Linguistics, the scientific study of language, explores numerous fascinating phenomena that enrich our communication and understanding. Among these phenomena, homonyms and homophones stand out as particularly intriguing, often causing amusement, confusion, or enlightenment. These linguistic elements underscore the complexity and beauty of language, demonstrating how words can sound alike or even look alike but carry entirely different meanings.
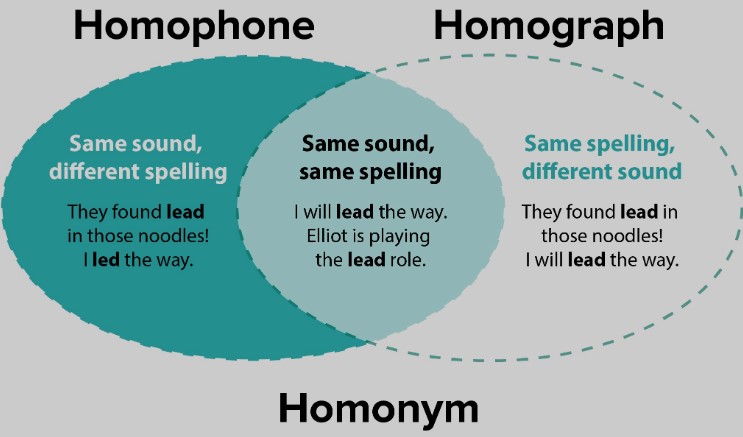
Homonyms are words that share the same spelling and pronunciation but have different meanings, while homophones are words that sound the same when pronounced but differ in meaning, spelling, or both. For instance, “bat” (a piece of sports equipment) and “bat” (an animal) are homonyms, whereas “to,” “too,” and “two” are classic examples of homophones, showcasing how phonetic similarities can link words with distinct meanings and uses.
The distinction between homonyms and homophones is more than just an academic curiosity; it plays a crucial role in effective communication. These linguistic features can enhance the richness of language, contribute to wordplay, and sometimes lead to misunderstandings if not properly grasped. Understanding their differences and applications can improve one’s grasp of language nuances, making for more precise and engaging communication.

Basic Definitions
Homonyms
General definition
Homonyms are words that share the same spelling and pronunciation but have different meanings. They represent the fascinating diversity within the English language, where context is key to deciphering the intended meaning. The existence of homonyms adds a layer of complexity and richness to language, making English both challenging and intriguing to learners and native speakers alike.
Examples in English
- Bat – This can mean a piece of sports equipment used in baseball or a nocturnal flying mammal.
- Bank – Refers either to a financial institution or the side of a river.
- Bark – Can mean the sound a dog makes or the outer covering of a tree.
These examples illustrate how a single word can embody multiple concepts, emphasizing the importance of context for correct interpretation.
Homophones
General definition
Homophones are words that sound the same when pronounced but differ in meaning, spelling, or both. Unlike homonyms, the key feature of homophones is their phonetic similarity, which can lead to confusion in both written and spoken communication if not carefully distinguished by context.
Examples in English
- To, Too, Two – “To” is a preposition, “too” means also or excessively, and “two” is the number after one.
- Flour, Flower – “Flour” is a food ingredient, while “flower” is a blooming plant.
- Knight, Night – “Knight” refers to a medieval warrior, whereas “night” signifies the time of day after sunset.
These examples highlight the importance of spelling and pronunciation in understanding and using English effectively.
Key Differences
Meaning and Usage
Homonyms and homophones are both pivotal in understanding language nuances. The distinct meanings of homonyms versus homophones illustrate the complexity of English. Homonyms demand an understanding of context to grasp the intended meaning, while homophones require knowledge of spelling to differentiate between words with similar sounds.
Phonetics and Orthography
The study of sound similarities and spelling differences is crucial in distinguishing homonyms from homophones. Homonyms share both spelling and pronunciation but differ in meaning. Homophones, conversely, share pronunciation but often have different spellings and meanings, showcasing the intricate relationship between sound and spelling in the English language.
Contextual Clarity
The role of context in distinguishing homonyms and homophones cannot be overstated. Context provides the necessary clues to decipher which word and meaning are intended in a given situation, making it a fundamental aspect of effective communication.
Common Examples
In Everyday Language
Homonyms and homophones are prevalent in everyday language, often without us even realizing it. Their presence can impact verbal and written communication, leading to enriching, and sometimes humorous, exchanges.
Popular homonyms and homophones include:
- Pair and Pare – While “pair” refers to a set of two, “pare” means to trim or cut.
- Mail and Male – “Mail” is postage, whereas “male” is a gender.
Understanding these can prevent misinterpretation and enhance clarity in communication.
In Literature
In poetry and prose, writers leverage homonyms and homophones to add depth and layers to their works. Their use can impact interpretation and analysis, allowing readers to explore multiple meanings and perspectives within the same text.
For example, Shakespeare often employed homonyms and homophones for wordplay and to convey double entendres, enriching the reading experience and offering insights into his characters’ thoughts and the plot’s complexities.
Educational Importance
Learning English
Challenges for Learners
Learning English presents unique challenges, especially when it comes to homonyms and homophones. For non-native speakers, these aspects of the language can be particularly perplexing due to their identical pronunciations or spellings but different meanings. The main hurdles include:
- Pronunciation and Listening Skills: Distinguishing between homophones by ear can be difficult without a clear understanding of context.
- Reading and Writing Skills: Homonyms require learners to pay close attention to context to grasp the intended meaning, which can be challenging without sufficient vocabulary and reading comprehension skills.
- Spelling and Grammar: Homophones often lead to spelling mistakes, as learners might know the word by sound but are unsure of the correct spelling for the given context.
Tips for Mastering Homonyms and Homophones
To overcome these challenges, here are some effective strategies:
- Contextual Learning: Practice using homonyms and homophones in sentences or stories to understand how context clarifies meaning.
- Listening Exercises: Engage in listening exercises that include homophones to train your ear to recognize differences based on context.
- Reading Widely: Exposure to varied reading materials helps encounter homonyms and homophones in different contexts, enhancing comprehension and usage skills.
- Practice Writing: Regular writing exercises that include these words can improve spelling and usage accuracy.
Language Development
Cognitive Skills Enhancement
Understanding and using homonyms and homophones effectively can significantly enhance cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving and critical thinking. Deciphering the correct meaning based on context requires learners to analyze information and make quick decisions, thereby improving mental agility and comprehension skills.
Vocabulary Expansion
Regular exposure to homonyms and homophones naturally leads to an expansion of vocabulary. Learners become more adept at recognizing and using a wider range of words correctly, which is beneficial for both personal and professional communication.
Misunderstandings and Errors
Common Mistakes
Typical Errors in Usage
One of the most common mistakes with homonyms and homophones is misusing them in sentences. For instance, confusing “their,” “there,” and “they’re” can alter the meaning of a sentence or render it grammatically incorrect. Such errors are often due to a lack of understanding of each word’s definition and proper context for use.
Strategies to Avoid Confusion
To minimize errors and avoid confusion, consider the following strategies:
- Create Mnemonics: Develop memory aids that help distinguish between homophones and homonyms, associating each with its meaning.
- Use Language Apps: Engage with language learning apps that offer practice exercises specifically designed to tackle these issues.
- Peer Review: Exchange writings with peers for review. Fresh eyes can catch mistakes you might have overlooked.
Impact on Communication
Potential for Misunderstanding
Misusing homonyms and homophones can lead to misunderstandings in both spoken and written communication. In spoken language, incorrect usage might simply lead to confusion or the need for clarification. In written communication, where tone and facial expressions are absent, the potential for misunderstanding increases significantly.
Importance of Precise Language
The use of precise language is essential for effective communication. Understanding and correctly using homonyms and homophones are critical components of this, as they help convey clear and accurate messages. Precision in language not only facilitates better understanding but also enhances the credibility of the speaker or writer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are homonyms?
Homonyms are words that are spelled and pronounced the same way but have different meanings. They are a testament to the linguistic diversity and complexity of the English language. Examples include “bank” (the side of a river) and “bank” (a financial institution), illustrating how one word can embody multiple concepts based on context.
How do homophones affect language learning?
Homophones pose a unique challenge in language learning, especially in mastering spelling and pronunciation. Their existence requires learners to pay extra attention to context and nuance, enhancing listening and reading skills. Understanding homophones is crucial for effective communication, as it helps in distinguishing between words like “wear” and “where,” which sound identical but have different meanings and spellings.
Can homonyms and homophones change over time?
Yes, homonyms and homophones can evolve over time as language itself changes. New words may arise, meanings can shift, and pronunciation may vary, leading to the creation or dissolution of these linguistic phenomena. This dynamic nature reflects the adaptability of language to cultural and societal changes, making the study of homonyms and homophones a continuous and evolving pursuit.
Why are homonyms and homophones important in literature?
In literature, homonyms and homophones enrich texts, adding layers of meaning and facilitating wordplay. Authors often leverage these linguistic features to create puns, enhance character dialogue, or embed double meanings. Their strategic use can deepen readers’ engagement with the text, offering a more nuanced and multifaceted reading experience.
Conclusion
The exploration of homonyms and homophones opens up a fascinating window into the intricacies of language, revealing the depth and breadth of linguistic variety. These elements not only enrich our vocabulary but also enhance our ability to communicate complex ideas and emotions through the nuanced use of language. They serve as a reminder of the endless possibilities contained within words, inviting us to explore and appreciate the subtle distinctions that make language an art form as much as a means of communication.
Recognizing and understanding the differences between homonyms and homophones is essential for anyone looking to master the English language or simply appreciate its beauty. As we navigate the complexities of communication, a deepened understanding of these linguistic phenomena can lead to more effective and expressive interactions, proving that the power of language lies in its details.