Clay minerals are ubiquitous in nature, playing pivotal roles in a variety of environmental and industrial processes. Among them, Kaolinite and Montmorillonite are particularly notable due to their distinct characteristics and uses. These minerals, while similar in their basic composition as clays, exhibit unique properties and formations that merit a closer examination.
Kaolinite and Montmorillonite differ primarily in their chemical structure, water content, and ion exchange capacities. Kaolinite, a more stable and less reactive mineral, has a 1:1 layer of silica and alumina, while Montmorillonite, known for its swelling properties, boasts a 2:1 layer structure that allows it to absorb water and expand.
The significance of these minerals extends beyond their geological presence, influencing various industries such as ceramics, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture. Their unique characteristics make them invaluable in specific applications, from improving soil structure to being used as drug delivery agents.

Mineral Composition
Basic Chemistry of Kaolinite
Kaolinite, a clay mineral part of the larger group of industrial minerals, has the chemical formula Al₂Si₂O₅(OH)₄. It is a silicate mineral, which means it contains silica and alumina layers, bonded together with hydrogen bonds. In its purest form, Kaolinite is white, though it can often appear in various shades due to impurities. Kaolinite is non-expanding, which makes it distinct from other clay minerals like Montmorillonite that can absorb water and expand.
Basic Chemistry of Montmorillonite
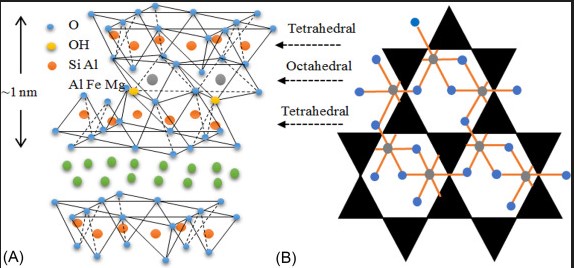
In contrast, Montmorillonite is a type of smectite clay with the chemical formula (Na,Ca)₀₃₃(Al,Mg)₂Si₄O₁₀(OH)₂·nH₂O. Its composition allows it to swell significantly when exposed to water. This characteristic is due to its unique structure, which includes water molecules within its interlayer spaces. Unlike Kaolinite, Montmorillonite’s ionic exchange capacity is high, which is crucial for many of its industrial uses, such as water purification.
Physical Properties
Structure of Kaolinite
The structure of Kaolinite is composed of one tetrahedral sheet of silica linked via oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina. This arrangement forms a 1:1 layer structure, which is relatively stable and resists expansion or contraction. This stability is a key attribute that influences its utility in various industrial contexts.
Structure of Montmorillonite
Montmorillonite, however, has a 2:1 layer structure, consisting of one octahedral alumina sheet sandwiched between two tetrahedral silica sheets. This configuration allows for the expansion as water molecules can enter the interlayer spaces, making it a versatile material in applications requiring absorbency.
Formation Processes
How Kaolinite Forms
Kaolinite typically forms through the weathering or hydrothermal alteration of alumino-silicate minerals such as feldspar. Often, this process occurs in tropical and subtropical environments where high rainfall rates wash away soluble ions such as calcium and sodium, leaving behind the less soluble aluminum and silica ions. These conditions are ideal for Kaolinite formation:
- High humidity
- Rich in alumino-silicate rocks
- Acidic conditions
How Montmorillonite Forms
Montmorillonite forms under somewhat different conditions. This mineral often results from the alteration of volcanic ash, particularly in marine environments. The presence of water is critical, as it facilitates the leaching of ions and subsequent rearrangement of the remaining silica and aluminum into the characteristic 2:1 structure of Montmorillonite. Key factors for its formation include:
- Volcanic ash deposits
- Presence of water
- Alkaline pH levels
Industrial Uses
Kaolinite in Industry
Kaolinite is extensively used across various industries due to its stability and non-reactivity. Here are a few key applications:
- Ceramics: Used to manufacture porcelain and as a glaze ingredient.
- Paper production: Acts as a filler to improve the paper’s brightness, gloss, and ink absorption.
- Paints and coatings: Used as an extender, improving the durability and color of paint.
Montmorillonite in Industry
Montmorillonite’s swelling ability and high cation exchange capacity lend it to a variety of uses that require absorbency and ion exchange. Its main industrial applications include:
- Drilling muds: Used in oil and water well drilling to stabilize boreholes.
- Environmental cleanup: Absorbs toxins and heavy metals from water and soil.
- Agriculture: Improves soil quality and water retention in sandy soils.
Environmental Impact
Kaolinite and Ecological Concerns
While Kaolinite is considered relatively inert environmentally, its mining and processing can have significant impacts. The primary concerns include:
- Land degradation: Large-scale removal of topsoil and vegetation reduces land fertility and increases erosion risks.
- Water pollution: Runoff from kaolinite mines can carry suspended particles, which may affect water bodies downstream.
- Air quality: Dust from mining operations can contribute to air pollution, potentially affecting respiratory health in nearby communities.
These issues necessitate the implementation of sustainable mining practices to minimize environmental disruption, such as proper land reclamation and dust control measures.
Montmorillonite and Ecological Concerns
Montmorillonite, due to its ability to swell, poses different environmental challenges. Concerns related to its extraction and use include:
- Water consumption: The extraction process can require significant amounts of water, potentially depleting local water resources.
- Disposal issues: Used Montmorillonite, particularly from industrial applications, can contain absorbed pollutants that may pose disposal challenges.
- Land impact: Similar to Kaolinite, the mining of Montmorillonite can lead to habitat destruction and soil destabilization.
Environmental regulations and water management strategies are crucial to address these impacts, ensuring that Montmorillonite’s benefits do not come at the cost of ecological health.
Health Implications
Health Benefits of Kaolinite
Kaolinite has several health applications, notably in the pharmaceutical industry. It is used for:
- Treating diarrhea: Its absorbent properties help remove toxins and pathogens from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Skin care products: Kaolinite clays are used in masks and cleansers to absorb excess oil and impurities from the skin.
- Supporting digestion: When used appropriately, it can help in adsorbing gases and toxins, promoting healthier digestion.
These benefits make Kaolinite a valuable component in health and wellness products, underlining the importance of controlled and safe use.
Health Benefits of Montmorillonite
Montmorillonite is valued for its:
- Detoxifying properties: Its high cation exchange capacity allows it to absorb heavy metals and other contaminants, often used in detox regimens.
- Digestive health: Like Kaolinite, it can help in managing diarrhea and removing toxins from the body.
- Wound care: Its antibacterial properties and ability to absorb moisture make it useful in healing ointments and creams.
Risks Associated with Each
However, the use of these minerals in health products is not without risks:
- Respiratory issues: Inhalation of fine clay particles can lead to respiratory problems.
- Contamination: Natural clays might be contaminated with trace metals, which could pose health risks if not properly processed.
Geographic Distribution
Where Kaolinite is Found
Kaolinite deposits are globally widespread, with significant occurrences in:
- United States: Particularly in the Southeastern region.
- Brazil: Large deposits due to extensive weathering of rocks.
- United Kingdom: Predominantly in Cornwall and Devon, used for china clay.
The wide availability of Kaolinite underscores its importance in various global industries.
Where Montmorillonite is Found
Montmorillonite is primarily found in regions with volcanic ash, such as:
- United States: Particularly in the Western states like Wyoming and Montana.
- Italy: Near volcanic areas such as Naples.
- Japan: Abundant in volcanic ash layers.
These locations highlight the geological processes that favor Montmorillonite’s formation, contributing to its unique properties.
Advancements in Research
Recent Studies on Kaolinite
Recent research on Kaolinite focuses on enhancing its usability in new applications, such as:
- Advanced ceramics: Improving heat resistance for aerospace applications.
- Environmental cleanup: Utilizing its adsorptive properties to remove pollutants from water.
Recent Studies on Montmorillonite
For Montmorillonite, research is directed towards:
- Medical applications: Developing drug delivery systems using its swelling properties.
- Agricultural improvements: Using modified Montmorillonite to improve soil water retention and fertility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Kaolinite used for?
Kaolinite is widely used in the production of ceramics, as a paper coating and filler, and in the manufacture of paint. It is also employed in pharmaceuticals as an ingredient in medications to treat diarrhea due to its adsorptive properties.
How is Montmorillonite different from Kaolinite?
Montmorillonite differs from Kaolinite mainly in its ability to swell and expand upon contact with water. This property makes it useful in industrial applications where absorbency is required, such as in drilling muds and as a sealant in geotechnical engineering.
Where can Montmorillonite be found?
Montmorillonite is typically found in sedimentary deposits, often in areas of volcanic ash. It is prevalent in regions like the United States, particularly in the western states, as well as parts of Europe and Asia where volcanic activity has deposited mineral-rich ash layers.
Can Kaolinite be harmful to health?
In general, Kaolinite is considered safe and is even used in health products. However, inhaling fine particles of Kaolinite dust can pose respiratory issues, particularly in industrial settings without proper safety measures.
Conclusion
Kaolinite and Montmorillonite serve as prime examples of how minerals can be both fundamentally similar yet functionally diverse. Their distinct properties shape their roles in natural and human-engineered processes, highlighting the importance of understanding their characteristics for effective application. As research continues, the potential for new uses and methods of enhancing their effectiveness in existing applications promises further advancements.
In conclusion, the study and application of Kaolinite and Montmorillonite represent a fascinating intersection of geology, chemistry, and engineering. With ongoing research and technological advances, the capabilities and understanding of these versatile minerals will continue to expand, offering new solutions to both existing and emerging challenges.
