When it comes to the study of solutions, two important laws are used to explain the behavior of dissolved substances: Raoult’s Law and Dalton’s Law. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the differences between the two laws and how they are used to calculate the vapor pressure of a solution. Understanding the basics of these two laws can help you better understand the complex interactions between liquids and solids.
Overview of the differences between raoult’s law and dalton’s law
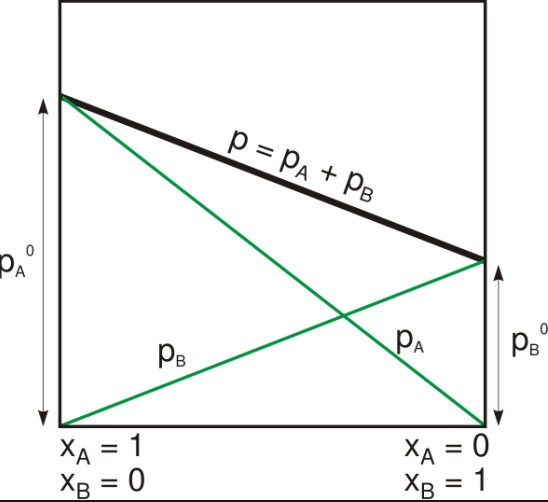
Raoult’s law and Dalton’s law are two important laws of thermodynamics that explain the behavior of solutions and mixtures. Although both laws are related to the same physical phenomenon, there is an important difference between them. Raoult’s law states that the partial pressure of each component in an ideal solution is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution.
Raoult’s law states that the partial pressure of each component in an ideal solution is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution. On the other hand, Dalton’s law states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each component in the mixture. In other words, the pressure of a mixture of gases is independent of the amount of each gas component in the mixture.
Thus, while Raoult’s law is concerned with the behavior of liquid solutions, Dalton’s law is concerned with the behavior of gases.
Explanation of raoult’s law

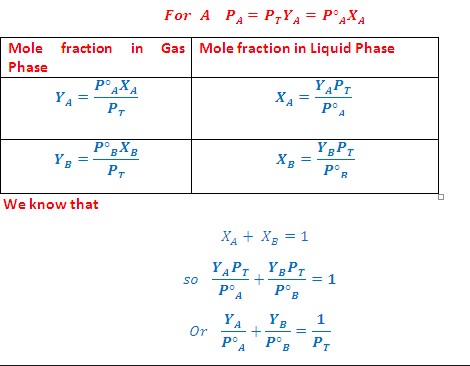
Raoult’s Law is a fundamental law of thermodynamics that describes the vapor pressure of a liquid in relation to its composition. In simple terms, it states that the vapor pressure of a liquid is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the liquid’s constituent components.
Whereas Dalton’s Law applies to mixtures of gases, Raoult’s Law applies specifically to mixtures of liquids.
Explanation of dalton’s law
Dalton’s law states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture. This law, proposed by John Dalton in 1801, is a cornerstone of physical chemistry.
It is important to understand the difference between Dalton’s law and Raoult’s law. While Dalton’s law states that the pressure of a gas is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture, Raoult’s law states that the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture is proportional to the mole fraction of that gas in the mixture. Therefore, Raoult’s law is only applicable when the two gases are in ideal solution, which is usually not the case.
Examples of raoult’s law and dalton’s law
Raoult’s law and Dalton’s law are two important concepts in chemistry that help us to understand the behavior of gases and vapors. Raoult’s law states that the vapor pressure of a solution is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solute in the solution. On the other hand, Dalton’s law states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas.
On the other hand, Dalton’s law states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas. Both of these laws are used to explain the behavior of gases and vapors in different scenarios. However, the main difference between Raoult’s law and Dalton’s law is that Raoult’s law only applies to solutions, while Dalton’s law applies to mixtures of gases.
Another difference is that Raoult’s law explains the behavior of a solution’s vapor pressure, while Dalton’s law explains the behavior of the total pressure of a mixture of gases.
Applications of raoult’s law and dalton’s law
Raoult’s law and Dalton’s law are two important laws in chemistry that describe the behavior of gases. The most notable difference between the two laws is that Raoult’s law deals with the vapor pressure of a mixture of liquids, while Dalton’s law deals with the total pressure of a mixture of gases.
Dalton’s law, on the other hand, states that the total pressure of a mixture of ideal gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the gases. Both of these laws are important for understanding the behavior of liquids and gases in a variety of applications.
For example, Raoult’s law is used to calculate the boiling point of a solution, while Dalton’s law is used to calculate the total pressure of a gas mixture. In addition, Raoult’s law can be used to calculate the vapor pressure of a mixture of liquids, while Dalton’s law can be used to calculate the partial pressures of a gas mixture.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, Raoult’s Law and Dalton’s Law have different applications in chemistry and are used to describe different phenomena. Raoult’s Law is used to calculate the vapor pressure of a liquid solution and is based on the idea that the vapor pressure of a solution is the sum of the vapor pressures of the individual components. Dalton’s Law, on the other hand, is used to calculate total pressure of a mixture of gases, and is based on the idea that the total pressure of the gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases.
Dalton’s Law, on the other hand, is used to calculate total pressure of a mixture of gases, and is based on the idea that the total pressure of the gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases.