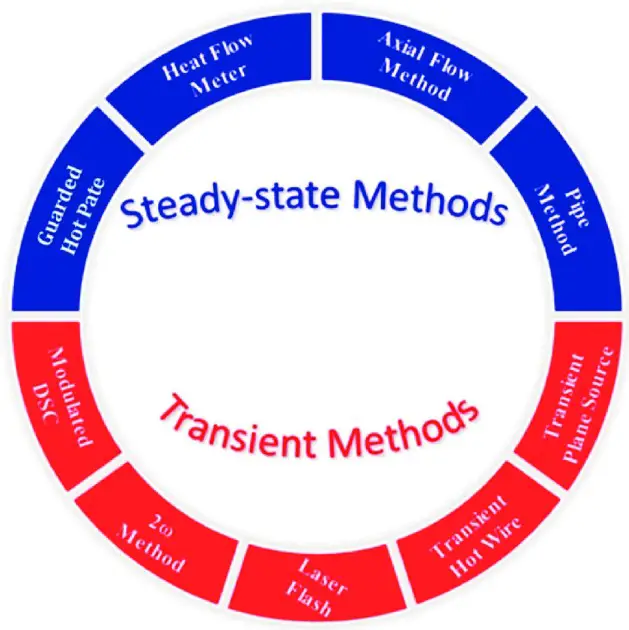
Thermal analysis is an essential technique used to understand the behavior of materials when exposed to thermal energy. The two main types of thermal analysis are steady state and transient. While both types of analyses are useful in different applications, understanding the difference between them is important for selecting the right analysis for a given situation.
While both types of analyses are useful in different applications, understanding the difference between them is important for selecting the right analysis for a given situation. This blog will explore the differences between steady state and transient thermal analysis and their respective uses.
Benefits and limitations of steady state thermal analysis
Steady state thermal analysis is a process used to evaluate the temperature of a system and its components under a constant set of conditions. It can be used to identify potential problems and areas of improvement in order to improve the efficiency and safety of a system. While steady state thermal analysis is a valuable tool for understanding and optimizing the thermal performance of a system, it has certain limitations.
One of the main differences between steady state and transient thermal analysis is that the former only considers thermal behavior over a fixed period of time, while the latter considers the behavior of the system over a range of changing conditions. As a result, steady state thermal analysis may not be able to provide accurate results for a system that is subjected to changing conditions, whereas transient thermal analysis is more suitable for such situations.
Additionally, steady state thermal analysis does not consider the heat transfer between components, which can be an important factor in determining the thermal performance of a system. Despite these limitations, steady state thermal analysis remains a valuable tool, allowing engineers to gain insight into the thermal behavior of their systems.
Benefits and limitations of transient thermal analysis
Transient thermal analysis is a powerful tool that can provide valuable insight into the dynamic behavior of a system. It is useful for predicting temperature distributions, heat fluxes, and the thermal response of components under varying conditions.
Compared to steady state thermal analysis, transient thermal analysis can provide significantly more information about the thermal response of a system. This includes the ability to capture changes in temperature over time and the effects of thermal gradients.
Additionally, transient thermal analysis can provide information about the system’s response to transient conditions, such as those resulting from start-up and shut-down operations. However, transient thermal analysis is also subject to certain limitations.
It can be computationally intensive and require significantly more data than steady state thermal analysis. Additionally, it can be difficult to accurately capture transient phenomena, such as thermal inertia, in a transient thermal analysis. As such, it is important to be aware of both the benefits and limitations of transient thermal analysis to ensure you get the most out of the tool.
Comparison of steady state and transient thermal analysis
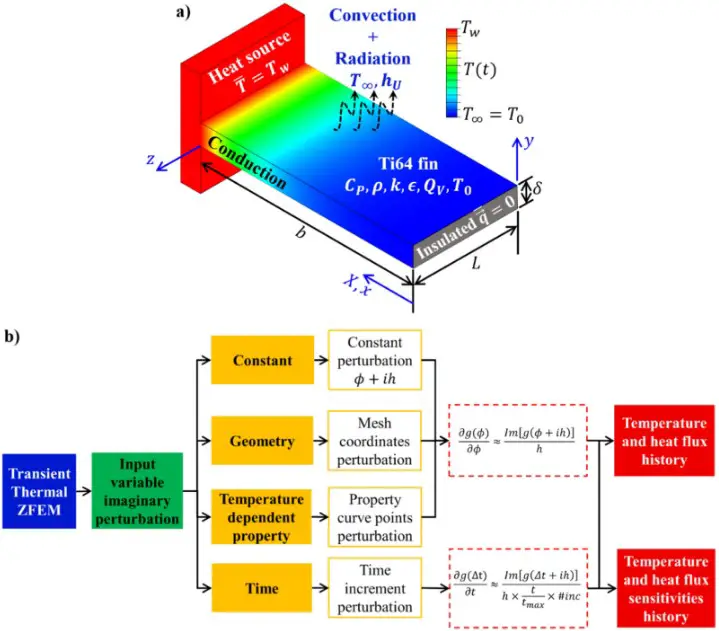
When it comes to designing products that can withstand extreme temperatures, it’s important to understand the differences between steady state and transient thermal analysis. Steady state thermal analysis assumes that a system is in a state of equilibrium, meaning that the temperatures of all parts of the system are constant over time.
As such, it’s able to provide more accurate results when predicting how a system will respond to temperature changes. This is especially important when it comes to designing products that are expected to endure long-term exposure to extreme temperatures.
By understanding the differences between steady state and transient thermal analysis, engineers can create products that are capable of performing even in the most challenging environments.
Applications of steady state and transient thermal analysis
When it comes to thermal analysis, there are two distinct types: steady state and transient. Steady state thermal analysis involves studying the temperature of a system over a long period of time, while transient thermal analysis looks at how the temperature of the system changes over a short period of time. Although both types of analysis are important, they have different applications.
Steady state thermal analysis can be used to identify the most efficient temperature settings for a system, while transient thermal analysis is best suited for studying the dynamics of how a system’s temperature changes over time. By using both analyses together, engineers are able to get a better understanding of the thermal characteristics of their systems.
References
Thermal analysis is a major factor in engineering, allowing us to determine the temperature profile of a system over time. There are two main types of thermal analysis: steady state and transient. Steady state thermal analysis is when the temperature of a system remains constant over time, while transient thermal analysis looks at the temperature profile of a system over a given period of time.
Steady state thermal analysis is when the temperature of a system remains constant over time, while transient thermal analysis looks at the temperature profile of a system over a given period of time. It is important to understand the difference between these two types of thermal analysis in order to accurately predict the temperature profile of a system.
Final Touch
In conclusion, steady state thermal analysis and transient thermal analysis are two different types of thermal analysis that are used to assess the thermal performance of a system. Steady state analysis is used to study a system under constant conditions, while transient analysis is used to study the effects of changing conditions over time. Steady state analysis can provide faster and more efficient results, but may not be able to capture the effects of changing conditions.
Steady state analysis can provide faster and more efficient results, but may not be able to capture the effects of changing conditions. Transient analysis can provide more accurate results, but may take longer to compute and requires more detailed input data. Both types of analysis can provide valuable insight into the thermal performance of a system, and which type to use depends on the particular needs of the system being studied.