This blog post will explore the differences between PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and real-time PCR (or quantitative PCR). We will look at the different components, methods, and applications of each technique to better understand their respective roles in the laboratory.
Finally, we will compare the two techniques and understand how they can be used together to achieve greater accuracy and precision in research.
Overview of pcr

PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a laboratory technique used to amplify a specific DNA sequence. It works by using enzymes to make multiple copies of a segment of DNA, allowing researchers to study and analyze it further. On the other hand, Real Time PCR (also known as quantitative PCR) is a more advanced version of PCR which uses fluorescent probes and special instruments to measure the amount of DNA present in a sample.
The main difference between PCR and Real Time PCR is that the latter allows researchers to track the progress of their reaction in real time, while the former only allows them to obtain the final results. Additionally, Real Time PCR is more accurate and can be used to detect and quantify the amount of DNA present in a sample.
Overview of real time pcr
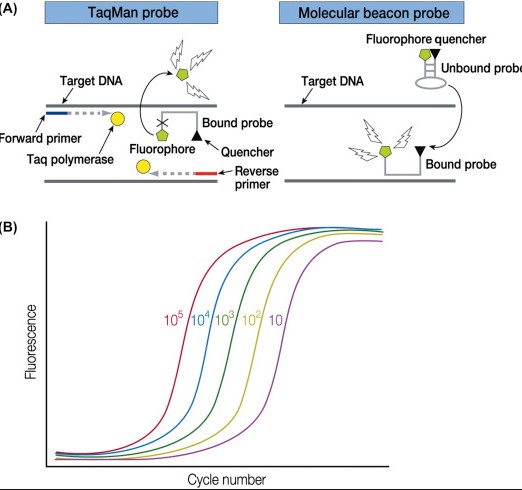
Real-time PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is a laboratory technique used to amplify DNA, which is then used to detect the presence of specific genetic sequences. It’s used to measure the amount of a specific gene or other DNA sequence present in a sample.
The main difference between traditional PCR and real-time PCR is that the latter uses fluorescent probes to detect the presence of the target sequence as the reaction proceeds in real time, while traditional PCR is a qualitative process. Real-time PCR is more sensitive and can detect even small amounts of the target sequence, while traditional PCR is more reliable and robust.
Benefits of real time pcr
Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) is a powerful tool in molecular biology that allows us to detect and measure very small amounts of DNA or RNA in a sample. Unlike traditional PCR, real-time PCR is able to provide quantitative data and can be used to accurately determine the amount of a particular molecule present in a sample.
The main difference between PCR and real-time PCR is that real-time PCR is able to provide quantitative data, meaning that it can measure the exact amount of a molecule present in a sample. This is because real-time PCR uses fluorescent dyes that emit light when the target gene is amplified.
By measuring the intensity of the emitted light, it is possible to calculate the amount of target present in the sample. Real-time PCR also offers a number of other benefits, such as increased sensitivity and accuracy, shorter analysis times, and the ability to detect multiple targets simultaneously. All of these features make real-time PCR an invaluable tool in the molecular biology lab.
All of these features make real-time PCR an invaluable tool in the molecular biology lab.
Applications of pcr and real time pcr

Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (Real-Time PCR) are two powerful tools used in molecular biology labs to amplify and analyze DNA and RNA. PCR is used to make millions of copies of a specific DNA segment, while Real-Time PCR can be used to measure the amount of target DNA or RNA present in a sample. The main difference between PCR and Real-Time PCR is that Real-Time PCR can simultaneously detect and quantify the amount of target DNA or RNA in a sample.
This makes Real-Time PCR ideal for applications such as measuring gene expression, detecting pathogens in clinical samples, and analyzing the sequence of DNA fragments.
Comparison of pcr and real time pcr
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and Real Time PCR (RT-PCR) are both important techniques in the world of molecular biology. While PCR is used for amplifying DNA sequences, RT-PCR has the additional purpose of monitoring DNA amplification in real time. The main difference between the two techniques lies in the detection method; PCR utilizes gel electrophoresis to detect DNA amplification, while RT-PCR uses fluorescent probes or other markers to detect the same.
PCR is a better choice for longer sequences, while RT-PCR works better for shorter sequences. PCR can only detect the presence of a specific sequence, while RT-PCR can also quantify the amount of that sequence in a sample.
PCR is more economical, while RT-PCR is more expensive. Lastly, PCR is more sensitive to contamination and errors, while RT-PCR has a higher sensitivity to minimize contamination and errors.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, PCR and real-time PCR are both techniques used to amplify and detect specific sequences of DNA. The main difference between PCR and real-time PCR is that PCR requires the DNA to be separated by gel electrophoresis to view the results, while real-time PCR provides results in real-time with fluorescence detection.
Both techniques are used in the field of molecular biology and are invaluable tools for research and medical diagnosis.

