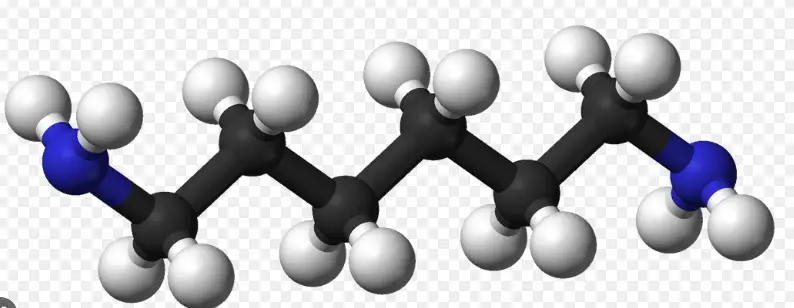
We often hear about methyl and methylene groups in chemistry, but what is the difference between them? In this blog post, we’ll discuss the chemical properties of methyl and methylene groups and how they differ from each other. We’ll look at what makes these chemical groups distinct and how they are used in various applications.
We’ll look at what makes these chemical groups distinct and how they are used in various applications. By the end of this post, you’ll have a better understanding of the difference between methyl and methylene groups and why they are important.
Properties of methyl and methylene groups
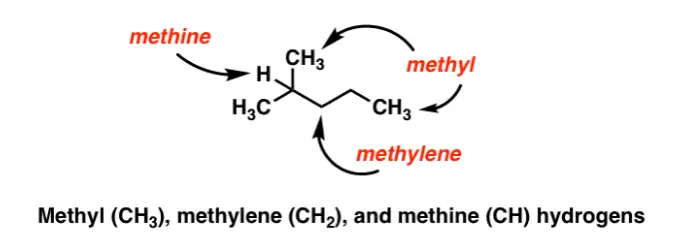
Methyl and methylene groups are two important groups of atoms found in organic chemistry. They both consist of one carbon atom and three hydrogen atoms bonded together, but they have a few notable differences. Methyl groups are sp3-hybridized, meaning that each of the four bonds is composed of a single sigma bond and a single pi bond.
Methyl groups are sp3-hybridized, meaning that each of the four bonds is composed of a single sigma bond and a single pi bond. Methylene groups, on the other hand, are sp2-hybridized, with three single sigma bonds and one double pi bond. This difference in hybridization results in a difference in shape, with methyl groups being tetrahedral and methylene groups being planar.
Additionally, methylene groups are more reactive than methyl groups because of the presence of the double pi bond.
Chemical reactions involving methyl and methylene groups
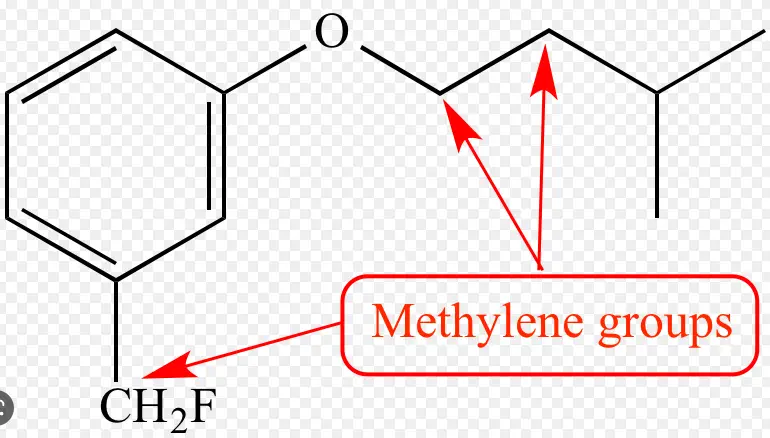
The difference between a methyl group and a methylene group can be a bit confusing for chemistry students. A methyl group is a common organic compound consisting of one carbon atom and three hydrogen atoms. This is often represented as CH
On the other hand, a methylene group is a hydrocarbon containing two carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms. In other words, it consists of two methyl groups linked together.
It is generally represented as CH There are various chemical reactions that involve methyl and methylene groups, and understanding the difference between them can be key in understanding the outcome of these reactions.
Applications of methyl and methylene groups
Methyl and methylene groups are both important functional groups used in organic chemistry. Both groups contain one carbon atom and three hydrogen atoms, but the difference lies in the way the carbon atom is bonded to the three hydrogen atoms.
In a methyl group, the carbon atom is bonded to all three hydrogen atoms directly, while in a methylene group, the carbon atom is bonded to only two hydrogen atoms, and the third hydrogen atom is bonded to the carbon atom through an oxygen atom. This difference in bonding leads to different applications of the two groups. Methyl groups are often used as a replacement for hydrogen atoms in organic compounds, and they are involved in many synthetic reactions such as Grignard and Wittig reactions.
Methylene groups, on the other hand, are mainly used as a bridge between two carbon atoms, and they are involved in a variety of organic syntheses such as oxidative addition and nucleophilic substitution.
Safety precautions when working with methyl and methylene groups
When working with organic compounds, it is important to understand the difference between methyl and methylene groups. Methyl groups consist of one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms, whereas methylene groups consist of two carbon atoms connected by a double bond, each of which is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Both types of groups are very reactive, so it is important to take safety precautions when working with them.
Both types of groups are very reactive, so it is important to take safety precautions when working with them. For instance, when handling these compounds, you should wear the appropriate protective gear and make sure that the environment is well ventilated in order to reduce the risk of exposure to toxic fumes. Additionally, you should avoid mixing methyl and methylene groups together, as this can create potentially dangerous reactions.
By following these simple precautions, you can ensure that you stay safe and secure when working with these potentially hazardous compounds.
Types of methyl and methylene compounds
Methyl and methylene compounds are two of the most common types of organic compounds that share a few similarities, yet have a few key differences. In terms of molecular structure, both contain a CH₂ group, which is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom. However, the difference lies in the arrangement of the atoms: methyl groups have two hydrogen atoms bonded to the same side of the carbon atom, while methylene groups have two hydrogen atoms bonded to opposite sides of the carbon atom.
This difference in arrangement affects the properties of the compound and how it behaves in different chemicals and environments.
Summary of the difference between methyl and methylene groups
The difference between a methyl and a methylene group can be a bit confusing; however, it is important to understand the distinction. A methyl group is an alkyl radical composed of one carbon atom and three hydrogen atoms, while a methylene group consists of two carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms. Both are classified as hydrocarbons, meaning they are composed only of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
The main difference between the two is that a methyl group is a single-bonded hydrocarbon, while a methylene group has two single bonds. The result is that a methylene group has a higher boiling point and is more electronegative than a methyl group.
Additionally, a methylene group is a larger, more stable molecule than a methyl group. In short, the difference between methyl and methylene groups lies in their structure and stability; while they are both hydrocarbons, methylene groups have two single bonds and are more stable than methyl groups.
Final Touch
In conclusion, it is clear that methyl and methylene groups have many similarities, but also some distinct differences. The methyl group is a single carbon atom with three hydrogen atoms attached, while the methylene group is a two-carbon chain with two hydrogen atoms.
Additionally, the methyl group is a common substitution for other functional groups, while the methylene group is often used to form double and triple bonds. By understanding these differences, chemists can better understand the properties and reactivity of organic molecules.