Spectroscopy is an analytical tool used to identify and measure the composition of molecules. Infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy are two of the most common forms of spectroscopy. In this blog post, we’ll discuss the differences between IR and Raman spectroscopy and how they can be used to analyze the composition of molecules.
In this blog post, we’ll discuss the differences between IR and Raman spectroscopy and how they can be used to analyze the composition of molecules. We’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of each technique, and look at the specific applications in which each is most useful. Finally, we’ll examine how the two techniques can be used together to get the most accurate results.
Compare and contrast between ir and raman spectroscopy

Infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy are both powerful techniques used in the identification and analysis of molecular structures. While both techniques involve the use of light to excite molecules and measure the resulting spectrum, there are several key differences between them.
IR spectroscopy measures the absorption of infrared radiation by a sample, while Raman spectroscopy measures the inelastic scattering of light from a sample. This difference in how the light interacts with the sample results in two distinct spectra. IR spectra are characterized by sharp peaks corresponding to the energy absorbed by the sample, while the Raman spectra have broader peaks resulting from the inelastic scattering.
In addition, while IR spectroscopy can be used to identify the functional groups present in a sample, Raman spectroscopy is more sensitive to the arrangement of the atoms within the sample, making it ideal for analyzing the structure of molecules.
Advantages and disadvantages of ir and raman spectroscopy
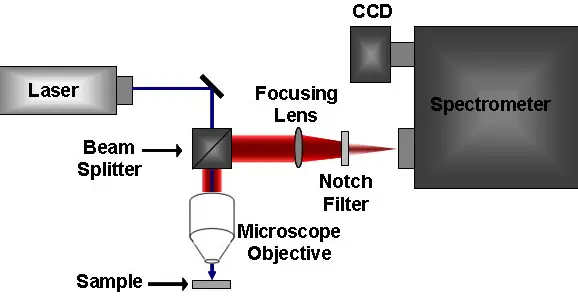
Infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy are two widely used techniques for analyzing molecules and identifying chemical compounds. Both techniques use light to measure the vibrational and rotational energy of molecules and can provide valuable insight into the structure and composition of a sample.
The main advantage of IR spectroscopy is its sensitivity, as it is capable of detecting even small concentrations of molecules. Additionally, IR spectroscopy can be used in both liquid and solid samples, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
On the other hand, Raman spectroscopy has a higher resolution than IR spectroscopy and can be used to measure the vibrational energy of molecules more accurately. However, Raman spectroscopy is limited to solid samples, making it less versatile than IR spectroscopy.
Another difference between IR and Raman spectroscopy is the types of information they can provide. IR spectroscopy is best for identifying functional groups in a sample, while Raman spectroscopy is more suitable for measuring the vibrational energies of molecules. Furthermore, Raman spectroscopy is more effective at detecting molecular vibrations, while IR spectroscopy is better suited for measuring the absorption of light.
Overall, both IR and Raman spectroscopy have their own distinct advantages and disadvantages. By understanding the differences between the two, scientists can choose the right technique to analyze their samples and obtain the most useful information.
Applications of ir and raman spectroscopy
Infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy are two powerful techniques used to analyze the structure of molecules. Both techniques are used to identify and characterize molecules based on their vibrational spectra.
IR spectroscopy relies on the absorption of infrared radiation by molecules. As molecules absorb radiation, they vibrate and produce a unique spectrum which can be used to identify the molecule.
In contrast, Raman spectroscopy relies on the scattering of light, which causes the frequency of the light to shift. This shift in frequency is used to identify the molecule. Another difference between IR and Raman spectroscopy is the type of information they provide.
Another difference between IR and Raman spectroscopy is the type of information they provide. IR spectroscopy provides information about the structure of molecules, while Raman spectroscopy provides information about the chemical bonds between atoms. This means that while IR spectroscopy can be used to identify the molecule, Raman spectroscopy can be used to understand the chemical environment of the molecule.
The applications of IR and Raman spectroscopy are vast, ranging from the identification of unknown compounds to the study of chemical reactions. IR spectroscopy is typically used to identify unknown compounds, while Raman spectroscopy is used to study chemical reactions and the nature of chemical bonds. Both techniques are invaluable tools for scientists, as they can provide detailed information about the structure of molecules.
Challenges and limitations of ir and raman spectroscopy
Infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy are two important techniques used to analyze the composition of substances. They have a lot of similarities, but there are also a few crucial differences that it’s important to be aware of.
In both IR and Raman spectroscopy, the sample is subjected to a beam of light, usually from a laser. Depending on the composition of the sample, different frequencies of light will be absorbed and re-emitted. By analyzing the frequencies of light that are absorbed, it’s possible to determine what elements are present in the sample.
The main difference between IR and Raman spectroscopy lies in the type of light that is re-emitted. In IR spectroscopy, the light is re-emitted as infrared radiation. This makes it possible to identify organic molecules and measure the strength of the bonds between them.
On the other hand, in Raman spectroscopy, the light is re-emitted as visible light. This makes it possible to identify inorganic molecules and measure the vibrational and rotational energy of the sample.
The main challenge of IR and Raman spectroscopy is that both techniques require a clean sample. Any impurities in the sample can interfere with the analysis, making it difficult to get accurate results. Additionally, both techniques can be time-consuming, as the sample must be exposed to the beam of light for a significant period of time. In conclusion, IR and Raman spectroscopy are two powerful techniques for analyzing the composition of substances. However, there are important differences between the two, and both techniques have their own challenges and limitations.
Further resources
If you’re looking for more information about the difference between Infrared (IR) and Raman Spectroscopy, you’ve come to the right place. IR spectroscopy is a type of vibrational spectroscopy that uses infrared radiation to identify molecules.
It measures the energy absorbed and emitted by the molecule, providing information about its composition and structure. On the other hand, Raman spectroscopy uses light to measure the vibrational modes of molecules and identify their structure. It is a powerful technique for analyzing different types of molecules, including organic and inorganic compounds.
The main difference between these two spectroscopic techniques lies in the way they interact with the sample molecules: IR spectroscopy measures the energy absorbed by the molecules, while Raman spectroscopy measures the energy scattered by the molecules. Both techniques provide useful information on the structure and composition of molecules, but Raman spectroscopy is more sensitive and provides more detailed information than IR spectroscopy.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, IR and Raman spectra are both useful techniques for analyzing the structure and composition of molecules. The primary difference between the two techniques is that IR spectra measure the absorption of infrared light while Raman spectra measure the scattering of light.
IR spectra provide a more detailed picture of molecular structure and composition, while Raman spectra are better suited for identifying functional groups. Both techniques are important tools in the study of molecular structure and composition.

