Peptides play a crucial role in various biological processes and have significant therapeutic potential. These small chains of amino acids are fundamental to the structure and function of living organisms, varying in size and complexity. Their diversity allows for a wide range of functions, from hormonal regulation to immune responses, making them essential for understanding life at the molecular level.
The difference between oligopeptides and polypeptides lies primarily in the number of amino acids they contain. Oligopeptides are short chains composed of 2 to 20 amino acids, whereas polypeptides are longer, containing more than 20 amino acids. This distinction is not just numerical but impacts their structure, function, and role in biological systems and therapeutic applications.
Focusing on oligopeptides and polypeptides reveals insights into how proteins are structured and function within our bodies. These molecules orchestrate a myriad of biological activities, from catalyzing biochemical reactions to serving as building blocks for larger protein complexes. Understanding their differences enriches our knowledge of biological processes and opens avenues for biomedical innovations.
Peptide Basics
Peptide Definition
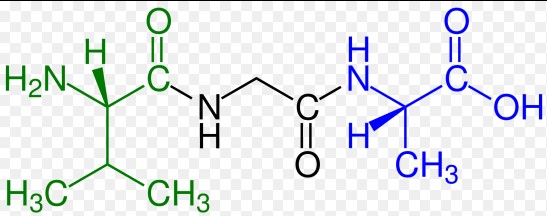
At the heart of biological processes and therapeutic development lies a fundamental class of molecules known as peptides. Peptides are chains of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds, a type of covalent bond that forms when the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another, releasing a molecule of water in the process. This formation is crucial for various biological functions, ranging from cell signaling to immunological responses. Their size and complexity can vary, but all peptides share this basic structural framework.
Types of Peptides
Peptides are categorized based on their size and the number of amino acids they contain. This classification includes:
- Dipeptides: Consist of two amino acids.
- Tripeptides: Made up of three amino acids.
- Oligopeptides: Contain 2 to 20 amino acids.
- Polypeptides: Comprise more than 20 amino acids, potentially reaching up to several hundred.
Each type plays distinct roles within the body, influencing a wide range of biological and chemical functions.
Oligopeptides Explained
Oligopeptide Characteristics
Oligopeptides are small peptides that consist of 2 to 20 amino acids. This size range allows them to be relatively simple in structure yet versatile in function. They are small enough to be synthesized relatively easily and can penetrate cells to exert their effects. The small size of oligopeptides impacts their solubility, stability, and biological activity, making them particularly interesting for both research and therapeutic use.
Oligopeptide Functions
Oligopeptides are essential in numerous biological processes and have significant therapeutic potential. Their roles include:
- Hormonal regulation: Acting as hormones or hormone-releasing factors.
- Signal transduction: Facilitating or inhibiting signals between cells.
- Immune responses: Participating in the body’s defense mechanisms.
- Enzyme function: Acting as substrates, inhibitors, or activators of enzymes.
Their ability to influence such processes makes oligopeptides critical targets and tools in biomedical research and drug development.
Polypeptides Explained
Polypeptide Characteristics
Polypeptides, with their greater than 20 amino acids, represent a more complex category of peptides. They can fold into specific three-dimensional structures, determined by their amino acid sequence, which dictates their function within an organism. This complexity allows them to perform a wide variety of functions, from catalysis to structural support in cells and tissues. The physical and chemical properties of polypeptides, such as their shape, charge, and hydrophobicity, play crucial roles in their biological functions.
Polypeptide Functions
Polypeptides are indispensable for cellular mechanisms and overall health, involved in:
- Structural roles: Providing support and shape to cells and tissues.
- Enzymatic activity: Catalyzing biochemical reactions essential for life.
- Transport and storage: Binding and carrying atoms and small molecules within cells.
- Signaling: Facilitating communication between cells and within cells.
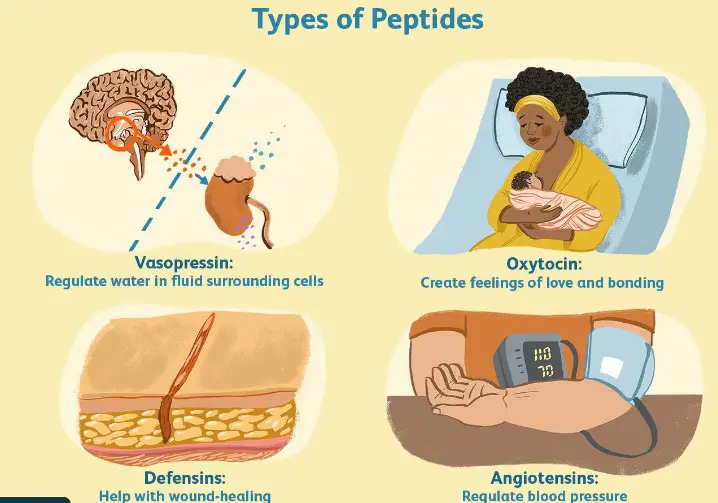
Key Differences
Size and Structure
The fundamental difference between oligopeptides and polypeptides lies in their size and structural complexity. Oligopeptides, composed of 2 to 20 amino acids, are relatively small and have a simpler structure. This simplicity often results in a linear shape, although they can also adopt limited secondary structures, such as alpha-helices or beta-sheets, under specific conditions. On the other hand, polypeptides, with more than 20 amino acids, exhibit a higher level of complexity. They can fold into intricate three-dimensional structures, which are stabilized by various interactions, including hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions. This complex folding is critical for their biological function, as the specific shape of a polypeptide determines its interaction with other molecules.
Biological Roles
Oligopeptides and polypeptides serve distinct yet equally important roles in biology, reflective of their size and complexity. Oligopeptides often function in signaling and regulatory roles. Their small size allows them to quickly and efficiently mediate and modulate biological processes, such as hormone release, pain perception, and immune responses. In contrast, polypeptides’ larger size and structural versatility enable them to take on more varied functions. They can act as enzymes, facilitating nearly all types of chemical reactions in the body, or as structural proteins, providing support and shape to cells and tissues. Additionally, polypeptides can function in transport, storage, and signaling within complex biological systems.
Therapeutic Uses
The differences in size, structure, and biological roles between oligopeptides and polypeptides extend to their therapeutic applications. Oligopeptides, due to their small size and ease of synthesis, are often used in drug design and development. They can mimic or inhibit natural biological molecules, making them effective in treatments for conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and various types of cancer. Oligopeptides can be engineered to cross cellular membranes, delivering therapeutic agents directly to their sites of action. Polypeptides, given their complexity, have been utilized in creating more sophisticated therapies, such as enzyme replacement therapies for genetic disorders or as vaccines. Their ability to fold into specific shapes also allows for the development of antibody therapies, where they can bind to and neutralize pathogens or diseased cells.
Importance in Research
Biomedical Research
Understanding the distinct characteristics and functions of oligopeptides and polypeptides is paramount in biomedical research. This knowledge aids in elucidating the molecular basis of diseases, which is essential for developing effective treatments and drugs. For instance, research into oligopeptides has led to the development of numerous peptide-based drugs that target specific cellular pathways with high precision and minimal side effects. Similarly, insights into the structure and function of polypeptides have paved the way for the creation of recombinant proteins, including hormones and vaccines, that have revolutionized the treatment of chronic diseases and infections. The study of peptides also contributes to the development of diagnostic tools, enabling early detection and monitoring of diseases at the molecular level.
Technological Advances
The ongoing advancements in peptide research have significantly impacted the development of new therapeutics. Technological innovations in peptide synthesis, sequencing, and analysis have dramatically expanded the potential of peptides as therapeutic agents. High-throughput screening and peptide library technologies have accelerated the discovery of peptides with desirable therapeutic properties. Moreover, advancements in bioinformatics and computational biology have enhanced the ability to design and optimize peptides for specific therapeutic targets. This has led to the development of peptide-based drugs with improved efficacy, stability, and bioavailability. Additionally, the integration of peptides with nanotechnology has opened new avenues for targeted drug delivery systems, offering promising strategies for treating complex diseases with precision medicine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are peptides?
Peptides are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. They are classified based on the number of amino acids they contain. Short chains of fewer than 10 amino acids are usually referred to as oligopeptides, while longer chains are known as polypeptides, which can fold into complex structures to form proteins.
How do oligopeptides differ from polypeptides?
Oligopeptides consist of 2 to 20 amino acids, making them smaller and often less structurally complex than polypeptides, which contain more than 20 amino acids. This size difference affects their biological roles and physical properties, with oligopeptides often participating in signaling and regulatory functions, while polypeptides may act as enzymes, structural components, or signaling molecules.
Why are peptides important in research and medicine?
Peptides are crucial for research and medicine due to their versatility and specificity in biological processes. Their ability to mimic or block biological signals makes them valuable in developing new therapies for a variety of conditions, including metabolic disorders, infections, and cancer. Additionally, their study enhances our understanding of life at a molecular level, contributing to advancements in biotechnology and pharmaceutical sciences.
Conclusion
The distinction between oligopeptides and polypeptides extends beyond mere numerical differences, touching upon fundamental aspects of biological organization and function. This differentiation not only provides a deeper understanding of protein structure and function but also opens new pathways for the development of targeted therapeutic strategies. By exploring the unique characteristics and roles of these peptides, researchers continue to uncover the complex tapestry of life at the molecular level.
Recognizing the significance of oligopeptides and polypeptides in biology and medicine underscores the importance of molecular biology in contemporary science. As research progresses, the potential for peptides in therapeutic applications continues to expand, promising innovative treatments for a broad spectrum of diseases. This growing knowledge enriches our comprehension of life’s molecular mechanisms, paving the way for future scientific and medical breakthroughs.