Spliceosomes and ribosomes are two of the most important cellular structures responsible for the production of proteins. Both of these structures play a critical role in the life of a cell, but there are key differences between them. In this blog, we will explore the differences between spliceosomes and ribosomes, and discuss how they relate to the production of proteins within a cell.
Overview of rna splicing
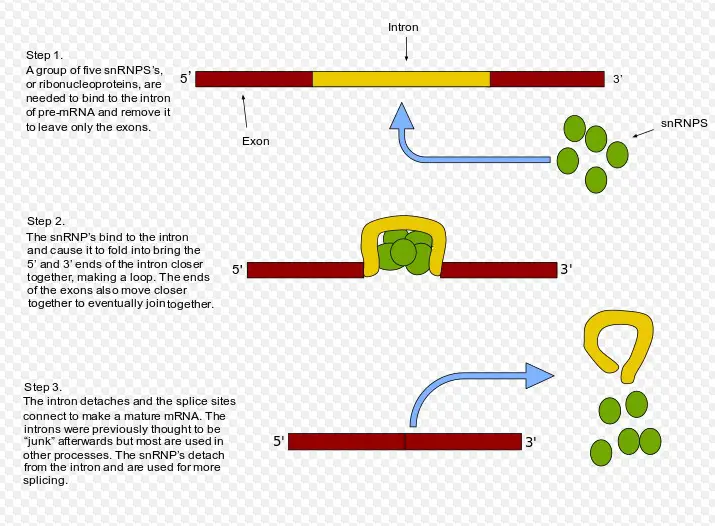
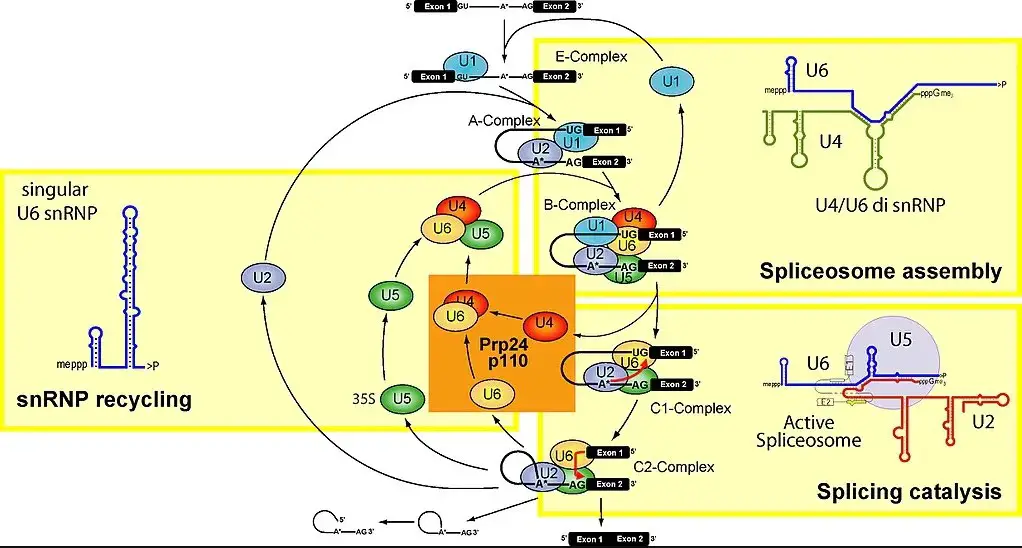
RNA splicing is an important process in gene expression that involves removing sections of RNA transcripts known as introns. The remaining sections, known as exons, are then spliced together to form the mature mRNA molecule. The process of splicing is carried out by spliceosomes, which are complex molecular machines composed of proteins and small nuclear RNAs.
The process of splicing is carried out by spliceosomes, which are complex molecular machines composed of proteins and small nuclear RNAs. In contrast to spliceosomes, ribosomes are much simpler molecular machines that are responsible for reading mRNA transcripts and translating them into proteins. In short, while spliceosomes remove introns and splice together exons to form mRNA, ribosomes use the mRNA to synthesize proteins.
Structural differences between spliceosomes and ribosomes
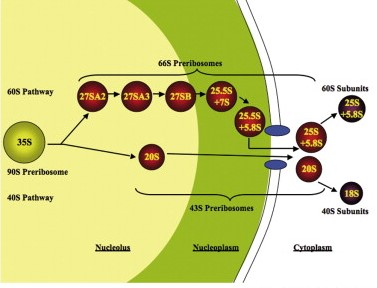
Ribosomes and spliceosomes are two complex macromolecular machines found in the cell. While they are both involved in protein processing, they have distinct structural differences that set them apart.
In addition, ribosomes are a stable structure that remains intact throughout the protein synthesis process, while spliceosomes are constantly changing, with the subunits interacting in various ways depending on the task at hand. Lastly, ribosomes use tRNA and mRNA to create polypeptides, while spliceosomes use snRNA to splice together pre-mRNA into mature mRNA.
All-in-all, these differences make it clear that while spliceosomes and ribosomes may be related, they are definitely not the same.
Functional differences between spliceosomes and ribosomes
Ribosomes and spliceosomes are two of the most important biological components when it comes to gene expression and translation. Both of these complexes are responsible for the formation of proteins from mRNA, but they do so in different ways. Ribosomes are responsible for the translation of mRNA into proteins, while spliceosomes are responsible for the removal of introns from pre-mRNA before the mRNA is translated into proteins.
Spliceosomes have a much more complex structure than ribosomes, and they are composed of five snRNPs as well as many other proteins. Ribosomes, on the other hand, are composed of two subunits and are much smaller in size.
Thus, the main difference between spliceosomes and ribosomes is that the former is responsible for the removal of introns from pre-mRNA while the latter is responsible for the translation of mRNA into proteins.
Role of spliceosomes and ribosomes in gene expression
The role of spliceosomes and ribosomes in gene expression is an important one. Both these organelles are essential for the proper functioning of cells.
Spliceosomes are responsible for the removal of introns from pre-mRNA, while ribosomes are responsible for the translation of mRNA into proteins. Spliceosomes are composed of several small subunits, while ribosomes are composed of larger subunits.
Furthermore, spliceosomes can be found in the nucleus as well as in the cytoplasm, while ribosomes are only found in the cytoplasm. Spliceosomes also work to splice together exons, while ribosomes work to link together amino acids.
In conclusion, spliceosomes and ribosomes are essential components of gene expression, but they serve different functions.
References
Ribosomes and spliceosomes are both essential components of gene expression. Ribosomes are responsible for translating messenger RNA (mRNA), produced by transcription of DNA, into proteins, while spliceosomes are involved in the process of removing introns from pre-mRNA before it is translated into a protein.
The main difference between the two is that ribosomes are responsible for the actual translation of mRNA into proteins, while spliceosomes are involved in the pre-processing of mRNA, preparing it for translation into a protein. Furthermore, ribosomes are composed of two subunits, while spliceosomes are composed of five small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (snRNPs). Ultimately, both components are essential for gene expression, but they serve different functions in the overall process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, spliceosomes and ribosomes are two distinct types of molecular complexes that play important roles in gene expression. Spliceosomes are responsible for removing non-coding regions from pre-mRNA during RNA splicing, while ribosomes are responsible for translating mRNA into proteins. Spliceosomes are made up of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, while ribosomes are composed of both ribosomal RNAs and proteins.
Spliceosomes are made up of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, while ribosomes are composed of both ribosomal RNAs and proteins. While spliceosomes are found in the nucleus, ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm. Spliceosomes are much larger in size than ribosomes and require more energy to function.
Ultimately, spliceosomes and ribosomes are essential components of gene expression and play key roles in the production of proteins.