Natural selection, the cornerstone of evolutionary biology, shapes the genetic framework of populations through various mechanisms. Among these, stabilizing and balancing selections stand out due to their unique influences on species’ genetic diversity and adaptive capabilities. By exploring these concepts, we can uncover how nature conserves certain traits while promoting diversity in others.
Stabilizing selection promotes genetic uniformity by favoring average phenotypes, reducing variation within a population. Conversely, balancing selection maintains genetic diversity by favoring multiple alleles in a population. These mechanisms ensure that species are equipped to adapt to their environments, highlighting the complexity and elegance of evolutionary processes.
As we explore the nuances of these selection types, it becomes evident that they represent more than just survival of the fittest. They are pivotal in shaping the genetic structure and evolutionary trajectory of species, affecting everything from individual survival to the overall health of ecosystems.
Selection Basics
Definition of Natural Selection
Natural selection is the process by which species adapt to their environment over generations. It acts on the genetic variation within a population, favoring traits that enhance survival and reproductive success. Over time, these advantageous traits become more common in the population, leading to evolutionary changes.
Key Mechanisms of Evolution
Evolution is driven by several key mechanisms that alter the genetic structure of populations. These include:
- Mutation: Random changes in DNA that can create new genes and traits.
- Gene Flow: The transfer of genes between populations through migration.
- Genetic Drift: Random fluctuations in the frequency of alleles in a small population.
- Natural Selection: The increase or decrease in allele frequency based on the allele’s impact on survival and reproduction.
These mechanisms work together to shape the diversity and adaptability of organisms.
Stabilizing Selection
Definition and Concept
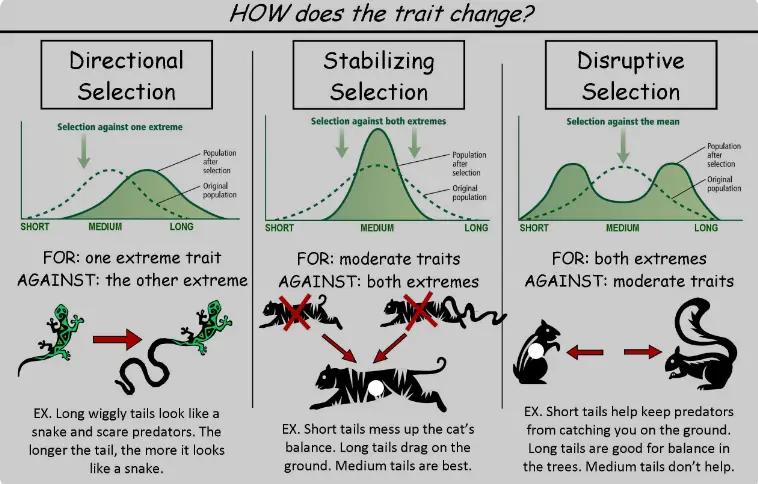
Stabilizing selection is a type of natural selection that favors the average phenotypes in a population. This selection process reduces the extremes in genetic traits, promoting stability in the population’s genetic makeup.
Examples in Nature
Many examples of stabilizing selection can be observed in nature:
- Human Birth Weight: Infants with weights too far below or above the average are less likely to survive, which means that the most common, middle-range birth weights are favored.
- Robin Clutch Size: In robin populations, the survival of offspring is highest for nests with an average number of eggs. Too few or too many reduce the survival rate, thus stabilizing the clutch size around an optimum number.
Impact on Population Genetics
Stabilizing selection impacts population genetics by:
- Reducing Genetic Variance: By favoring average traits, it reduces the range of variation and maintains consistency.
- Preserving Successful Traits: It helps preserve successful genetic formulations over time, contributing to the stability of crucial traits within the environment.
Balancing Selection
Definition and Concept
Balancing selection occurs when multiple alleles (variants of a gene) are actively maintained in a population at higher frequencies than would be expected from genetic drift alone. This type of selection enhances genetic diversity.
Examples in Nature
Balancing selection can be seen through several well-documented cases:
- Sickle Cell Anemia and Malaria: Individuals carrying just one copy of the sickle cell allele are resistant to malaria, a significant advantage in malaria-endemic regions. This maintains the presence of the sickle cell allele in the population despite its detrimental effects when two copies are inherited.
- Human Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC): Diversity in the MHC genes is crucial for immune system effectiveness. Balancing selection maintains a variety of alleles that are beneficial for pathogen recognition.
Role in Maintaining Diversity
The role of balancing selection in maintaining diversity includes:
- Adaptability: By preserving a range of genetic variations, populations can quickly adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Ecological Interactions: Diverse genetic profiles enable more complex interactions within ecosystems, enhancing species survival under various conditions.
Comparative Analysis
Differences in Definition
Stabilizing and balancing selections, while both crucial mechanisms of natural selection, operate under different premises. Stabilizing selection tends to favor the norm or average within a population, effectively reducing deviation from the mean and discouraging extremes. On the other hand, balancing selection encourages genetic diversity by supporting multiple alleles within the population, even those that might be detrimental under certain circumstances but beneficial under others.
Impact Comparison on Genetic Variation
The impacts of these selection types on genetic variation are markedly distinct:
- Stabilizing Selection: This form reduces genetic diversity by selecting against extreme phenotypes. Over time, this can lead to a decrease in genetic variance within the population, as the gene pool stabilizes around certain favored traits.
- Balancing Selection: Contrarily, balancing selection maintains or increases genetic diversity. It supports the presence of multiple alleles in the gene pool, which can be advantageous in fluctuating environmental conditions.
Real-World Implications for Species
The real-world implications of these selection processes are significant:
- Stabilizing Selection: This selection type can lead to a population that is highly specialized for particular environmental conditions but potentially less adaptable to sudden changes in those conditions.
- Balancing Selection: Provides a broader range of genetic tools for species to adapt to diverse and changing environments, potentially enhancing long-term survival.
Evolutionary Significance
Role in Adaptive Evolution
Balancing and stabilizing selections play critical roles in the adaptive evolution of species:
- Stabilizing Selection: It ensures that advantageous adaptations are preserved, providing stability within the environment.
- Balancing Selection: Promotes adaptability and resilience, allowing species to respond to environmental challenges and opportunities dynamically.
Long-Term Effects on Biodiversity
The long-term effects on biodiversity also vary between these selection types:
- Stabilizing Selection: While it promotes stability, it may also limit the range of possible adaptations, potentially making a population more vulnerable to drastic environmental shifts.
- Balancing Selection: Encourages a wider array of traits within a population, increasing the likelihood of survival through various environmental changes and thus promoting greater overall biodiversity.
Human Impact
Influence of Human Activity on Selection Processes
Human activities have significantly influenced natural selection processes, often altering the natural balance and dynamics of evolutionary pressures:
- Environmental Changes: Pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change can shift the selective pressures on populations, sometimes favoring different traits or entirely new adaptations.
- Artificial Selection: Through selective breeding practices, humans have directly manipulated genes in both crops and livestock, showcasing a direct form of selection that often prioritizes traits beneficial to humans but not necessarily advantageous for the species in natural environments.
Conservation and Management Implications
The understanding of stabilizing and balancing selection is crucial for effective conservation and management practices:
- Conservation Strategies: Knowledge of these selection mechanisms helps in developing strategies that maintain genetic diversity, crucial for the resilience of populations.
- Management Practices: In managing natural resources and wildlife, incorporating the principles of both stabilizing and balancing selection can aid in fostering healthier ecosystems and more sustainable interactions between humans and nature.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Natural Selection?
Natural selection is a fundamental biological process where organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and reproduce more than others. This process leads to the gradual development of more adaptively fit organisms over generations.
How does stabilizing selection operate?
Stabilizing selection works by favoring phenotypes that are closer to the population mean, thereby reducing extremes in trait distributions. This selection type is crucial for maintaining consistency and functionality in traits that are already well-suited to a stable environment.
What is balancing selection?
Balancing selection refers to natural selection that maintains genetic diversity within a population by favoring multiple alleles. It often occurs in scenarios where different genetic variations convey advantages under varying environmental conditions.
Why is genetic diversity important?
Genetic diversity is vital for a population’s health and survival as it enhances the ability of organisms to adapt to changing environments. It reduces the risk of diseases and increases the chances of survival against environmental challenges.
Conclusion
The interplay between stabilizing and balancing selection highlights the intricacy of evolutionary processes. These mechanisms not only mold the genetic fabric of populations but also ensure that biodiversity is preserved, showcasing nature’s foresight in maintaining life’s resilience. By understanding these principles, we gain insights into the adaptive strategies that sustain life across various ecosystems.
As we continue to study these evolutionary dynamics, we deepen our appreciation of the natural world and enhance our ability to conserve the biodiversity that sustains our planet. Through such knowledge, we can better navigate the challenges of environmental changes and species preservation.