The flash point of a combustible liquid is an important safety measure, and it’s important to know the difference between open cup and closed cup flash point tests. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the differences between these two types of flash point tests, and the advantages and disadvantages of each. We’ll also provide some tips for ensuring the accuracy of your flash point tests.
By the end of this post, you’ll have a better understanding of which flash point test is the right choice for your needs.
Open cup vs closed cup flash point

The difference between an open cup and closed cup flash point is an important distinction in the world of combustible materials. In basic terms, the open cup flash point is the lowest temperature at which a liquid gives off enough vapor to ignite when exposed to a flame. The closed cup flash point is the lowest temperature at which the vapor of a liquid is ignitable in an enclosed container.
This distinction is important when assessing the risk and safety of combustible materials, as the open cup flash point is generally lower than the closed cup flash point. Knowing this information can help to determine the best practices for storing and handling combustible materials, ensuring a safe and secure environment.
Advantages and disadvantages of open cup flash point
The open cup and closed cup flash point tests are two common methods used to measure the flash point of a material, or the temperature at which it ignites and forms a flame. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. The open cup method is best used for volatile liquids, since it exposes the liquid to the air, thus allowing it to reach its flash point more quickly.
The open cup method is best used for volatile liquids, since it exposes the liquid to the air, thus allowing it to reach its flash point more quickly. However, it can be difficult to control the conditions of the test, as the environment can affect the accuracy of the results. The closed cup method is best used for materials with a high flash point, as the liquid is contained in an environment with limited oxygen, which prevents it from igniting prematurely.
However, it can take longer to reach the flash point, as the heat must be applied for a longer period of time. Ultimately, the choice of method depends on the material being tested and the accuracy of the results required.
Advantages and disadvantages of closed cup flash point
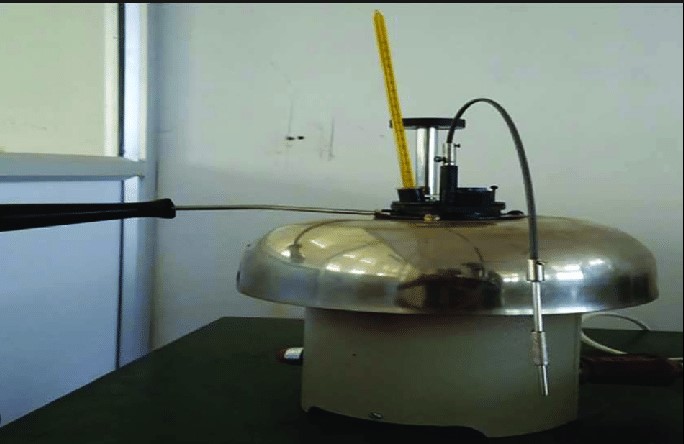
Closed cup and open cup flash points are two of the most widely used methods of determining the flash point of a combustible liquid. While both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, there are some notable differences between the two.
Closed cup flash point is the temperature at which a combustible liquid gives off sufficient vapor to form an ignitable mixture with air, near the surface of the liquid. The sample is heated in a closed cup and the temperature is observed when a small flame is applied to the cup. Open cup flash point is the temperature at which a combustible liquid gives off sufficient vapor to form an ignitable mixture with air, away from the surface of the liquid.
The sample is heated in an open cup and the temperature is observed when a small flame is applied to the cup. The main difference between the two methods is that open cup flash point is generally a higher temperature than closed cup flash point.
This is because the combustible vapors are more easily dispersed away from the surface of the liquid in an open cup. The advantage of closed cup flash point is that it is a more accurate method of measuring the flash point, since the vapors are more concentrated near the surface of the liquid. The disadvantage of closed cup flash point is that it is a slower method of determining the flash point, as it requires more heating time.
Open cup flash point is faster to measure, but is less accurate than closed cup flash point.
Factors to consider when choosing between open cup or closed cup flash point
When it comes to testing the flash point of a substance, there are two primary methods: open cup and closed cup. Knowing the difference between the two methods is important when deciding which one is best for your needs. Open cup flash point testing involves applying a flame to the sample in an open vessel, while closed cup flash point testing involves heating the sample within an enclosed vessel.
The open cup method is the most common and widely accepted method for determining flash point, as it is the simplest and most straightforward. However, the open cup method may not be suitable for certain samples, such as highly volatile samples, as the flame could cause a rapid and dangerous increase in pressure.
Additionally, samples with a high boiling point and high viscosity are more likely to have an inaccurate result when tested with the open cup method. The closed cup method is more suitable for these types of samples, as the closed vessel prevents the flame from coming into contact with the sample directly.
Additionally, the closed cup method is usually more accurate and is more suitable for testing samples with a low flash point. When choosing between the open cup and closed cup flash point testing method, it is important to consider the sample and the desired accuracy.
Open cup flash point testing is simple and straightforward, but may not be suitable for certain samples. Closed cup flash point testing is more accurate and is better for samples with a low flash point. Ultimately, the choice should depend on the specific needs of the test.
Common uses of open cup and closed cup flash point
The difference between open cup and closed cup flash point testing is a common question in the field of petroleum testing. In a nutshell, the open cup flash point is the temperature at which a substance can combust and ignite when exposed to open air, while the closed cup flash point is the temperature at which a substance can combust and ignite when exposed to a closed environment.
Generally, the closed cup flash point is higher than the open cup flash point, as the closed environment reduces the risk of accidental ignition. Open cup flash point testing is often used in the production and storage of combustible substances, while closed cup flash point testing is the preferred method for testing fuels.
Final Touch
In conclusion, the difference between open cup and closed cup flash points is that the open cup flash point is the temperature at which a combustible liquid gives off enough vapor to form an ignitable mixture with the air near the surface of the liquid, while the closed cup flash point is the temperature at which a combustible liquid gives off enough vapor to form an ignitable mixture with the air within a container. Open cup flash points are generally considered more accurate than closed cup flash points as the container can alter the flash point of the sample.

