Sequence alignment is an important tool used in bioinformatics to identify relationships between different biological sequences. In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between similarity and identity in sequence alignment, and how this knowledge can be used to improve the accuracy of sequence alignment results. We’ll also discuss the various methods used to measure similarity and identity, and how they are used to determine the best alignment.
Finally, we’ll look at some of the applications of sequence alignment in the field of bioinformatics.
Definition of sequence alignment
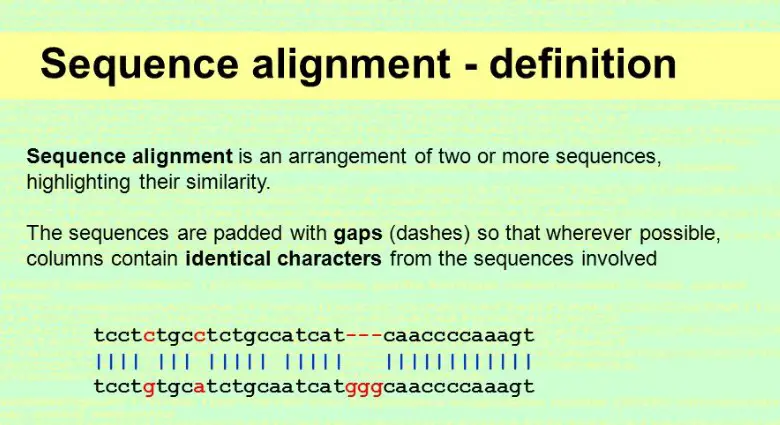
Sequence Alignment is a process used in bioinformatics to identify regions of similarity between two sequences of DNA, RNA, or proteins. It is an important tool used in molecular biology to study the evolutionary relationships between proteins or nucleic acid sequences. Sequence Alignment compares the sequences and determines the similarity between them.
The main difference between similarity and identity in sequence alignment is that identity refers to the exact same sequence of characters between two sequences, while similarity refers to the degree of similarity between two sequences, which may differ in some characters. Sequence Alignment can be used to find out relationships between two sequences, such as homology, which is the evolutionary relationship between two sequences.
Overview of similarity and identity

Similarity and identity are two related terms used in sequence alignment. While both measure the degree of similarity between two sequences, there is a distinct difference between the two.
For example, two identical sequences will have 100% identity, but two related sequences may have less than 100% identity but still have a high degree of similarity. Sequence alignment is used to determine a measure of similarity or identity between two sequences, providing a useful tool for bioinformatics research.
Difference between similarity and identity in sequence alignment
Sequence alignment is a process used to compare two or more biological sequences to determine their similarities and differences. The overall goal is to identify regions of similarity that may be indicative of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. While similarity and identity are both measures of comparison, there is an important distinction between the two when it comes to sequence alignment.
Similarity refers to the degree of sequence similarity between two sequences, while identity refers to the percentage of identical characters between two sequences. In other words, similarity is a measure of how closely two sequences match each other, while identity is a measure of how many characters in a sequence are exactly the same.
Applications of sequence alignment
Sequence alignment is a powerful tool used to compare sequences of nucleic acids or proteins. It helps determine the similarity between two sequences by calculating the number of identical and similar residues.
The difference between similarity and identity in sequence alignment lies in the type of residue. When the number of identical residues is calculated, only identical residues are counted. However, when the number of similar residues is calculated, both identical and similar residues are included.
This is an important distinction to make, as it allows us to assess the level of similarity between two sequences. Applications of sequence alignment include phylogenetic analysis, molecular evolution, and structure prediction.
Resources
Comparing the similarities and differences between two sequences is an important part of understanding biological relationships. Sequence alignment is a powerful tool for analyzing these similarities and differences, and can help determine the evolution of one sequence from another. The primary difference between similarity and identity in sequence alignment is that similarity measures the overall level of similarity between two sequences, while identity measures the exact matches between them.
The primary difference between similarity and identity in sequence alignment is that similarity measures the overall level of similarity between two sequences, while identity measures the exact matches between them. When two sequences are similar, they contain a high degree of shared characters, while when they are identical, they contain the same characters in the same order. This distinction can be used to understand the relationship between two sequences, whether they have evolved from one another or not.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the difference between similarity and identity in sequence alignment lies in the degree of similarity between the sequences. Similarity measures the percentage of matching bases in the two sequences, while identity measures the percentage of exact matches between the two sequences.

