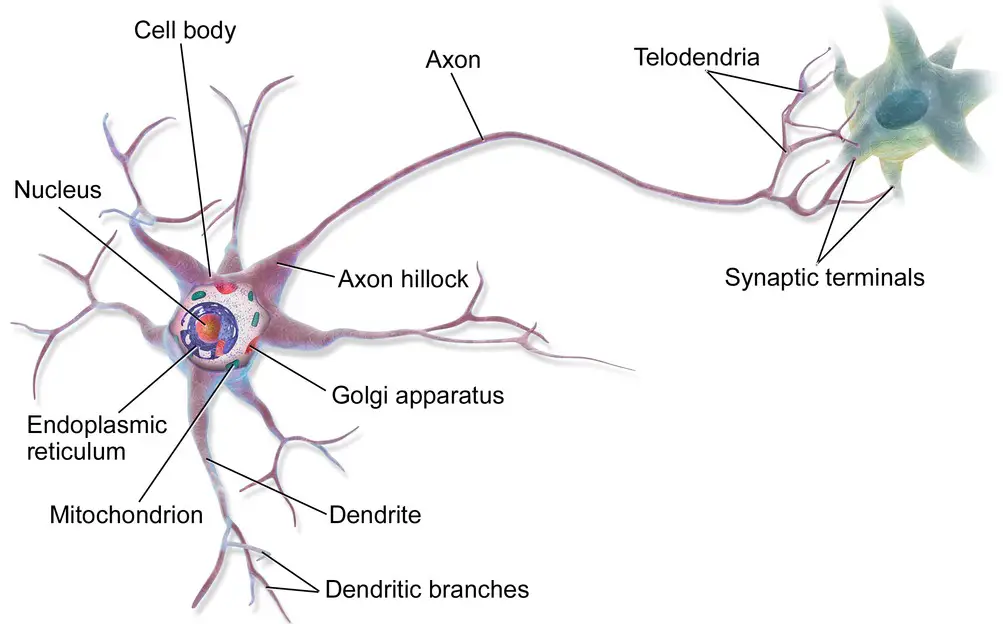
Neurons are the basic building blocks of the nervous system and are responsible for communication between different parts of the body. Understanding the differences between multipolar, bipolar, and unipolar neurons is essential for understanding how the nervous system works.
Structure and function of multipolar neurons

Multipolar neurons are the most common type of neuron in the human body, and they come in three varieties: unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar. Each type of neuron has a unique structure and function.
Bipolar neurons, on the other hand, have two axons that extend from the cell body and branch into several dendrites. Finally, multipolar neurons have many axons that extend from the cell body and branch into numerous dendrites.
The difference between these neurons lies in the way they transmit signals. Unipolar neurons transmit signals from a single point, while bipolar neurons transmit signals between two points, and multipolar neurons transmit signals from multiple points.
This allows the neurons to send signals to different parts of the body, allowing us to carry out various tasks.
Structure and function of bipolar neurons
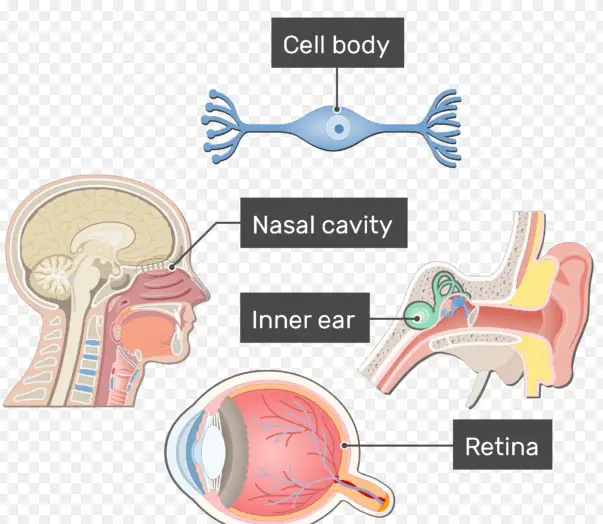
Bipolar neurons are nerve cells that feature two distinct processes, or extensions, extending from their cell bodies. As the name suggests, these neurons possess two poles, or ends, which makes them distinct from other types of neurons such as multipolar or unipolar neurons.
Bipolar neurons are commonly found in sensory organs, responsible for detecting and relaying information from the environment to the central nervous system. The two processes of bipolar neurons are also responsible for transmitting signals from one neuron to another. The main difference between multipolar bipolar and unipolar neurons lies in the number of processes they possess.
Multipolar bipolar neurons have multiple processes and unipolar neurons only have one process. Unipolar neurons are commonly found in the peripheral nervous system, while multipolar bipolar neurons are found in the central nervous system. Both types of neurons are responsible for relaying nerve impulses and processing information, but bipolar neurons are capable of transmitting information more quickly and efficiently due to their two processes.
Both types of neurons are responsible for relaying nerve impulses and processing information, but bipolar neurons are capable of transmitting information more quickly and efficiently due to their two processes.
Structure and function of unipolar neurons
Unipolar neurons are unique in their structure and function among other neuron types. Unlike multipolar and bipolar neurons, which have multiple branches off their cell body, unipolar neurons have a single, elongated extension that separates from the cell body.
The axon also contains numerous small branches, called collaterals, which help to spread the electrical signals to other neurons. Unipolar neurons are found in invertebrates and are involved in sensation, such as touch, pain, and temperature.
They are also involved in the transmission of signals from the central nervous system to the peripheral organs, such as muscles. The axon of the unipolar neuron is especially important because it is the only way to transmit signals away from the cell body, allowing it to connect with other neurons and contribute to the communication of the nervous system.
Comparative anatomy of multipolar, bipolar and unipolar neurons
The human nervous system is a complex network of billions of neurons that send signals throughout the body. Among these neurons, there are three main types of neurons: multipolar, bipolar, and unipolar neurons. Each type of neuron is unique in its structure and function, and understanding the differences between them is important for understanding the nervous system as a whole.
Each type of neuron is unique in its structure and function, and understanding the differences between them is important for understanding the nervous system as a whole. Multipolar neurons have multiple dendrites and one axon, which makes them capable of receiving and sending multiple signals at once. Bipolar neurons have two dendrites and two axons, allowing them to send and receive signals from two different sources.
Finally, unipolar neurons have just one dendrite and one axon, meaning they can only send and receive signals from one source. Each type of neuron plays an important role in the functioning of the nervous system, and understanding the differences between them can help us better understand how the system works.
Clinical significance of multipolar, bipolar and unipolar neurons
The human body is made up of billions of neurons, each with a unique structure and function. Of these neurons, there are three major types: multipolar, bipolar, and unipolar.
While all three types of neurons play an important role in the body, there are distinct differences between them. Multipolar neurons are the most common type of neuron, consisting of multiple dendrites that receive signals and one axon that sends signals. Bipolar neurons have two processes, one dendrite and one axon, and are often found in the sensory organs of the body.
Finally, unipolar neurons only have one process, receiving signals from other neurons and sending them to the central nervous system. Each type of neuron has a different role in the body and plays a critical role in the functioning of the nervous system.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, the difference between multipolar, bipolar, and unipolar neurons lies in their structure. Multipolar neurons have multiple dendrites and axons, while bipolar neurons have two dendrites and one axon.
Each type of neuron plays an important role in the nervous system, and understanding the difference between them is essential for understanding how the nervous system works.