Amino acids and phospholipids are pivotal to our physiological well-being, each serving distinct roles within the human body. While amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, essential for various metabolic processes, phospholipids form integral parts of cellular membranes, influencing cell structure and signaling. This discourse focuses on L Serine and Phosphatidylserine, two compounds fundamental in biological systems but differing significantly in function and structure.
L Serine, a non-essential amino acid, synthesizes proteins and several metabolic compounds, playing a crucial role in brain function and overall health. Phosphatidylserine, on the other hand, is a phospholipid that aids in cognitive functions and cellular signaling in neurons. The distinction between these two compounds lies in their chemical structure and their unique roles within the body.
Exploring these differences not only enhances our understanding of human biochemistry but also guides us in optimizing our health through diet and supplementation. These compounds, though similar in name, offer diverse benefits critical to maintaining cognitive function and metabolic health.
L Serine Basics
Definition and Role
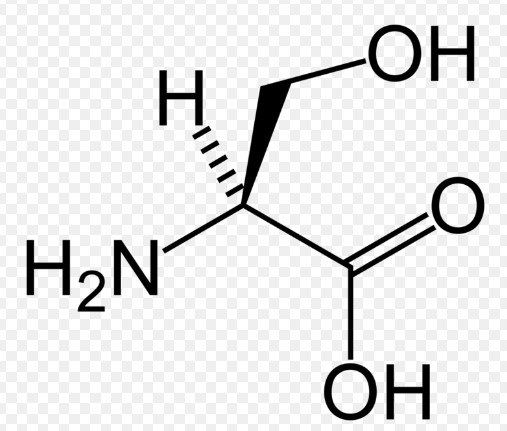
L Serine is a non-essential amino acid, critical for various biological processes. It is classified as non-essential because the human body can synthesize it internally, though dietary intake can still play a beneficial role. This amino acid is fundamental for protein synthesis, which impacts nearly every bodily function from muscle growth to immune response.
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of L Serine occurs through the glycolytic pathway, where it is derived from another amino acid called glycine or from 3-phosphoglycerate, an intermediate in glycolysis. This process involves several enzymes, each playing a specific role to ensure efficient conversion:
- 3-phosphoglycerate is converted to 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate by the enzyme phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase.
- This compound is then transformed into 3-phosphoserine through the action of phosphoserine aminotransferase.
- Finally, 3-phosphoserine is converted into L Serine by phosphoserine phosphatase.
Functions in the Body
L Serine is indispensable for many physiological functions:
- Protein synthesis: It contributes to the structure of proteins needed for muscle and tissue integrity.
- Neurotransmission: Acts as a precursor for several neurotransmitters that regulate mood, cognition, and muscle control.
- Cellular health: Involved in the formation of phospholipids, which are essential for cellular structure and function.
Phosphatidylserine Basics
Definition and Structure
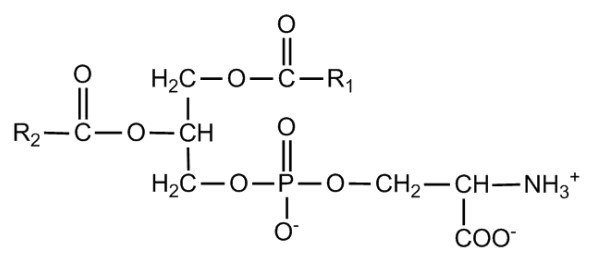
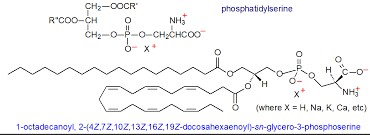
Phosphatidylserine is a phospholipid, which means it is a fatty compound that includes phosphorus. It forms a key part of the cell membrane, helping to maintain the barrier and fluidity of cells. Structurally, it consists of two fatty acid chains and a phosphate group linked to serine.
How It Is Made
Phosphatidylserine is synthesized in the body from phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine through a process known as the base exchange reaction. Here’s how it is typically formed:
- Serine is exchanged with the ethanolamine or choline of phosphatidylcholine or phosphatidylethanolamine.
- This exchange is facilitated by the enzyme phosphatidylserine synthase.
Key Functions
Phosphatidylserine plays several critical roles in body function, notably:
- Cognitive function: It is vital for brain health, aiding in nerve cell communication and memory formation.
- Cell signaling: Helps in the transmission of signals between cells, essential for various biological responses.
Chemical Differences
Molecular Structure Comparison
Though both L Serine and Phosphatidylserine include serine, their structures are distinctly different. L Serine is a simpler molecule, consisting of only amino and hydroxyl groups along with the backbone. Phosphatidylserine, however, is much more complex with additional fatty acid chains and a phosphate group.
Key Biochemical Properties
The presence of fatty acids in Phosphatidylserine gives it hydrophobic (water-repelling) properties, allowing it to integrate into cell membranes. In contrast, L Serine is more hydrophilic (water-attracting), which influences its role in aqueous environments like cellular fluids.
Biological Roles
L Serine in Metabolism
L Serine is crucial in metabolism, contributing to several pathways:
- Glycine production: It acts as a precursor to glycine, another amino acid essential for various metabolic functions.
- One-carbon metabolism: Plays a role in the methylation processes important for DNA and RNA production.
Phosphatidylserine in Brain Health
Phosphatidylserine’s role in brain health is profound. It supports:
- Memory function: Helps in the formation and recall of memory.
- Mood regulation: Influences neurotransmitters that affect mood and stress responses.
Health Benefits
L Serine Benefits
L Serine is more than just a building block for proteins; it plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health. The benefits of L Serine include:
- Mental function: Enhances cognitive processes and may improve memory, focus, and the ability to learn.
- Mood regulation: Supports the production of serotonin and dopamine, which can improve mood and help manage stress.
- Muscle growth: Aids in the synthesis of muscle proteins and can be beneficial for muscle recovery post-exercise.
Phosphatidylserine Advantages
Phosphatidylserine is particularly known for its positive impact on cognitive health, but its benefits extend beyond:
- Enhanced brain health: Promotes cognitive functions such as memory, concentration, and the speed of thinking.
- Stress reduction: Helps mitigate the physical and psychological effects of stress by lowering cortisol levels.
- Exercise performance: May improve athletic performance by enhancing mood and reducing fatigue.
Dietary Sources
Foods Rich in L Serine
To boost levels of L Serine through diet, consider including the following foods:
- Soy products: Tofu, soybeans, and soy milk are excellent sources.
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and peanuts provide good amounts of L Serine.
- Eggs: Particularly the white part, which is rich in proteins including L Serine.
Foods Containing Phosphatidylserine
Phosphatidylserine is found in several food sources, although in smaller quantities compared to other nutrients:
- Animal organs: Particularly heart and liver are rich in Phosphatidylserine.
- Fish: Mackerel, herring, and tuna are good sources due to their high fat content.
- White beans: Also provide a modest amount of Phosphatidylserine.
Supplement Use
L Serine Supplements
L Serine is available as a dietary supplement and is commonly used for:
- Mental clarity and mood: Helps people seeking to improve mental function and mood stability.
- Sleep quality: May aid in the production of sleep-regulating hormones.
When choosing L Serine supplements, consider:
- Quality and purity: Opt for products tested for purity and potency.
- Dosage: Follow recommended dosages to avoid potential side effects.
Phosphatidylserine Supplements
Phosphatidylserine supplements are often sought after for their neuroprotective properties, especially among the elderly and athletes:
- Cognitive health: Commonly used to preserve memory and cognitive function.
- Sport performance: May reduce muscle soreness and protect against the stress of exercise.
When using Phosphatidylserine supplements, it’s essential to:
- Consult healthcare providers: Especially for those with pre-existing health conditions.
- Brand reputation: Choose supplements from reputable manufacturers.
Clinical Research
Studies on L Serine
Research on L Serine has shown promising results in various areas:
- Neuroprotection: Studies suggest L Serine may play a role in protecting nerve cells, potentially beneficial in neurological disorders.
- Metabolic enhancement: Research indicates improvements in metabolic parameters with L Serine supplementation.
Research on Phosphatidylserine
Phosphatidylserine research focuses extensively on its role in cognitive health:
- Memory improvement: Clinical trials have demonstrated benefits in memory function in older adults.
- Cognitive decline prevention: Some studies suggest it may help slow the progression of cognitive decline in the elderly.
Safety and Side Effects
L Serine Safety Profile
L Serine is generally considered safe when consumed in amounts found in food and typical supplements:
- Well-tolerated: Most people do not experience adverse effects from L Serine at recommended doses.
- Monitor intake: High doses may lead to gastrointestinal symptoms and should be avoided.
Phosphatidylserine Side Effects
Phosphatidylserine is also safe for most people, but some points to consider include:
- Possible side effects: Although rare, some individuals may experience stomach upset or insomnia.
- Interaction with medication: As with any supplement, it’s crucial to consider potential interactions with other medications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is L Serine?
L Serine is a non-essential amino acid involved in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is vital for various physiological functions, including muscle growth, immune system support, and neurotransmission.
How does Phosphatidylserine support brain health?
Phosphatidylserine plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular function in the brain. It helps in the formation of memory, improves concentration, and enhances cognitive ability by facilitating cell-to-cell communication.
Can L Serine be synthesized in the body?
Yes, L Serine can be synthesized in the human body from other metabolites through various biochemical pathways, which means it is not strictly required in the diet, though dietary sources can supplement bodily levels.
What are the dietary sources of Phosphatidylserine?
Phosphatidylserine is primarily found in foods like soybeans, white beans, egg yolks, chicken liver, and Atlantic mackerel. Regular consumption of these foods can help maintain adequate levels of Phosphatidylserine in the body.
Is supplementation of L Serine and Phosphatidylserine safe?
Supplementation of both L Serine and Phosphatidylserine is generally considered safe when taken within recommended doses. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Conclusion
The exploration of L Serine and Phosphatidylserine reveals a fascinating glimpse into the world of biochemistry and its impact on human health. Each compound, through its unique structure and function, offers significant benefits that contribute to maintaining and enhancing bodily functions, particularly in cognitive and metabolic processes.
Incorporating these compounds through diet or supplementation can significantly impact overall health. As scientific research progresses, the potential of these compounds to support human health continues to emerge, promising further insights and benefits in future applications.