Sodium chloride and sodium nitrate are two chemical compounds that are integral to various aspects of daily life, yet they are often misunderstood. Both are salts of sodium, a critical element necessary for biological and industrial processes, but their chemical compositions and uses differ significantly. Despite their common sodium base, these substances interact with their environments in unique ways, which have profound implications for both health and industry.
Sodium chloride, commonly known as table salt, is primarily used for culinary purposes and in food preservation. It is an ionic compound consisting of sodium and chloride ions. Sodium nitrate, on the other hand, often serves as a fertilizer in agriculture and as an ingredient in food preservation and manufacturing. It contains sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen, making it distinct in both structure and function from sodium chloride.
The impact of these compounds extends beyond their most common uses. Sodium chloride is essential for maintaining human physiological balance, while sodium nitrate plays a crucial role in plant nutrition and industrial synthesis. Both have environmental effects, from influencing water salinity to affecting soil composition. Understanding their properties, applications, and implications helps in making informed choices in their respective uses.
Sodium Chloride Explained
Chemical Properties
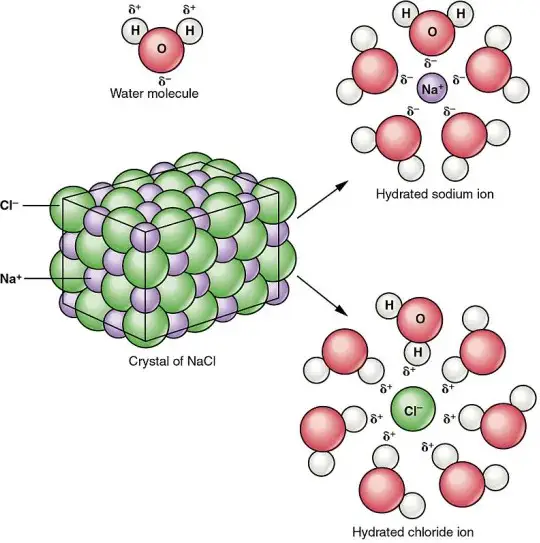
Sodium chloride, also known as table salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl. It forms when sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) atoms exchange electrons and create a stable ionic bond. Each sodium ion carries a positive charge, while each chloride ion carries a negative charge. This electrostatic attraction forms a crystalline lattice that is characteristic of table salt. Sodium chloride dissolves readily in water, breaking into Na+ and Cl- ions, a process essential for many biological and chemical applications.
Common Uses
Sodium chloride is used widely across various sectors:
- Food Industry: Sodium chloride is a fundamental seasoning, used not only to enhance flavor but also to preserve food. It inhibits the growth of bacteria by creating a hostile environment for microbial activity.
- Medical Field: In medicine, saline solutions, which are water and salt mixtures, are used for IV infusions to help maintain cellular function and fluid balance.
- Industrial Applications: Large quantities of salt are used in manufacturing processes, including the production of chlorine and caustic soda, and in water treatment plants to soften hard water.
Health Impacts
While sodium chloride is essential for human health, its excessive intake can lead to health issues such as:
- High Blood Pressure: High salt intake has been linked to hypertension, a risk factor for heart disease and stroke.
- Heart Conditions: Excessive salt can cause fluid retention, leading to an increased workload on the heart.
- Kidney Disease: Overconsumption can strain the kidneys, which regulate sodium levels, potentially leading to kidney disease.
Sodium Nitrate Overview
Chemical Characteristics
Sodium nitrate (NaNO3), also known as Chile saltpeter, is another important sodium compound. It is an ionic salt composed of sodium ions and nitrate ions. This compound is naturally found in mineral deposits in arid regions such as Chile and Peru. Sodium nitrate is highly soluble in water and is thermally stable up to high temperatures before decomposing into sodium nitrite and oxygen.
Applications in Industry
Sodium nitrate has several critical industrial applications:
- Agriculture: As a nitrogen-rich compound, it is commonly used as a fertilizer to improve crop yield and soil health.
- Food Preservation: It acts as a preservative and color fixative in cured meats, preventing bacterial growth and maintaining the red color of the meat.
- Chemical Manufacturing: It serves as a raw material in the production of nitric acid, a key component in fertilizers and explosives.
Health and Safety Concerns
Despite its usefulness, sodium nitrate poses several health risks:
- Cancer Risk: Long-term exposure and consumption can lead to the formation of nitrosamines, which are potential carcinogens.
- Methemoglobinemia: High levels of nitrates can convert hemoglobin into methemoglobin, which does not carry oxygen efficiently, posing serious health risks, particularly in infants.
Key Differences
Chemical Structure
The chemical structures of sodium chloride and sodium nitrate differ primarily in their ionic components. Sodium chloride consists of sodium and chloride ions, forming a simple cubic structure. In contrast, sodium nitrate contains a nitrate group, which impacts its chemical behavior and uses.
Industrial Uses Compared
In industry, the uses of these compounds are quite distinct:
- Sodium Chloride: Used mainly for flavoring, food preservation, and as a deicing agent.
- Sodium Nitrate: Primarily used in the manufacture of fertilizers and explosives, and as a food preservative.
Health Effects Comparison
The health implications of sodium chloride and sodium nitrate also differ significantly:
- Sodium Chloride: Mainly associated with cardiovascular risks due to high intake.
- Sodium Nitrate: Concerns include the potential to form carcinogenic nitrosamines and other health issues like methemoglobinemia.

Environmental Impact
Sodium Chloride Effects
Sodium chloride impacts the environment in several significant ways. When used as a road deicer, it can lead to increased salt levels in nearby water bodies. This phenomenon, known as salinization, can reduce water quality and affect aquatic life by disrupting osmotic balances critical to fish and other aquatic organisms. Additionally, the accumulation of salt in the soil can inhibit plant growth, leading to decreased biodiversity in terrestrial ecosystems.
Sodium Nitrate Contributions
Conversely, sodium nitrate, primarily used in agriculture, can contribute to water pollution through runoff. When used excessively as a fertilizer, it can leach into groundwater and surface waters, leading to nitrate pollution. This type of contamination is associated with eutrophication, where increased nutrient levels cause excessive growth of algae and depletion of oxygen in water bodies, harming aquatic life and affecting water usability.
Comparative Analysis
Comparing the environmental effects of these two compounds:
- Sodium chloride affects both soil and water ecosystems through physical changes and toxicity.
- Sodium nitrate primarily affects water systems by altering chemical balances and contributing to nutrient overload.
Industry Applications
Sodium Chloride in Food
In the food industry, sodium chloride is indispensable due to its role in flavor enhancement and food preservation. It helps to:
- Preserve food by creating an inhospitable environment for microbial growth.
- Enhance flavor, making it a staple in kitchens and food processing.
Sodium Nitrate in Agriculture
Sodium nitrate is valued in agriculture for its nitrogen content, essential for plant growth. As a fertilizer, it:
- Provides readily available nitrogen to plants, promoting growth and increasing crop yields.
- Improves the quality of the soil when used in proper amounts, enhancing its nutrient content without causing harmful buildup.
Technological Uses
Both compounds also have technological applications:
- Sodium chloride is used in water treatment facilities to regenerate ion exchange resins that soften water and remove contaminants.
- Sodium nitrate has applications in the production of pyrotechnics and solar power plants, where it’s used as a heat transfer fluid to store solar energy efficiently.
Safety Guidelines
Handling Sodium Chloride
Handling sodium chloride requires basic safety measures to prevent irritation and ensure safe usage:
- Wear protective gear such as gloves and goggles when handling large quantities, especially in industrial settings.
- Prevent contamination of the environment by controlling runoff and managing storage and disposal properly.
Precautions for Sodium Nitrate
Handling sodium nitrate requires more stringent precautions due to its chemical properties and health risks:
- Use protective clothing, including gloves, masks, and eye protection, to prevent inhalation or direct contact.
- Store in a cool, dry place to prevent decomposition, which can lead to the release of toxic gases.
Regulatory Standards
Both substances are regulated by various health and safety guidelines to minimize their environmental and health impacts:
- Regulations for Sodium Chloride: Includes guidelines for permissible exposure levels in the workplace and recommendations for environmental management.
- Regulations for Sodium Nitrate: More stringent due to its potential health risks, including limits on usage in food and requirements for handling in agricultural and industrial applications.

FAQs
What is Sodium Chloride?
Sodium chloride, known as table salt, is an essential compound used extensively in cooking and food preservation. It is composed of sodium and chloride ions, making it crucial for maintaining fluid balance and nerve function in humans.
What is Sodium Nitrate?
Sodium nitrate is a chemical compound predominantly used as a fertilizer in agriculture and as a preservative in cured meats. Its composition includes sodium, nitrogen, and oxygen, which are vital for promoting plant growth and preserving food quality.
How do Sodium Chloride and Sodium Nitrate differ?
While both compounds contain sodium, their chemical structures and uses vary greatly. Sodium chloride is primarily an ionic compound used for seasoning and preserving food, whereas sodium nitrate is used in agriculture to enrich soil with nitrogen and in food processing as a preservative.
Are there health risks associated with Sodium Nitrate?
Sodium nitrate can pose health risks if consumed in large quantities. It is associated with the formation of nitrosamines, compounds that can be carcinogenic. Thus, it is crucial to monitor its intake through preserved foods.
Can Sodium Chloride be substituted for Sodium Nitrate?
Sodium chloride cannot substitute for sodium nitrate due to their differing chemical properties and effects. Sodium chloride is ineffective as a nitrogen source for plants and does not have the preservative properties provided by the nitrates in sodium nitrate.
Conclusion
The nuances between sodium chloride and sodium nitrate highlight the complexity and specificity of chemical compounds in their applications and impacts. As we navigate their uses, it becomes evident that each plays a unique role in both industrial and biological contexts. Awareness and understanding of their differences are essential for optimizing their benefits while mitigating potential risks.
As industries and consumers continue to utilize these compounds, informed decisions can lead to better health outcomes and more sustainable practices. The evolving study and application of sodium chloride and sodium nitrate will undoubtedly continue to influence a wide range of fields from culinary arts to environmental science.
