Phenols and polyphenols are two categories of chemical compounds that hold significant importance across various fields, ranging from medicine to food preservation. Both types of compounds are known for their robust antioxidant properties and their role in promoting health and preventing diseases. While they share some similarities, their differences are crucial in their applications and effects on health.
Phenols are simple compounds characterized by a hydroxyl group attached to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. They are commonly found in natural products and are essential in the synthesis of plastics and pharmaceuticals. Polyphenols, on the other hand, consist of multiple phenol units and are primarily noted for their presence in a wide variety of plant-based foods, contributing significantly to the antioxidant qualities of these foods.
The impact of phenols and polyphenols extends beyond simple chemical interest; their influence on health is profound. They have been studied for their potential in reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Their distinct chemical structures, which contribute to their unique properties, make them a subject of interest in both scientific research and dietary considerations.
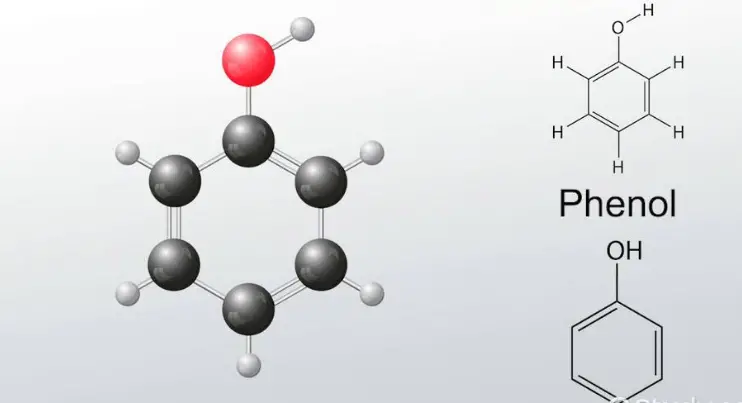
Phenols Explained
Definition and Chemical Structure
Phenols are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the phenol family is phenol itself, C6H5OH, often referred to simply as carbolic acid. Phenols are characterized by their aromatic ring, which significantly influences their chemical properties, making them somewhat more acidic than typical alcohols.
Common Sources
Phenols are widespread in nature, primarily found in plants. They are also synthetically produced. Natural sources include:
- Fruits: such as apples, cherries, and grapes.
- Vegetables: particularly in onions, parsley, and potatoes.
- Spices: like cloves and oregano are rich in phenolic compounds.
In industrial settings, phenols are derived from coal tar or petroleum distillates in the production of plastics, drugs, and dyes.
Uses in Industry
Phenols have diverse applications in various industries, highlighting their versatility:
- Plastics: Phenolic resins are used extensively in the manufacture of laminates, adhesives, and molding compounds.
- Pharmaceuticals: Phenolic compounds serve as precursors for the synthesis of drugs, including pain relievers and antiseptics.
- Dyes and Pigments: Phenols are foundational in creating some of the vibrant dyes used in textiles and inks.
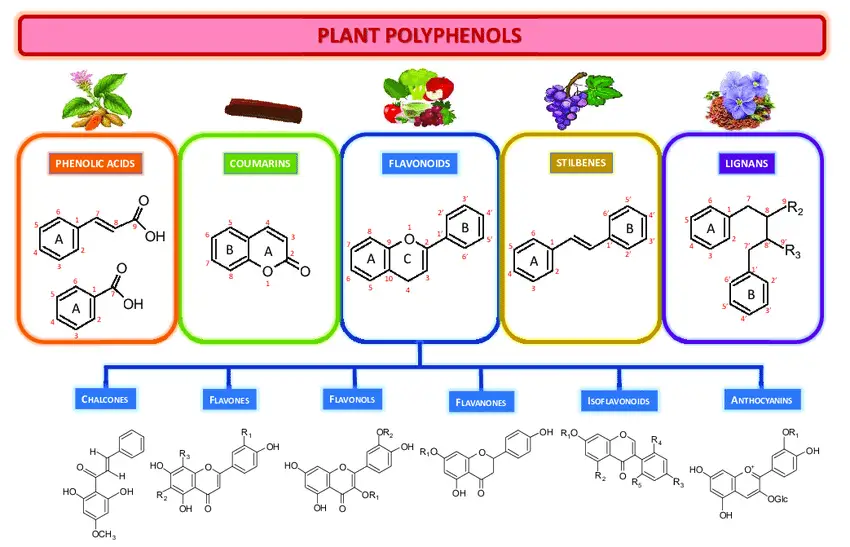
Polyphenols Overview
Definition and Classification
Polyphenols are a category of compounds naturally found in plants, characterized by the presence of multiple phenol structural units. These compounds are categorized into several classes, including flavonoids, lignans, tannins, and phenolic acids, each differing in structure and function.
Natural Sources
The richest sources of polyphenols are plant-based foods. Some of the most polyphenol-rich foods include:
- Fruits: particularly berries, plums, and apples.
- Vegetables: such as spinach, olives, and artichokes.
- Beverages: green tea, coffee, and red wine are excellent sources.
These natural sources are not only common in diets but are also crucial for their health benefits attributed to their high polyphenol content.
Role in Health
Polyphenols play a critical role in maintaining and improving health through various mechanisms:
- Antioxidant activity: They combat oxidative stress, reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Polyphenols help reduce inflammation, a key factor in many health conditions.
- Support heart health: By improving endothelial functions and lowering blood pressure.
Chemical Properties
Structural Differences
Phenols and polyphenols differ significantly in structure. While phenols contain a single phenolic group, polyphenols consist of multiple such groups. This structural complexity impacts their chemical behavior and biological activities.
Reactivity and Stability
- Reactivity: Phenols react with bases and oxidizing agents, whereas polyphenols, due to their structure, show varied reactivity based on the number of hydroxyl groups and their placement.
- Stability: Polyphenols are generally less stable than simple phenols due to their complex structures, which can lead to rapid degradation when exposed to light, heat, or air.
Biological Roles
Antioxidant Properties
Both phenols and polyphenols are celebrated for their antioxidant properties. They neutralize free radicals, thereby preventing cellular damage and oxidative stress, which are linked to aging and various diseases.
Impact on Human Health
The impact of phenols and polyphenols on human health is profound. They have been associated with a lower risk of several chronic diseases:
- Heart Disease: By reducing oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and improving arterial function.
- Cancer: Some studies suggest that polyphenols can inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: There is growing evidence that polyphenols can help protect against diseases like Alzheimer’s by influencing various pathways involved in neuronal health.
Phenols vs Polyphenols
Key Differences in Structure
The primary distinction between phenols and polyphenols lies in their molecular structure. Phenols consist of a single benzene ring with one or more hydroxyl groups attached, whereas polyphenols contain multiple phenol units, which can vary greatly in their complexity. This structural variation significantly affects their physical properties and biological activities, making polyphenols generally more potent but also more sensitive to environmental factors.
Comparison of Biological Effects
The biological impacts of phenols and polyphenols differ mainly due to their structure:
- Antioxidant Capacity: Polyphenols tend to have stronger antioxidant properties because of their multiple reactive sites compared to single-ring phenols.
- Metabolic Processing: Polyphenols are typically processed differently within the body, often requiring breakdown by gut bacteria before they can be absorbed, which influences their bioavailability and efficacy.
Diverse Applications
Both phenols and polyphenols are utilized across various industries but their applications vary based on their chemical properties:
- Food Preservation: Polyphenols are often used in food preservation for their ability to inhibit oxidation.
- Medical Treatments: Phenols are used in simpler medicinal formulations, including antiseptics and disinfectants.
Industry Applications
Phenols in Pharmaceuticals
Phenols have been a cornerstone in pharmaceuticals due to their antiseptic and analgesic properties:
- Aspirin, one of the most well-known analgesics, is derived from salicylic acid, a type of phenol.
- Antiseptic solutions often contain phenols because of their effectiveness in killing bacteria and fungi.
Polyphenols in Food Industry
In the food industry, polyphenols are prized for their role in enhancing the nutritional and sensory qualities of food:
- Color and Flavor: Polyphenols contribute to the color and taste of many fruits and beverages.
- Shelf Life: Their antioxidant properties help extend the shelf life of perishable goods.
Advances in Cosmetic Formulations
Polyphenols have found their way into cosmetic formulations due to their antioxidant and protective properties:
- Skin Care Products: Polyphenols are common in creams and lotions, where they help protect the skin from UV damage and improve skin hydration.
- Anti-Aging Effects: These compounds are used for their potential to slow the signs of aging by protecting skin cells from oxidative stress.
Health Implications
Cardiovascular Benefits
Polyphenols are highly regarded for their cardiovascular benefits. They help lower blood pressure and reduce cholesterol levels, which are key factors in cardiovascular disease prevention.
Anti-inflammatory Effects
Both phenols and polyphenols exhibit anti-inflammatory properties, but polyphenols, in particular, are effective in modulating inflammatory pathways in the body, aiding in the management of conditions like arthritis and asthma.
Longevity and Disease Prevention
Regular consumption of polyphenol-rich foods is associated with enhanced longevity and reduced incidence of chronic diseases such as:
- Cancer: Studies suggest that polyphenols can help reduce the risk of various cancers by inhibiting tumor growth and inducing apoptosis in cancer cells.
- Type 2 Diabetes: By improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammatory markers, polyphenols help manage and potentially prevent type 2 diabetes.
Research and Innovations
Latest Studies on Phenols
Recent research has focused on the development of new phenol-based drugs that are more effective and have fewer side effects. Innovations in synthetic chemistry have allowed for the creation of novel phenolic compounds with enhanced therapeutic properties.
Cutting-edge Research on Polyphenols
The latest research on polyphenols explores their use in neuroprotective therapies, particularly for diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. The neuroprotective effects of polyphenols are attributed to their ability to modulate neuronal signaling and protect neural cells from oxidative stress.
Future Directions in Science
The future of phenol and polyphenol research is promising, with ongoing studies aimed at:
- Enhanced Bioavailability: Developing methods to increase the absorption and effectiveness of polyphenols in the body.
- Targeted Therapies: Using phenolic compounds in targeted therapies for more precise treatment of diseases, reducing side effects and improving outcomes.
FAQs
What are Phenols?
Phenols are aromatic compounds containing a hydroxyl group directly attached to a benzene ring. They serve as key intermediates in the production of many industrial chemicals and pharmaceuticals and exhibit antibacterial and antifungal properties.
How do Polyphenols differ from Phenols?
Polyphenols are complex molecules containing multiple phenol units. Unlike simple phenols, polyphenols are primarily found in plants and are major contributors to the antioxidant activity in the human diet, helping to combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Why are Polyphenols important in diet?
Polyphenols are vital due to their role in preventing and managing various chronic diseases through their antioxidant properties. They are linked to reduced risks of heart disease, certain cancers, and other conditions associated with aging and oxidative stress.
Can Phenols be toxic?
While phenols are valuable in many industrial applications, they can be toxic to humans and the environment at high concentrations. Proper handling and usage are critical to avoid adverse health effects.
How are Polyphenols used in cosmetics?
Polyphenols are incorporated into cosmetic products due to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. They help in skin protection, reduction of aging signs, and improvement of skin vitality.
Conclusion
Phenols and polyphenols are pivotal compounds with wide-reaching effects on health and industry. Their distinctive properties not only make them invaluable in medical and industrial applications but also play a crucial role in enhancing dietary benefits through their preventive capabilities against various chronic ailments. As research continues to unfold, the potential for these compounds in new therapeutic and commercial applications looks promising.
Understanding the broad implications of phenols and polyphenols enhances our appreciation of how integral these compounds are to advancing health and technology. Their ongoing study and application hold the key to unlocking further benefits, which may contribute significantly to health advancement and disease prevention strategies in the future.