Body positions, specifically prone and supine, play crucial roles in various aspects of healthcare, physical fitness, and daily comfort. While they may seem straightforward, understanding these positions can significantly impact one’s health and wellness. Prone and supine are terms used to describe different ways humans can orient themselves while lying down, each having specific applications and benefits.
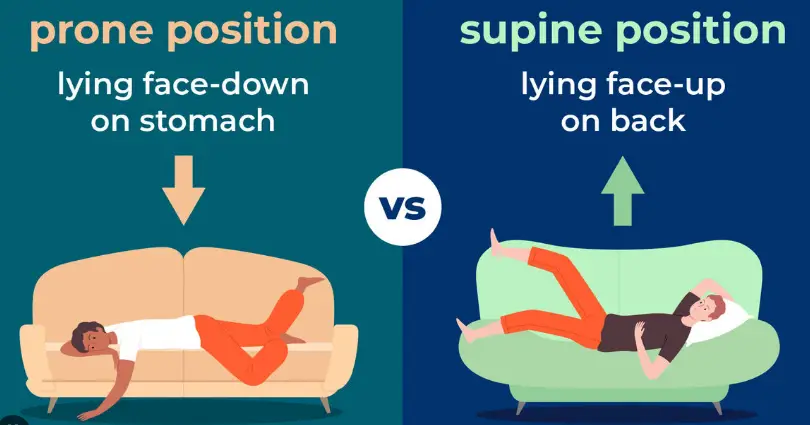
The prone position refers to lying flat on one’s stomach, face down. In contrast, the supine position describes lying on one’s back, face up. These positions are not just relevant in medical examinations or during exercise; they affect spinal health, breathing, and even muscle tone. Knowing when and how to use each can enhance well-being and aid in recovery processes.
Discussing the differences between prone and supine positions sheds light on their unique benefits and potential drawbacks. For instance, the prone position can improve oxygenation in certain medical conditions, whereas the supine position might be better for spinal health during rest. Such distinctions are critical for leveraging each position’s advantages in medical settings, therapy, or even in improving sleep quality.
Prone Position
Definition
The prone position refers to lying flat on the stomach with the face and torso facing down. It is a basic yet essential posture used in various settings, from medical procedures to everyday activities like reading a book on the floor.
Common Uses
- Medical Examinations: Doctors often use the prone position to access the back for examinations and treatments.
- Physical Therapy: This position is beneficial for exercises that strengthen the back and shoulder muscles.
- Surgeries: Certain surgical procedures require patients to be in a prone position to provide surgeons better access to the operative site.
- Sleeping and Relaxation: Some people find relief from back pain by lying in this position.
Benefits
- Improved Oxygenation: For patients with respiratory issues, the prone position can help enhance lung function.
- Access for Treatment: Provides optimal access for treatments like spinal adjustments and massages.
- Muscle Strengthening: Helps in strengthening the dorsal muscles, which are crucial for posture and spinal support.
Supine Position
Definition
The supine position is characterized by lying on one’s back with the face up. It is the most common resting position used in various aspects of healthcare and personal care.
Common Uses
- Medical Assessments: Widely used during medical exams, especially for abdominal assessments.
- Recovery Post-Surgery: Often recommended for patients recovering from surgery, as it allows the body to maintain a neutral position.
- Sleeping: It is the preferred sleeping position for many, promoting spinal alignment and reducing back pain.
Benefits
- Spinal Health: Encourages proper spinal alignment and reduces pressure on the discs.
- Safety: Reduces the risk of choking and is recommended for infant sleep to prevent Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS).
- Versatility: Suitable for various therapeutic, diagnostic, and comfort-related applications.
Comparative Analysis
Positioning Differences
- Orientation: Prone involves lying face down, while supine involves lying face up.
- Physical Impact: Each position impacts different muscle groups and bodily functions.
Impact on Health
- Respiratory and Cardiac Health: Supine position may exacerbate conditions like sleep apnea, whereas prone can be beneficial for certain types of respiratory distress.
- Digestive Health: Supine can aid in the digestion process by aligning the body in a neutral position.
Practical Applications
- Medical and Therapeutic Use: Each position has specific indications in medical and therapeutic contexts based on the patient’s needs.
- Daily Activities: From sleeping to performing certain exercises, choosing the right position can enhance effectiveness and comfort.
Health Implications
Effects on Spine
The positioning of the body plays a pivotal role in spinal health. The prone position can reduce pressure on certain parts of the spine and is beneficial for engaging and strengthening the muscles along the back. However, it might increase stress on the neck if the head is turned to one side for prolonged periods.
Conversely, the supine position naturally aligns the spine and distributes body weight across a larger surface area, minimizing pressure points and supporting the natural curvature of the spine. This position is particularly beneficial for people suffering from lower back pain as it allows the intervertebral discs to relax and hydrate.
Circulation Considerations
The impact of body positions on blood circulation is significant. Lying in a supine position generally promotes efficient blood circulation by allowing blood to flow back to the heart more easily, aiding in the reduction of swelling in the lower extremities. This position is recommended for patients who have suffered from venous leg ulcers or those at risk of deep vein thrombosis.
On the other hand, the prone position can enhance circulation in the anterior parts of the body and improve blood flow to the limbs, which is beneficial in certain therapeutic settings or during specific medical procedures to reduce the risk of pressure sores.
Breathing Effects
Body positioning affects respiratory function in several ways. Lying in a prone position can dramatically improve oxygenation and lung volume in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). This position allows for better expansion of the dorsal lung regions, which are often compressed when a person is lying on their back.
The supine position, while generally comfortable, can exacerbate respiratory conditions like sleep apnea, where the tongue falls backward, obstructing the airway. This position can also lead to reduced lung capacity in some individuals, particularly those who are obese or have severe pulmonary diseases.
Therapeutic Use
Medical Procedures
Both prone and supine positions are extensively used in medical procedures:
- Prone: Frequently used in surgeries involving the lower back, such as lumbar decompression or neurosurgery. This position provides surgeons optimal access to the operative site.
- Supine: The standard position for most surgical procedures including cardiac, abdominal, and pelvic surgeries, as it provides stability and easy access to the body’s front.
Physical Therapy
Positional therapy plays a crucial role in rehabilitation:
- Prone exercises: These include back extensions and leg lifts that target the posterior chain muscles, essential for improving posture and alleviating back pain.
- Supine exercises: Activities like pelvic tilts and knee-to-chest stretches performed in this position help strengthen the core and pelvic muscles, supporting spinal alignment.
Sleep and Comfort
Sleep position is critical for overall health and can be optimized using both prone and supine positions:
- Supine: Widely recommended for a restful sleep, especially for those with spinal and neck issues. It allows the mattress to support the body evenly and is often the most comfortable position for maintaining long-term sleep quality.
- Prone: While not typically recommended for sleeping due to potential neck and back strain, some find this position helps with digestion and can ease some types of lower back pain.
FAQs
What defines the prone position?
The prone position is defined as lying flat on the stomach with the face directed downward. It’s often used in medical settings to improve access to the back and might help in certain respiratory conditions by facilitating better lung expansion.
How does the supine position affect the spine?
Lying in the supine position naturally aligns the spine, reducing stress on the vertebrae and muscles. This position is commonly recommended for sleeping because it allows the spinal discs to relax and expand, aiding in recovery and preventing back pain.
When is the prone position recommended?
The prone position is recommended in therapeutic settings, particularly for certain types of surgeries and therapies. It’s also useful in physical therapy to strengthen the muscles of the back and shoulders, and in some cases, to improve respiratory mechanics.
Is one position better for circulation?
Both positions impact circulation differently; the supine position generally promotes better venous return to the heart. However, the prone position can sometimes aid circulation in the lower extremities and increase blood flow to certain areas.
Can sleeping position affect breathing?
Yes, sleeping positions significantly affect breathing. The supine position can exacerbate sleep apnea in some individuals, while the prone position might improve respiratory function, especially in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between the prone and supine positions is more than academic knowledge; it’s a practical insight that can enhance one’s health and comfort. Each position has specific benefits that can be maximized with proper knowledge and application, making this information invaluable for anyone looking to improve their physical well-being.
Conclusively, whether it’s adjusting sleep habits, recovering from an injury, or managing specific health conditions, the choice between prone and supine positioning can have substantial implications. This knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and wellness strategies, tailored to their specific needs.