Synthetic rubber has become indispensable in modern industry, with Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) and Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) being two of the most crucial types. These elastomers are valued for their unique properties and are deployed in numerous applications ranging from automotive to oil and gas sectors. By exploring their characteristics and differences, industries can make informed choices suited to specific needs.
NBR is a synthetic rubber made from acrylonitrile and butadiene, known for its good resistance to oil, while HNBR is an enhanced version of NBR, offering superior resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals. The main difference between NBR and HNBR lies in their resistance to environmental factors, which directly influences their performance and longevity in harsh conditions.
The significance of choosing the right type of synthetic rubber cannot be overstated, especially in critical applications. Both NBR and HNBR hold pivotal roles in manufacturing due to their versatile properties, but the decision to use one over the other should be based on specific industry requirements and environmental conditions.
What is NBR?
Definition and Production
Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR), also known as Buna-N, is a synthetic rubber copolymer derived from acrylonitrile and butadiene. The production of NBR involves a process known as emulsion polymerization where these two monomers are emulsified in water with catalysts and a surfactant. The resulting copolymer is then precipitated, dried, and rolled into sheets or formed into pellets. This method allows for the precise adjustment of the acrylonitrile content, which directly influences the rubber’s resistance to oils and fuels.
Key Properties of NBR
NBR is celebrated for its excellent resistance to oils and greases. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -40 to 108 degrees Celsius, making it suitable for various industrial applications. The rubber’s composition provides superior resistance to aliphatic hydrocarbons and other chemicals. It is also known for its good abrasion and compression set resistance, essential for dynamic seals and gaskets.
Common Uses in Industry
NBR finds widespread use across multiple sectors:
- Automotive: for fuel and oil hoses, gaskets, and seals.
- Manufacturing: as conveyor belts and other components requiring chemical resistance.
- Oil and Gas: for O-rings and valve seals exposed to harsh environments.
What is HNBR?
Explanation of HNBR
Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (HNBR) is an advanced form of NBR. It is produced by hydrogenating NBR rubber to reduce unsaturated bonds in the butadiene component of the polymer. This modification significantly enhances the material’s thermal stability and strength, extending its use to more demanding applications.
Distinctive Properties
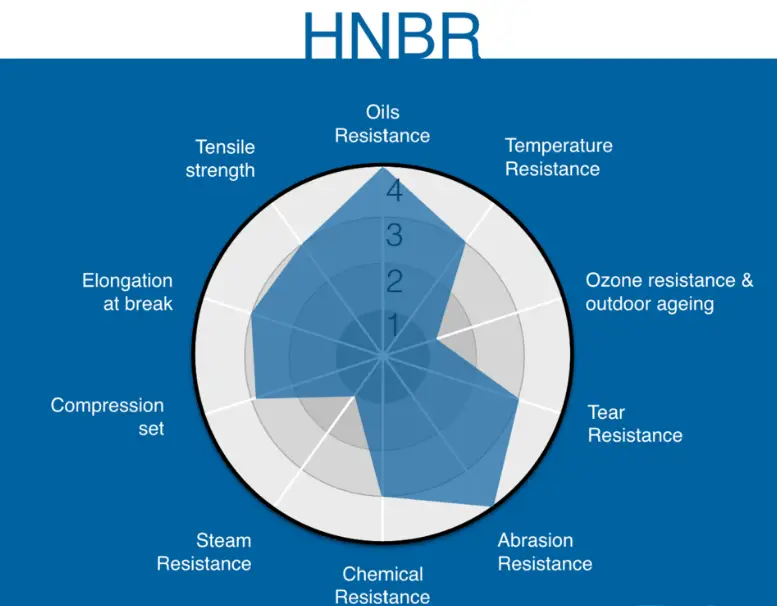
HNBR stands out due to its improved resistance to heat, up to 150 degrees Celsius, and chemicals, including oils, fuels, and various solvents. Its enhanced strength and oxidation resistance make it ideal for dynamic conditions where regular NBR might fail.
Industrial Applications
HNBR’s properties make it especially useful in:
- Automotive: for timing belts and engine seals.
- Oil and Gas: in blowout preventers and drilling equipment.
- Construction: for window and door seals exposed to extreme environments.
Production Differences
NBR Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of NBR includes:
- Polymerization: Acrylonitrile and butadiene are polymerized.
- Recovery: The polymer is recovered as a crumb, washed, and dried.
- Compounding: Additives are mixed in to enhance properties like elasticity or resistance.
HNBR Manufacturing Enhancements
HNBR’s production builds upon NBR’s by adding a hydrogenation step. This process involves:
- Hydrogenation: Saturating the NBR polymer to improve its temperature and chemical resistance.
- Post-treatment: Further curing and stabilization to prepare HNBR for extreme uses.
Property Comparison
Temperature Resistance
- NBR: Suitable for temperatures between -40 to 108 degrees Celsius.
- HNBR: Handles up to 150 degrees Celsius without degradation.
Oil and Chemical Resistance
- NBR: Excellent resistance to oils and mild chemicals.
- HNBR: Even greater resistance, including to harsh chemicals and ozone.
Physical Durability
- NBR: Good for applications where abrasion and compression resistance are needed.
- HNBR: Superior strength and durability, suitable for high-stress environments.
Performance in Industries
Automotive Applications
NBR and HNBR are essential in the automotive sector due to their oil and fuel resistance qualities. NBR is commonly used for manufacturing fuel hoses, O-rings, and gaskets because it performs well in moderate temperatures and conditions. HNBR, on the other hand, is utilized in more demanding parts such as engine seals and timing belts due to its superior heat and chemical resistance. This allows vehicles to operate efficiently in harsher conditions without component failure.
Oil and Gas Sectors
In the oil and gas industry, the requirements for rubber materials are stringent due to extreme conditions. HNBR is favored for its excellent resistance to sour gas, ozone, and oxidized fuels, making it ideal for sealing solutions in drilling and extraction equipment. NBR is also used but typically in less critical applications where extreme temperatures and chemicals are not present. The selection heavily depends on the resilience required to avoid downtime and equipment failure.
Comparison in Consumer Products
In consumer products like footwear, adhesives, and sportswear, NBR is often chosen for its balance of cost and performance, particularly where oil resistance is necessary but extreme conditions are not encountered. HNBR is used in more specialized products that must endure rigorous use or exposure, such as in protective equipment and high-performance gear.
Advantages of HNBR over NBR
Enhanced Performance Features
HNBR’s main advantages over NBR include:
- Higher temperature tolerance: HNBR can withstand environments where temperatures reach up to 150 degrees Celsius.
- Better chemical resistance: Provides durability in aggressive chemical exposures, such as in oil wells and industrial cleaning processes.
- Improved mechanical properties: Offers better tensile strength and elongation before break, making it suitable for dynamic systems under mechanical stress.
Longevity and Reliability
HNBR’s enhanced properties directly translate to longer life and reliability, which are critical in applications where failure can lead to significant operational disruptions and financial losses. This durability also means fewer replacements and maintenance needs, contributing to cost savings over time, despite the higher initial investment.
Cost Implications
Cost Comparison of NBR and HNBR
While NBR is less expensive to produce and purchase, HNBR’s cost is justified by its extended lifespan and ability to operate in more severe conditions. The decision between using NBR or HNBR should consider not just the initial cost but the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, replacement, and potential downtime costs.
Factors Affecting Prices
The prices of NBR and HNBR are influenced by:
- Raw material costs: Fluctuations in the prices of acrylonitrile and butadiene.
- Production complexities: Hydrogenation of NBR to produce HNBR involves additional processes and costs.
- Market demand: Higher demand for specific properties can drive up prices.
Environmental Impact
Ecological Considerations
Both NBR and HNBR are synthetic and their production involves petrochemicals, which have ecological impacts. However, the industries are moving towards more sustainable practices, including better catalysts and greener manufacturing processes.
Recycling and Disposal of NBR and HNBR
Recycling practices for both rubbers include mechanical grinding to reuse as filler or energy recovery through incineration. Proper disposal is crucial to minimize environmental impact, with ongoing research into more sustainable disposal methods and the development of bio-based alternatives.
Selecting Between NBR and HNBR
Factors to Consider
Choosing between NBR and HNBR should be based on:
- Application requirements: Temperature and chemical exposure.
- Cost-effectiveness: Considering both initial and long-term costs.
- Environmental policies: Compliance with regulations and sustainability goals.
Guidance for Specific Applications
- For moderate conditions: NBR is sufficient and cost-effective.
- For extreme environments: HNBR is recommended due to its enhanced properties and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is NBR used for?
NBR, or Nitrile Butadiene Rubber, is commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries for making oil-resistant gaskets, hoses, and seals. It’s also popular in the manufacture of gloves and other protective gear due to its resistance to oils, fuels, and other chemicals.
How is HNBR different from NBR?
HNBR, or Hydrogenated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber, differs from NBR in its enhanced resistance to heat, oil, and chemicals due to the hydrogenation process. This makes HNBR more suitable for harsher environments and demanding applications, such as in the oil and gas industry where thermal and chemical stability is crucial.
What factors affect the choice between NBR and HNBR?
The choice between NBR and HNBR typically depends on the operational environment and the specific properties required. Key factors include temperature extremes, exposure to chemicals, and the need for durability. Cost and environmental impact may also influence the decision.
Can NBR and HNBR be recycled?
Both NBR and HNBR can be recycled, though the process and efficiency vary. Recycling methods include grinding the rubber into powder for reuse in other products, promoting environmental sustainability and reducing waste.
Conclusion
The decision between using NBR and HNBR is more than just a choice between materials; it represents a critical decision point in the design and longevity of industrial components. Each type of synthetic rubber offers unique benefits tailored to specific environmental and operational demands.
By understanding their distinct properties and the specific applications they are best suited for, industries can optimize performance and cost-effectiveness. Choosing the right material not only ensures the durability and efficiency of products but also supports sustainability efforts in rubber production and recycling.


Want regular updated on journals