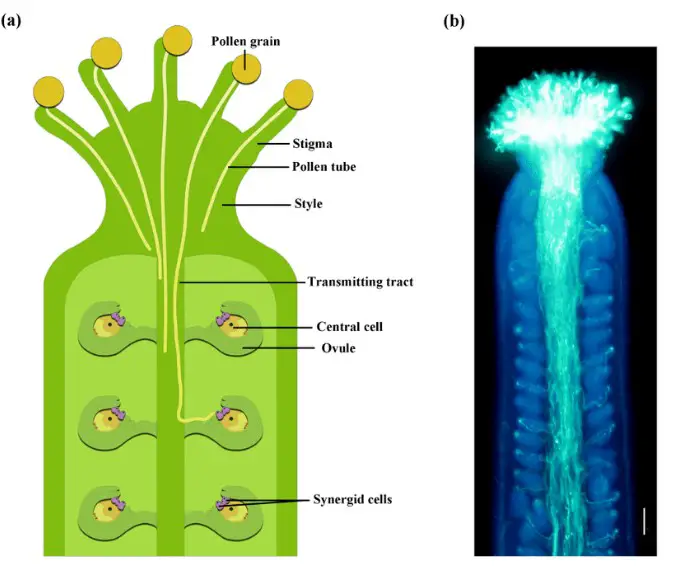
Plant reproduction is a fascinating and intricate process, crucial for the survival and diversity of plant species. At the heart of this process are two key components: the pollen tube and the style. Both play pivotal roles in ensuring the successful fertilization of plants, but they operate in markedly different ways. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone interested in botany, agriculture, or the natural world.
The pollen tube is a structure that forms from a pollen grain and grows towards the ovary through the style, facilitating the transport of sperm cells for fertilization. The style, on the other hand, is a part of the female reproductive organ of a flower, serving as a conduit through which the pollen tube grows. It plays a critical role in capturing pollen and hosting the pollen tube’s journey towards the ovule.
The interaction between the pollen tube and the style is a prime example of nature’s precision. The formation and growth of the pollen tube, guided by the style, highlight a complex communication and cooperation between male and female reproductive structures. This process not only ensures the transfer of genetic material but also influences the genetic diversity and evolution of plant species.
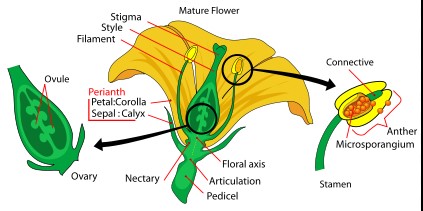
Pollen Tube Basics
Definition and Role
The pollen tube is a critical structure in the plant kingdom, serving as the conduit for sperm cells to travel from the pollen grain to the ovule for fertilization. Think of it as nature’s microscopic delivery system, ensuring the continuation of plant species through sexual reproduction. This process begins when a pollen grain adheres to the stigma of a flower, germinating to form the pollen tube, which then extends down the style to the ovary, carrying sperm cells to the egg.
Formation Process
How and Where a Pollen Tube Forms
The formation of a pollen tube is a fascinating process that occurs in several stages:
- Pollen grain adherence: First, a pollen grain lands on the stigma of a compatible flower.
- Germination: Moisture and nutrients from the stigma trigger the pollen grain to germinate.
- Tube growth: The pollen tube begins to grow, extending down through the style towards the ovary.
Stages of Pollen Tube Development
- Germination stage: Upon landing on the stigma, the pollen grain absorbs water and swells.
- Tube emergence: A tube-like structure emerges from the pollen grain, beginning its journey down the style.
- Guided growth: The tube navigates through the style, guided by chemical signals, towards the ovule.
Characteristics
Physical Attributes
Pollen tubes are long, slender structures, visible only under a microscope. They exhibit rapid growth, capable of navigating through the style’s complex environment to reach the ovule.
Genetic Makeup and Variations
The genetic makeup of pollen tubes can vary significantly between species, influencing their growth rate, behavior, and interaction with the style. These variations are a subject of ongoing research, offering insights into plant reproductive strategies and evolution.
Style Essentials
Definition and Function
The style is an elongated part of the flower’s pistil, connecting the ovary to the stigma. Its primary role is to support the growth and guidance of the pollen tube towards the ovule, facilitating fertilization and ensuring the production of seeds.
Structure Details
Anatomy of the Style
The style’s anatomy is designed to support its reproductive function. It consists of a solid or hollow tube through which the pollen tube grows. The internal structure of the style is lined with cells that can interact with the pollen tube, providing it with necessary nutrients and directional cues.
Variations Across Plant Species
Styles can vary widely in length, thickness, and internal structure across different plant species. These variations are adapted to the specific needs of the plant’s reproductive strategy, influencing the compatibility with pollen grains and the efficiency of pollen tube growth.
Biological Processes
Pollen Reception
Upon landing on the stigma, the pollen grain’s compatibility is assessed, determining whether it will germinate and form a pollen tube. This selective process ensures that only compatible pollen can fertilize the ovule.
Supporting Pollen Tube Growth
The style plays a crucial role in guiding and supporting the pollen tube’s journey towards the ovule. It provides:
- Nutritional support: Supplying the growing tube with carbohydrates and lipids.
- Directional cues: Emitting chemical signals that guide the pollen tube to the ovule.
Key Differences
Structural Contrast
While the pollen tube and style are both essential components of plant reproduction, their structures differ significantly. The pollen tube is a transient, growing entity that forms from the pollen grain, whereas the style is a permanent, structural part of the flower.
Functional Disparities
Roles in Plant Reproduction
The pollen tube’s sole function is to transport sperm cells to the ovule for fertilization. In contrast, the style has multiple roles, including serving as a pathway for the pollen tube, filtering incompatible pollen, and facilitating fertilization.
Interaction with Pollen Grains and Tubes
The style interacts with pollen grains at the very beginning of the reproductive process, determining compatibility. The pollen tube, on the other hand, is a product of this interaction, growing within the style towards the ovary.
Genetic and Biochemical Aspects
Genetic Makeup Comparison
The genetic composition of pollen tubes and styles differs, reflecting their distinct roles in reproduction. Research into these differences provides insights into the complex mechanisms of plant fertilization and the evolution of reproductive strategies.
Biochemical Processes
The biochemical processes within the pollen tube and style are tailored to their functions. The style produces substances that support pollen tube growth and guide it towards the ovule, while the pollen tube’s growth is driven by its own genetic and biochemical machinery.
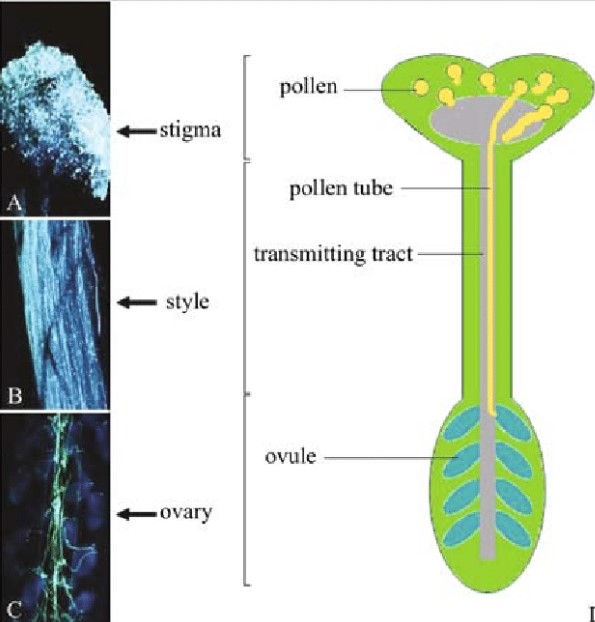
Pollination and Fertilization
Integration in Reproduction
Pollination and fertilization are two pivotal processes in the plant reproduction cycle, ensuring the continuation of species and the diversity of plant life. The pollen tube and style play critical roles in these processes. Pollination begins when pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of a flower, a process that can be facilitated by wind, water, or pollinators such as bees and butterflies. Once a pollen grain lands on the stigma, it germinates and forms a pollen tube if the conditions are favorable and the plant species are compatible. This tube then grows down the style, serving as a passage for sperm cells to reach and fertilize the ovule, leading to seed formation.
The style’s role in this process is not passive. It acts as a selective barrier, permitting only compatible pollen to germinate and grow a tube. Furthermore, the style provides the necessary nutrients and chemical signals guiding the pollen tube’s growth towards the ovule. This meticulous coordination ensures successful fertilization, highlighting the intricate relationships between different plant structures in reproduction.
Impact on Plant Diversity
Influence on Genetic Variation and Species Evolution
The interaction between the pollen tube and style has profound implications for plant diversity and evolution. By selectively allowing certain pollen grains to fertilize ovules, the style contributes to genetic variation within plant populations. This variation is the cornerstone of evolutionary processes, enabling species to adapt to changing environments, resist pests and diseases, and explore new ecological niches.
Role in Hybridization and Breeding
Hybridization, the process of crossing different species or varieties to produce a hybrid, is another area where the pollen tube and style are fundamental. In many cases, breeders rely on the pollen tube’s ability to overcome the style’s barriers to create new plant varieties with desirable traits, such as increased resistance to diseases, improved yield, and better nutritional qualities. This has significant implications for agriculture, food security, and conservation.
Technological and Research Implications
Agricultural Advancements
Manipulation of Pollen Tubes and Styles for Crop Improvement
The manipulation of pollen tubes and styles represents a frontier in agricultural science, offering potential for significant crop improvements. Scientists and agriculturalists exploit these plant parts to enhance fertilization success rates, increase genetic diversity, and produce crops with desirable traits. Techniques such as controlled pollination, genetic modification, and molecular breeding allow for precise adjustments to the pollen tube growth rate and the style’s selective properties, leading to optimized plant breeding outcomes.
Scientific Research
Studies Focusing on Understanding Reproductive Mechanisms
The quest to understand the molecular and genetic mechanisms guiding the pollen tube’s growth through the style has spurred extensive scientific research. Studies often focus on identifying the genes and signaling pathways involved in this process, shedding light on how plants regulate fertilization and ensure reproductive success. Such research not only deepens our understanding of plant biology but also identifies targets for genetic engineering and breeding programs aimed at improving crop resilience and yield.
Future Directions for Plant Biology Research
The future of plant biology research holds exciting prospects, particularly in the realm of reproductive biology. Emerging technologies, such as CRISPR/Cas9 for gene editing, offer unprecedented opportunities to manipulate the pollen tube and style’s functions at the genetic level. Researchers are also exploring the potential of artificial intelligence and machine learning to predict and enhance plant breeding outcomes. Additionally, the growing concern over climate change underscores the need for plants capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions, pests, and diseases, driving research towards developing more resilient crop varieties through innovative manipulation of pollen tubes and styles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a pollen tube?
A pollen tube is an elongated structure that emerges from a pollen grain, growing through the style to deliver sperm cells to an ovule for fertilization. It is a crucial element in the reproductive process of seed plants, enabling the sperm to travel from the pollen to the egg cell located within the ovary.
How does the style aid in plant reproduction?
The style plays a significant role in plant reproduction by serving as the channel through which the pollen tube grows towards the ovary. It is part of the pistil, the female reproductive organ of a flower, and is responsible for intercepting pollen and facilitating the growth of the pollen tube, ultimately leading to fertilization.
Why are pollen tubes and styles important for plant diversity?
Pollen tubes and styles are essential for plant diversity because they enable sexual reproduction, allowing for the exchange of genetic material between different plants. This genetic exchange leads to variation within plant populations, which is a key driver of evolution and adaptation in the plant kingdom.
Conclusion
The complexities of plant reproduction, underscored by the roles of the pollen tube and style, are more than just fundamental biological processes; they are reflections of the intricate dance of life that underpins our natural world. The pollen tube’s journey through the style to achieve fertilization represents a critical step in the perpetuation of plant species, contributing to the genetic diversity that is vital for adaptation and survival.
Understanding the difference between pollen tubes and styles not only enriches our knowledge of plant biology but also highlights the importance of each component in the broader context of ecology and evolution. As we continue to explore and appreciate the nuances of the natural world, the study of these reproductive mechanisms remains a beacon of insight into the life cycles that sustain the planet’s biodiversity.