In the intricate world of business management, distinguishing between project management and operation management is crucial for the strategic allocation of resources and achieving organizational goals. These two disciplines, though often interlinked, cater to different aspects of business functionality, focusing on the execution of temporary ventures and the smooth running of ongoing operations, respectively. Understanding their differences is not just academic; it impacts how organizations structure their teams, prioritize tasks, and plan for the future.
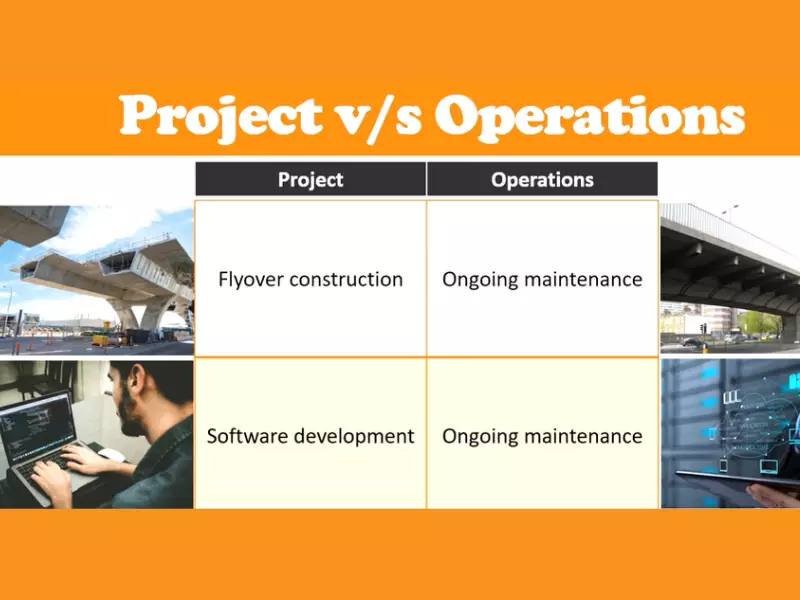
Project management and operation management serve distinct purposes within an organization. The former revolves around the planning, executing, and closing of projects—defined endeavors with a specific start and end date, aimed at achieving unique goals and objectives. On the other hand, operation management focuses on ensuring that the day-to-day operations of a company run efficiently and effectively, aiming to improve productivity and quality while reducing costs.
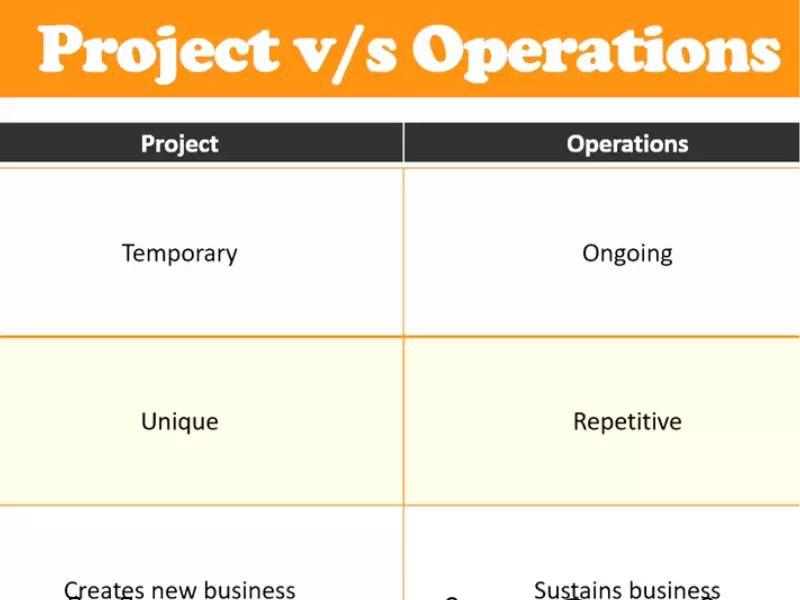
The significance of delineating these two management spheres lies in their operational focus and outcome. Project management is project-centric, often characterized by its temporality, uniqueness, and the pursuit of specific objectives. In contrast, operation management is process-centric, emphasizing ongoing activities that are repetitive, permanent, and aimed at sustaining business operations. By recognizing these differences, organizations can better structure their management practices, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall performance.
Core Concepts
Project Management Defined
Definition and Objectives
Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements. It is a strategic competency for organizations, enabling them to tie project results to business goals and thus, compete more effectively in their markets. The primary objectives of project management include completing a project within the set scope, on time, and within budget while meeting or exceeding stakeholders’ expectations.
Key Characteristics
- Temporary: Projects have a defined beginning and end.
- Unique: Each project is distinct in its objectives and outcomes.
- Goal-oriented: Projects aim to achieve specific objectives.
- Resource-dependent: Utilizes allocated resources, including time, money, and manpower.
Operation Management Defined
Definition and Objectives
Operation management involves the planning, organizing, and supervising of production, manufacturing, or the provision of services. Its emphasis is on efficiency and effectiveness of processes. The primary objective of operation management is to improve the production of goods and services by ensuring that operations are efficient in terms of using as little resource as needed, and effective in terms of meeting customer requirements.
Key Characteristics
- Continuity: Operations are ongoing and repetitive.
- Process-focused: Concentrates on optimizing and managing processes.
- Efficiency and effectiveness: Aims to maximize output while minimizing inputs.
- Quality control: Ensures products or services meet quality standards.
Key Differences
Understanding the distinctions between project management and operation management is crucial for applying the correct strategies and methodologies in each area.
Scope and Objectives
Project Management Scope
Project management focuses on specific, short-term goals aimed at producing a unique product, service, or result. Its scope is defined by the project’s objectives, resources, and timeline.
Operation Management Scope
In contrast, operation management has a broader scope that involves managing ongoing operations and processes within an organization. It aims to ensure long-term efficiency and effectiveness in producing goods or providing services.
Time Frame
Project Management Duration
Projects are temporary endeavors. They have a defined start and end date, and their duration is contingent upon achieving the project’s specific objectives.
Operation Management Continuity
Operation management is continuous, focusing on sustaining business operations indefinitely. It aims to create a stable and efficient environment for ongoing activities.
Change and Stability
Projects and Change
Project management is inherently dynamic, embracing change to achieve its goals. Projects often introduce new processes, tools, or innovations to an organization.
Operations and Stability
Operation management, however, emphasizes stability and consistency in processes. It seeks to maintain order and efficiency, minimizing variations and disruptions.
Skills and Roles
Project Manager Responsibilities
A project manager’s responsibilities include planning, executing, and closing projects. They must manage teams, resources, and stakeholder expectations, ensuring the project meets its objectives.
Operation Manager Responsibilities
An operation manager focuses on process optimization, quality control, and efficiency improvement. They oversee daily operations, manage resources, and implement strategies to meet production goals.
Integration in Organizations
Collaboration between Project and Operation Managers
For businesses to thrive, collaboration between project and operation managers is essential. They must work together to ensure that project outcomes align with ongoing operations, facilitating a seamless transition from project completion to business-as-usual.
Areas of Collaboration
- Resource allocation: Sharing insights on resource management to optimize usage.
- Process improvement: Implementing project innovations into regular operations.
- Strategic planning: Aligning project goals with operational strategies for cohesion.
Benefits of Effective Collaboration
Effective collaboration leads to enhanced efficiency, innovation incorporation, and strategic alignment, ensuring that projects support and enhance operational capabilities.
Impact on Business Success
Project Management Contributions
Project management drives innovation and change, introducing new products, services, or processes that can significantly enhance an organization’s competitive edge.
Operation Management Contributions
Operation management ensures the sustainability and efficiency of business operations, which is crucial for long-term success and profitability.
Strategies for Optimization
Enhancing Project Management
Techniques and Tools
Project management benefits greatly from an array of techniques and tools designed to improve efficiency and effectiveness. Key among these are:
- Agile methodologies: Enhance flexibility and responsiveness.
- Project management software: Tools like Asana, Trello, and JIRA streamline task assignments, progress tracking, and collaboration.
- Risk management tools: Identify and mitigate potential risks early in the project lifecycle.
Best Practices
Adopting best practices in project management is crucial for success. These include:
- Clear goal setting: Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives.
- Regular communication: Ensure all stakeholders are informed and engaged.
- Continuous learning: Incorporate lessons learned from past projects to improve future outcomes.
Streamlining Operation Management
Efficiency Models
In operation management, efficiency models such as Lean, Six Sigma, and Total Quality Management (TQM) play vital roles. These models focus on:
- Reducing waste: Streamlining processes to eliminate unnecessary steps.
- Improving quality: Enhancing the consistency and reliability of output.
- Optimizing resource use: Ensuring resources are used as effectively as possible.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement, or Kaizen, is a cornerstone of effective operation management. This approach involves:
- Regular evaluation of processes.
- Employee involvement in suggesting improvements.
- Iterative enhancements to workflows and processes.
Real-world Applications
Case Studies: Project Management Success
Example Projects and Outcomes
One notable project management success story involves the construction of the Burj Khalifa, the world’s tallest building. The project was completed on time and within budget through meticulous planning, risk management, and the use of advanced construction technologies.
Case Studies: Operation Management Excellence
Example Operations and Achievements
A standout in operation management excellence is Toyota’s production system, renowned for its Just-In-Time (JIT) manufacturing process. This system minimizes inventory costs and enhances efficiency, setting a benchmark for manufacturing industries worldwide.
Challenges and Solutions
Addressing Project Management Challenges
Common Issues and Solutions
Project management often faces challenges such as scope creep, budget overruns, and team conflicts. Solutions include:
- Scope management: Implement rigorous change control processes.
- Budget planning: Use detailed cost estimations and contingency funds.
- Conflict resolution: Adopt effective communication and mediation strategies.
Overcoming Operation Management Hurdles
Common Obstacles and Strategies
Operation management challenges include process inefficiencies, quality control issues, and supply chain disruptions. Strategies to overcome these obstacles involve:
- Process re-engineering: Redesign processes for greater efficiency.
- Quality assurance programs: Implement stringent quality control measures.
- Supply chain management: Develop robust relationships with suppliers and implement backup plans.
Future Trends
Innovations in Project Management
Emerging Technologies and Methodologies
The future of project management is being shaped by innovations such as AI and machine learning, which can predict project risks and outcomes, and virtual reality (VR) for immersive project planning and stakeholder engagement.
Advances in Operation Management
New Trends and Their Implications
In operation management, trends such as sustainability practices, focusing on eco-friendly processes, and automation and robotics for improving efficiency, are becoming increasingly significant. These advances promise to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impact, marking the next wave of operational excellence.
FAQs
What is Project Management?
Project management is the discipline of initiating, planning, executing, monitoring, controlling, and closing the work of a team to achieve specific goals and meet specific success criteria. It involves temporary endeavors with a defined beginning and end.
What is Operation Management?
Operation management focuses on the administration of business practices to create the highest level of efficiency possible within an organization. It involves managing the process that converts inputs (in the forms of materials, labor, and energy) into outputs (in the form of goods and services).
How do Project Management and Operation Management Differ?
While project management focuses on the successful execution of specific projects within a set timeframe, operation management is concerned with the ongoing operations of a company. The key difference lies in the temporality and specificity of projects versus the continuity and repetitiveness of operations.
Why is it Important to Distinguish Between the Two?
Distinguishing between project management and operation management is essential for effective resource allocation, strategic planning, and achieving organizational goals. It helps in assigning the right personnel, tools, and approaches to the right tasks, ensuring both projects and operations are managed efficiently.
Conclusion
The distinction between project management and operation management underpins the framework within which businesses operate and evolve. Recognizing the unique characteristics and objectives of each management discipline allows for the strategic alignment of resources, ensuring that projects are completed successfully while operations continue to run smoothly. This understanding is not just theoretical but practical, enabling organizations to thrive in a competitive landscape by maximizing efficiency and fostering innovation.
In summary, while project management and operation management are both critical to the success of a business, their distinct roles and focuses necessitate a clear understanding and approach. By effectively navigating these management disciplines, businesses can ensure the optimal use of resources, meet project objectives, and maintain efficient operations, paving the way for sustained growth and success.
