the plant material.
- Vaporizing the plant’s volatile compounds along with the steam.
- Condensing the vapor mixture back into a liquid to separate the essential oils.
Equipment Used
The equipment for steam distillation typically includes:
- Boiler to generate steam.
- Distillation chamber where raw materials are held.
- Condenser to cool and condense the vapor.
- Separator to extract essential oils from the condensed liquid.
Benefits and Uses
Steam distillation is prized for its ability to efficiently extract essential oils without degrading the quality of the oil. This method is widely used in the production of perfumes, flavorings, and in aromatherapy products, as it preserves the integrity of the delicate aromatic compounds.
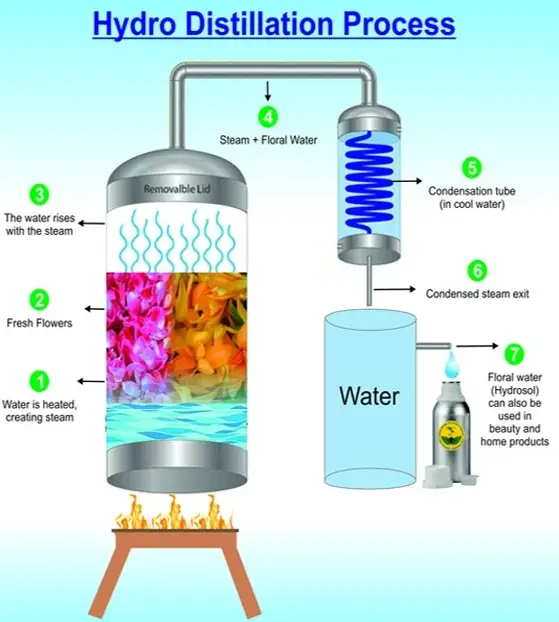
Hydrodistillation
Process Description
Hydrodistillation involves boiling plant material directly in water. The process can be outlined as follows:
- Plant materials and water are combined in a distillation pot.
- The mixture is then heated to boiling, releasing steam that carries essential oils.
- The steam and oils are condensed back into a water-oil mixture, which is then separated.
Key Equipment
The key equipment for hydrodistillation includes:
- Distillation pot for heating plant materials in water.
- Heating source to bring the water to a boil.
- Cooling system to condense the steam into liquid.
Advantages and Applications
Hydrodistillation is advantageous for extracting oils from more robust, moisture-rich plant materials. It’s widely used in the production of essential oils that are less sensitive to heat, and in situations where steam distillation is not viable due to the plant material’s nature.

Comparing Methods
Efficiency Factors
Comparing steam distillation and hydrodistillation in terms of efficiency involves several factors:
- Time: Steam distillation usually requires less time than hydrodistillation.
- Energy consumption: Hydrodistillation can consume more energy as it requires heating a larger volume of water.
- Yield: Steam distillation often provides a higher yield of oil per unit of plant material.
Quality of Output
The quality of essential oils extracted via steam distillation is generally higher as it prevents the overheating of the botanicals, thus preserving sensitive compounds. Hydrodistillation, while effective, might result in slight degradation of some compounds due to direct contact with boiling water.
Suitability for Materials
The choice between steam and hydrodistillation often depends on the botanical material involved:
- Delicate materials such as flowers and leaves are better suited to steam distillation.
- Robust materials like seeds and woody parts may benefit from hydrodistillation, where direct contact with water isn’t a concern.
Practical Considerations
Cost Implications
When adopting either steam distillation or hydrodistillation, businesses must consider initial investments and operational expenses. Steam distillation equipment, while costly to set up, tends to offer long-term savings through higher efficiency and lower energy use per unit of product compared to hydrodistillation. Hydrodistillation, though cheaper to initiate, often leads to higher energy bills due to the extensive heating required.
- Installation: Higher for steam distillation systems due to their complexity.
- Energy Usage: Hydrodistillation consumes more energy, impacting long-term operational costs.
Scalability Issues
Scalability is a critical factor for businesses looking to expand their production capacity. Steam distillation scales more effectively, allowing for increased production without substantial additional costs. Hydrodistillation, however, may require proportional increases in energy and water use as production scales, which can be cost-prohibitive.
- Modularity: Steam distillation systems can be easily expanded with additional modules.
- Resource Requirements: Scaling hydrodistillation increases resource consumption linearly.
Safety Measures
Implementing robust safety measures is essential to minimize risks associated with high temperatures and pressures.
- Pressure Relief: Steam systems must include safety valves to prevent pressure build-up.
- Thermal Regulation: Both systems require accurate temperature controls to ensure safety and efficiency.
Industry Applications
Aromatherapy Oils
Steam distillation is preferred for producing high-quality aromatherapy oils, which require the preservation of delicate aromatic compounds.
- Product Purity: Essential for therapeutic effectiveness.
- Production Efficiency: Steam distillation can process large quantities of botanicals efficiently.
Pharmaceutical Uses
Both distillation methods are utilized in pharmaceuticals to extract and purify chemical compounds necessary for medication production.
- Consistency and Quality: Critical for pharmaceutical compounds.
- Regulatory Compliance: Methods must adhere to stringent health and safety standards.
Food and Beverage Industry
The flavor and fragrance industry heavily relies on distilled extracts. Steam distillation is especially beneficial here due to its ability to produce consistent and pure extracts.
- Flavor Integrity: Maintaining flavor consistency across batches.
- Safety: Ensuring that extracts are free from contaminants and safe for consumption.
Future Trends
Technological Advances
Technological innovations continue to enhance distillation processes, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly.
- Automated Systems: Improve precision and control in distillation operations.
- Energy-efficient Designs: Newer models reduce energy consumption significantly.
Environmental Impact
The environmental sustainability of distillation processes is increasingly important. Advances aim to reduce water and energy use, minimizing the ecological footprint of distillation operations.
- Water Recycling: Techniques that allow the reuse of water in hydrodistillation.
- Solar Heating: Utilizing renewable energy sources to power distillation processes.
Market Growth
The market for distilled products, particularly essential oils and specialty beverages, is expanding rapidly due to consumer demand for natural and organic products.
- Consumer Preferences: Shifting towards sustainable and ethically produced goods.
- Regulatory Trends: Increased regulations promoting natural over synthetic ingredients.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is steam distillation?
Steam distillation involves heating water to produce steam, which then passes through plant material to vaporize volatile compounds. The vapor mixture of steam and volatile compounds is then cooled, allowing the extraction of the oil as it separates from water.
How does hydrodistillation differ?
Hydrodistillation requires submerging the plant material in water and then boiling the mixture. This process extracts essential oils as the plant’s cellular structure breaks down, releasing the oils into the steam that forms from the boiling water.
Which method is more efficient?
Efficiency in distillation depends on several factors, including the type of plant material and the desired purity of the end product. Generally, steam distillation is faster and can yield a higher purity of essential oil, making it suitable for more delicate botanicals.
What industries use these distillation methods?
Both methods are widely used in the production of essential oils, which are integral to industries such as aromatherapy, cosmetics, food flavoring, and pharmaceuticals. Each method has specific advantages that make it preferable under certain conditions.
Conclusion
The choice between steam distillation and hydrodistillation hinges on various factors, including operational efficiency, cost, and the specific requirements of the end product. While steam distillation is often favored for its speed and the high purity of oil it produces, hydrodistillation remains indispensable for certain applications where the complete extraction of aromatic compounds is necessary.
In conclusion, understanding the technical nuances and practical applications of each method allows for informed decision-making in the production of essential oils. As advancements in technology continue to evolve, these distillation techniques are likely to become even more efficient and tailored to meet the growing demands of different industries.