Phagocytosis and opsonization are two different processes involved in the immune response, but they are often confused for one another. In this blog, we’ll discuss the differences between the two processes and how they work together to protect the body from foreign invaders.
Finally, we’ll discuss how understanding the differences between phagocytosis and opsonization can help scientists develop better treatment and prevention strategies for diseases.
Overview of the mechanisms of phagocytosis
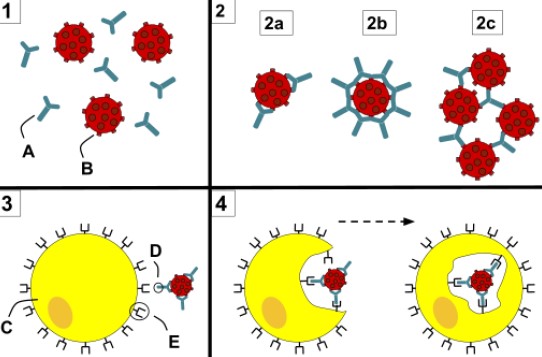
Phagocytosis and opsonization are two very important mechanisms in the human body’s defense against foreign particles. Phagocytosis is the process of engulfing and destroying foreign particles, such as bacteria, by the white blood cells.
On the other hand, opsonization is the process of making foreign particles easier to be engulfed and destroyed by the white blood cells. The main difference between phagocytosis and opsonization is that phagocytosis is the process of engulfing and destroying foreign particles, while opsonization is the process of making foreign particles easier to be engulfed and destroyed. Both of these processes work together to help the body defend itself from harmful particles.
Overview of the mechanisms of opsonization
Opsonization is an important process of the immune system in which cells, bacteria, and other foreign particles are marked for destruction, allowing them to be recognized and engulfed by phagocytic cells such as macrophages. It is a crucial process for the prevention of infections and the maintenance of homeostasis. Although it is closely related to phagocytosis, there are some important differences between the two.
Although it is closely related to phagocytosis, there are some important differences between the two. Opsonization marks the target particle so that it is more easily identified by phagocytic cells, while phagocytosis is the actual process of engulfing and destroying the marked particle. Opsonization helps to increase the efficiency and speed of phagocytosis, as well as to reduce the risk of infections.
How do phagocytosis and opsonization differ

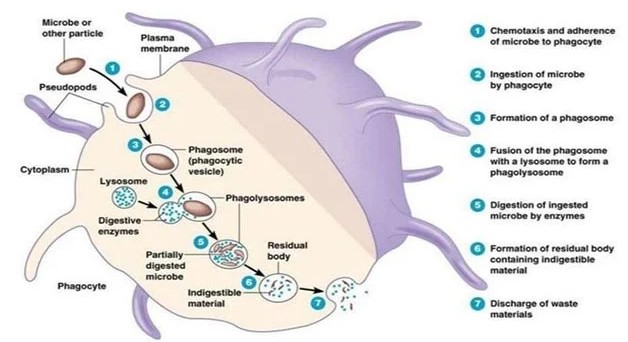
Phagocytosis and opsonization are both part of the body’s immune system and involve the ingestion of foreign particles. However, the two processes differ in several ways. Phagocytosis is the process by which certain cells, called phagocytes, engulf and ingest external particles including bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
The particles are then digested and destroyed, keeping the body safe from infection. On the other hand, opsonization is a process by which antibodies attach to a pathogen in order to make it easier for phagocytes to recognize and ingest it.
The antibodies act as markers, signaling to the phagocytes that the pathogen is a target and needs to be destroyed. Put simply, phagocytosis is the act of engulfing and ingesting, while opsonization is the act of marking and signaling.
Practical applications of phagocytosis and opsonization
The difference between phagocytosis and opsonization may seem subtle at first glance, but understanding the distinction between these two processes is essential for understanding their practical applications. In short, phagocytosis is the process by which a cell engulfs and destroys foreign particles or pathogens, while opsonization is the process by which a cell is able to recognize and bind to an invading particle or pathogen, making it more easily recognized and engulfed by phagocytosis.
Both processes are essential for immune system defense against pathogens and foreign particles. In the case of phagocytosis, an invading particle or pathogen is engulfed by a cell, which then releases lysosomal enzymes that break down and destroy the intruder. Opsonization, on the other hand, works to make the intruder more easily recognized and engulfed by phagocytosis by coating the particle or pathogen with proteins called opsonins.
This coating allows for a more efficient recognition and engulfment of the particle or pathogen by the cell. Together, phagocytosis and opsonization form an important part of the body’s immune system response, helping to protect the body from invading particles and pathogens.
Further resources and references
When we discuss the differences between phagocytosis and opsonization, it is important to understand the importance of each of these processes in our immune system defense. Phagocytosis is the process by which a cell engulfs a particle, such as a bacteria or virus.
On the other hand, opsonization is the process of coating the particle in antibodies, which makes it easier for the cell to recognize, target, and engulf it. In other words, opsonization is used to prepare a particle for phagocytosis. This is a critical step in ensuring our body is able to recognize and eliminate bacteria and viruses, and it is an important part of our immune system’s defense.
Final Touch
In conclusion, the main difference between phagocytosis and opsonization is that phagocytosis involves the engulfment and destruction of foreign particles, while opsonization is the process by which foreign particles are coated with specialized proteins, making them easier to be recognized and destroyed by phagocytes. While both processes are important for the body’s immune system, they have different functions and serve different purposes.