The cellular world is fascinating! It can be easy to get lost in the details of the complex structures and functions of the both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
We will explore how these structures are formed and the roles they play in cell migration. Get ready to delve into the world of cellular biology – let’s get started!
Morphology and structural differences
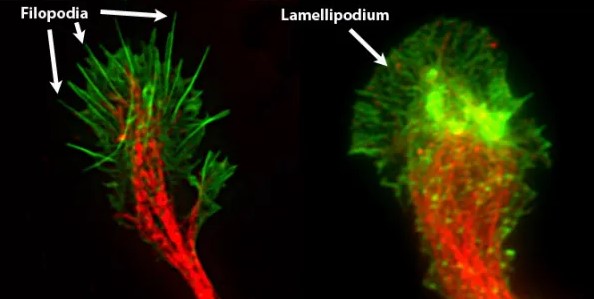
Morphology and structural differences between lamellipodia and filopodia provide insight into the different roles of these cellular protrusions. Lamellipodia are broad, flat extensions of the cell membrane that fan out and range from hundreds to thousands of nanometers wide. Filopodia, on the other hand, are thin, filamentous structures that reach up to a few micrometers in length and are composed of actin filaments in the cytoskeleton.
Filopodia, on the other hand, are thin, filamentous structures that reach up to a few micrometers in length and are composed of actin filaments in the cytoskeleton. Not only do these distinct shapes provide different functions, but they also differ in terms of protein makeup and composition. Lamellipodia contain more actin filaments than filopodia and are also supported by a meshwork of actin-binding protein complexes, allowing them to spread out and cover large areas of the cell membrane.
In contrast, filopodia contain fewer actin filaments and rely on formin proteins to maintain their shape and length. Overall, the differences between lamellipodia and filopodia are key to understanding the roles they play in cell motility and adhesion.
Functional differences
Lamellipodia and filopodia are both cellular structures that are involved in a variety of cell activities, such as cell motility, adhesion, and migration. However, there are some key differences between these two structures.
Lamellipodia are sheet-like protrusions that extend from the cell, providing a substrate for cell movement. In contrast, filopodia are thin, finger-like projections that are involved in sensing the environment. They help the cell to detect and respond to the presence of other cells, as well as chemical or physical cues.
Furthermore, lamellipodia are involved in the formation of focal adhesions, while filopodia are not. Focal adhesions are important for cell-cell communication and the promotion of proper cell migration. Ultimately, lamellipodia and filopodia are both essential components of cellular structure and function, but their differences should be noted.
Role in cell movement
Cell movement is a crucial process that helps organisms to grow and thrive. This is achieved through the use of two dynamic cellular protrusions known as lamellipodia and filopodia. While both of these protrusions are important for cell movement, they have some distinct differences that are important to understand.
Lamellipodia are flat, sheet-like protrusions that form around the cell’s leading edge. They are rich in actin filaments and serve to increase the cell’s surface area, allowing it to move more quickly.
Filopodia, on the other hand, are thin, finger-like protrusions that are composed of bundles of actin filaments. These structures are responsible for pushing the cell forward, providing it with the necessary forward thrust to move. Together, these structures allow cells to move quickly and efficiently.
Examples of cells with lamellipodia or filopodia
Cells are amazing, and one of the most interesting ways they move is through the use of lamellipodia and filopodia. But what is the difference between these two structures?
Lamellipodia are flat sheet-like structures that extend out from the cell, while filopodia are thin, thread-like structures. Lamellipodia are used for cell crawling and spreading, while filopodia are used for exploring the environment and providing traction. Lamellipodia are typically larger than filopodia, and they also contain a high density of actin filaments that allow them to extend and retract quickly.
Filopodia, on the other hand, contain fewer actin filaments and are primarily used for sensing the environment. Both structures play an important role in the movement of cells, and understanding the difference between them is crucial in understanding cell biology.
Significance of lamellipodia and filopodia in cellular processes

Lamellipodia and filopodia are two unique and important components of cellular processes. Both structures are composed of thin, filamentous networks of proteins that protrude from the cell membrane and help the cell move, respond to external stimuli, and interact with the environment. While their functions are similar, the difference between lamellipodia and filopodia lies in their structure and behavior.
Lamellipodia are flat and fan-like in shape, while filopodia are thin and pointed. They also vary in their ability to stick to surfaces and their speed of movement.
Lamellipodia can crawl over surfaces and move relatively slowly, while filopodia can quickly penetrate into the environment and are able to attach firmly to surfaces. The importance of these structures lies in their role in cellular processes such as cell migration, cell adhesion, and cell signaling. By studying the differences between lamellipodia and filopodia, scientists can gain insight into the mechanisms of cellular processes and how they can be manipulated to treat diseases.
By studying the differences between lamellipodia and filopodia, scientists can gain insight into the mechanisms of cellular processes and how they can be manipulated to treat diseases.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, lamellipodia and filopodia are both cellular extensions that help a cell move and interact with its environment. However, they differ in their structure, composition, and function. Lamellipodia are made up of a sheet of actin filaments that extends outward from the cell, providing stability and allowing for efficient movement over a wide area.
Lamellipodia are made up of a sheet of actin filaments that extends outward from the cell, providing stability and allowing for efficient movement over a wide area. Filopodia are composed of thin, elongated bundles of actin filaments that extend outward from the cell, providing the cell with a sense of direction and allowing it to explore its environment. Both are essential components of the cell’s movement and ability to interact with its environment.