Plants exhibit an array of fascinating structures that play critical roles in their survival and reproduction. Among these, the operculum and peristome stand out as features specific to certain plant groups, each serving unique functions. These structures are not only essential for the biological success of these plants but also intrigue botanists and plant enthusiasts alike due to their complex nature and evolutionary significance.
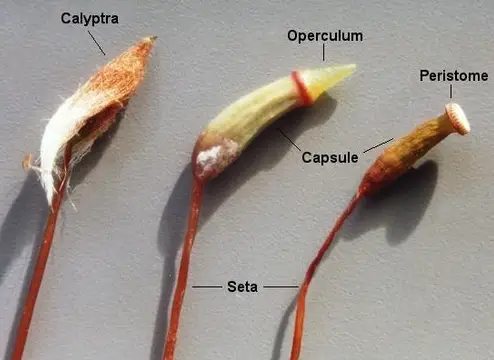
The operculum and peristome are distinct structures found in different groups of plants. The operculum, primarily observed in mosses, acts as a cap that covers the spore capsule and falls off when the spores are ready to be dispersed. In contrast, the peristome, which is also a feature of some mosses, surrounds the mouth of the capsule and consists of tooth-like structures that aid in the gradual release of spores.
These structural features are pivotal for the reproductive strategies of the plants that possess them. While they might seem minor, the operculum and peristome play key roles in protecting and dispersing spores, which ensures the proliferation and survival of their species across various environments. Their design and functionality not only reflect the ecological adaptability of these plants but also highlight their evolutionary innovation.
Operculum Explained
Definition and Function
The operculum is a critical structure in the reproductive system of certain plants, particularly mosses and some ferns. Essentially, it serves as a protective cap that covers the spore capsules of these plants. Its primary function is to shield the developing spores from environmental hazards, such as harsh weather and pests, until they are ready to be released into the environment. Once the spores mature, the operculum detaches, facilitating their dispersal by wind or water.
Types of Opercula in Different Plants
Opercula vary significantly across different plant species, adapting to their specific environmental and reproductive needs:
- Mosses: In mosses, the operculum is typically dome-shaped and snaps off from the capsule in a lid-like fashion. This is crucial for the timing of spore release, which is often synchronized with favorable environmental conditions.
- Certain Ferns: Some fern families, like the Polypodiaceae, exhibit opercula that assist in managing moisture levels around the spore cases, although they are structurally different from those in mosses.
Role in Plant Survival and Reproduction
The operculum plays a pivotal role in the survival and propagation of plants by ensuring that spores are only released when they have the best chance of survival and successful germination. This strategic release helps maintain the species’ population and facilitates colonization of new areas, which is essential for ecological resilience and adaptation.
Peristome Detailed
Definition and Characteristics
A peristome is another specialized structure found in some plants, notably in many moss species. It consists of a ring of teeth-like structures that line the mouth of the spore capsule. These teeth are hygroscopic, meaning they respond to humidity changes, which allows them to control the release of spores based on the moisture in the air.
Variations Across Plant Species
The structure and functionality of the peristome can vary widely among different plant species:
- Mosses: In mosses, peristomes can be simple, with a single ring of teeth, or complex, featuring multiple rings of teeth that can move in response to environmental conditions.
- Adaptation to Environment: The variations often reflect adaptations to specific climatic conditions, with certain designs better suited to moist environments and others to drier ones.
Functionality in Seed Dispersal
The peristome’s design ingeniously regulates spore dispersal. The teeth move in response to humidity, opening to release spores when conditions are dry (favorable for dispersal) and closing when it is wet (to prevent spore loss). This responsiveness ensures that spores have the best chance of landing in environments where they can thrive, which is crucial for the reproductive success of the plant.
Comparative Analysis
Structural Differences
While both operculum and peristome are involved in spore dispersal, their structures are fundamentally different:
- Operculum: Typically acts as a simple lid that detaches completely to open the spore capsule.
- Peristome: Consists of a complex arrangement of teeth that can actively respond to environmental stimuli.
Functional Contrasts
The functionality of these structures also differs significantly:
- Operculum: Its function is mainly protective, keeping the spores safe until they are ready for dispersal.
- Peristome: Plays a more active role in managing the timing and pattern of spore release, adapting to environmental conditions to maximize dispersal efficiency.
Ecological Significance
The ecological roles of the operculum and peristome are vital for the propagation and survival of plant species:
- Operculum: Ensures that spores are mature and ready for dispersal, contributing to the genetic diversity and spread of the plant.
- Peristome: Enhances the likelihood of spore survival by regulating dispersal, crucial for colonization in new and potentially hostile environments. This adaptability is key to ecological succession and diversity.
Evolutionary Perspectives
Evolutionary Development of Operculum
The evolution of the operculum in plants represents a significant adaptation to terrestrial life. Fossil records suggest that the operculum developed as plants transitioned from aquatic to terrestrial environments, where spore dispersal became increasingly challenging due to the absence of water currents. This evolutionary adaptation helped ensure that spores could still be effectively released and dispersed by air currents, even in dry conditions.
- Early Land Plants: Among the earliest land plants, the development of a protective operculum helped guard spores against desiccation and physical damage, enabling them to survive in harsh terrestrial climates.
- Adaptive Advantage: The operculum provided these pioneering plants with a competitive edge, allowing them to colonize new territories far from water bodies.
Evolutionary Development of Peristome
Similarly, the peristome is a product of evolutionary innovation, particularly among mosses. Its development is closely tied to the need for precise spore release mechanisms in environments where wind patterns and humidity could greatly influence spore dispersal success.
- Hygroscopic Properties: The hygroscopic nature of peristome teeth, which open and close in response to moisture changes, represents an advanced evolutionary trait that optimizes spore dispersal timing based on environmental conditions.
- Evolutionary Refinement: Over millions of years, these structures have evolved to become more complex and efficient, responding to even slight changes in environmental moisture.
Comparative Evolutionary Advantages
Both operculum and peristome offer distinct evolutionary advantages that have played crucial roles in the survival and expansion of species equipped with these structures:
- Operculum: Provides physical protection and a controlled release mechanism for spores, critical in preventing premature dispersal and ensuring spore viability.
- Peristome: Enhances dispersal efficiency by leveraging environmental conditions, thus maximizing the potential for colonization in suitable habitats.
Practical Implications
Importance in Taxonomy and Identification
The presence and characteristics of operculum and peristome are not only fascinating from an evolutionary standpoint but also have practical implications in the field of taxonomy:
- Species Differentiation: These features are key to identifying and classifying different species of mosses and certain ferns. Detailed examination of operculum and peristome structures can reveal subtle differences that define specific taxa.
- Taxonomic Keys: Botanists use these structures as critical elements in taxonomic keys, aiding in the accurate identification and classification of plant species within ecological studies and herbarium management.
Implications for Horticulture and Conservation
In horticulture and conservation, understanding the role of operculum and peristome can greatly impact the cultivation and preservation of species:
- Seed Germination and Growth: Knowledge of spore dispersal mechanisms helps in creating optimal growing conditions in nurseries and restoration projects.
- Conservation Strategies: Effective management practices for rare or endangered moss species often depend on an understanding of their reproductive biology, including spore dispersal and viability.
Use in Research and Studies
The study of operculum and peristome structures extends beyond basic botanical interest, contributing to broader scientific research:
- Ecological Studies: These features are studied to understand plant community dynamics, ecological succession, and the adaptive strategies of plants in varying climates.
- Climate Change Research: Changes in operculum and peristome function can indicate shifts in environmental conditions, serving as biological indicators in climate change studies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Operculum?
The operculum in plants is a lid-like structure that covers the spore capsules, particularly in mosses. It serves to protect the developing spores from environmental factors until they are mature enough to be released, at which point the operculum detaches to allow spore dispersal.
How Does a Peristome Help in Spore Dispersal?
A peristome enhances spore dispersal through its intricate structure of teeth or segments that respond to humidity changes. This responsiveness allows the peristome to control the release of spores, ensuring they are dispersed under optimal environmental conditions to maximize survival chances.
Are Operculum and Peristome Found in All Plants?
No, opercula and peristomes are not found in all plants but are specific to certain groups of non-flowering plants, primarily mosses. These structures are adapted to the life cycles and reproductive strategies of these plants, playing crucial roles in spore dispersal.
Can the Presence of an Operculum or Peristome Identify Plant Species?
Yes, the presence and specific characteristics of an operculum or peristome can help in identifying plant species, especially among mosses. Botanists use these features to classify and differentiate species within similar groups based on their distinct structural adaptations.
Conclusion
The operculum and peristome are exemplary of nature’s ingenuity in plant evolution. These structures not only fulfill essential biological functions by aiding in spore protection and dispersal but also offer key insights into the adaptive strategies of mosses within their ecosystems. Their study reveals much about the evolutionary pressures that have shaped plant life on Earth.
Understanding these plant parts enhances our appreciation of biodiversity and the complexity of plant life forms. As we continue to study these and other botanical features, we gain further insights into the delicate balance of ecosystems and the intricate relationships that sustain plant communities across the globe.