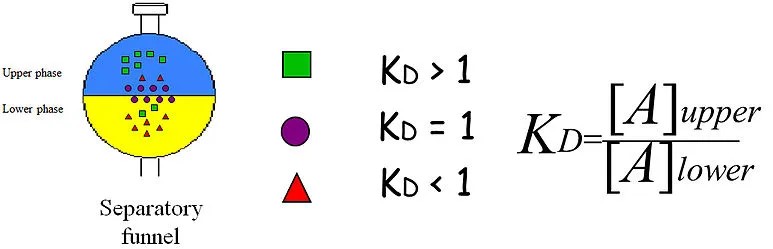
Partition coefficient and distribution coefficient are two terms often used in the field of chemistry, but they are not the same. This blog will explain the difference between these two terms, and provide examples of each to help better understand their meanings.
Definition of partition coefficient

Partition coefficient and distribution coefficient are both important parameters used in chemistry to measure the affinity of a substance for a solvent. Partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a solute in a given solvent, relative to its concentration in another solvent. Distribution coefficient, on the other hand, is the ratio of the concentration of a solute between two immiscible solvents, such as aqueous and organic phases.
In simpler terms, the partition coefficient measures the ability of a solute to move between two solvent phases, while the distribution coefficient measures the ability of a solute to move between two immiscible solvents.
Definition of distribution coefficient
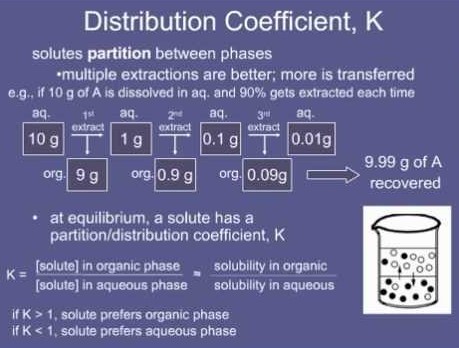
Distribution coefficient is a measure of the relative solubility of a substance in two different immiscible phases. It is also known as the partition coefficient and is the ratio of the concentration of a compound in one phase to its concentration in the other phase.
The difference between partition coefficient and distribution coefficient is that the partition coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of a compound in one phase to its concentration in the other phase, while the distribution coefficient is the ratio of the concentration of the compound in both phases.
Difference between partition coefficient and distribution coefficient
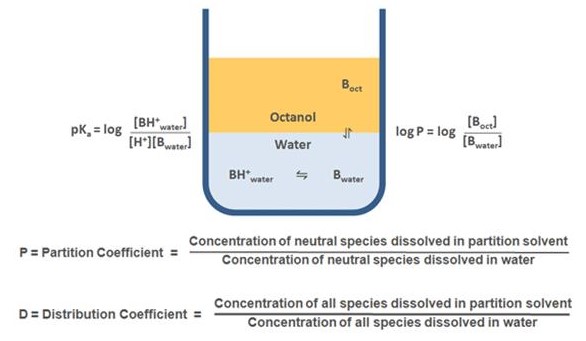
Partition and distribution coefficients are two important concepts in chemistry. The main difference between them is that partition coefficient refers to the ratio of concentrations of a solute between two immiscible phases, while distribution coefficient is the ratio of concentration of a solute between a solid and liquid phase.
Distribution coefficient, on the other hand, is used to describe how soluble a solute is in a solid phase compared to a liquid phase. This is determined by calculating the ratio of the solute in the solid phase to the solute in the liquid phase.
Benefits of knowing the difference between partition coefficient and distribution coefficient
When it comes to chemical properties, it is important to understand the difference between partition coefficient and distribution coefficient. Partition coefficient is a measure of how a compound distributes itself between two immiscible phases, such as an aqueous and organic phase. On the other hand, distribution coefficient is a measure of how a compound distributes itself between two miscible phases, such as two different aqueous solutions.
On the other hand, distribution coefficient is a measure of how a compound distributes itself between two miscible phases, such as two different aqueous solutions. Both these coefficients are essential in order to accurately calculate the amount of solute that will be present in each phase in any given system. Knowing the difference between these two coefficients is key to understanding the behavior of chemicals in different mixtures.
Examples of partition coefficient and distribution coefficient
Partition coefficient and distribution coefficient are two terms that are often confused. Although they sound similar, they are actually quite different.
Partition coefficient is a measure of the relative solubility of a compound between two immiscible phases, such as water and oil. Distribution coefficient, on the other hand, is the ratio of the concentration of the compound in the two phases of a mixture. An example of a partition coefficient is the octanol-water partition coefficient (KOW), which is a measure of the relative solubility of a compound between octanol and water.
An example of a distribution coefficient is the n-octanol/water distribution coefficient (KD), which is the ratio of the concentration of a compound in n-octanol and water.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, the difference between partition coefficient and distribution coefficient is that partition coefficient is a measure of the relative solubility of a compound in two different immiscible solvents, while distribution coefficient is a measure of the relative concentrations of a compound between two phases, such as aqueous and organic. Partition coefficient is more relevant for solubility and distribution coefficient is more relevant for distribution. Both coefficients are useful for understanding the physical and chemical behavior of compounds in different solvents and phases.