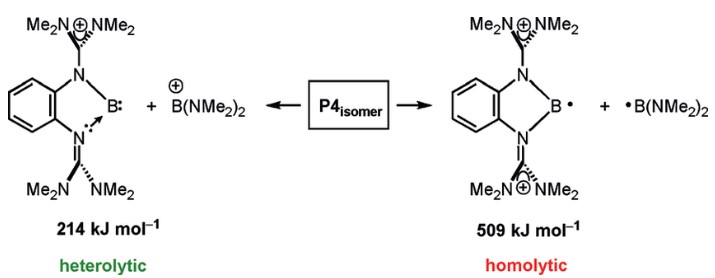
In chemistry, the difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies can be difficult to understand. This blog post will explain the concept of bond dissociation energy, the differences between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies, and how these energies affect chemical reactions.
By the end of the post, you should have a better understanding of these two terms and how they can affect the behavior of molecules.
Definition of homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energy
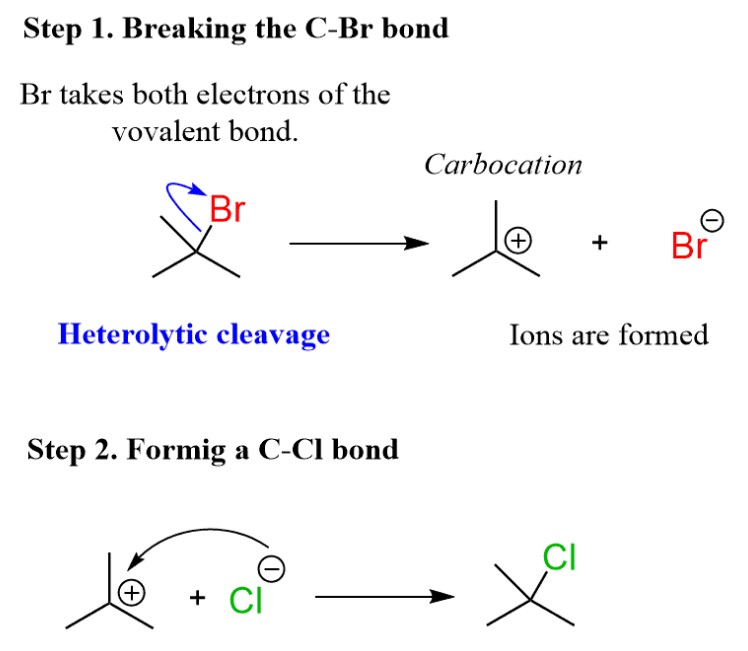
Bond dissociation energy is the measure of how much energy is required to break a chemical bond. Homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies are two types of bond dissociation energies that can be used to measure the strength of a particular bond.
The main difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies is the way in which the bond is broken. In homolytic bond dissociation energy, the bond is broken into two identical fragments, while in heterolytic bond dissociation energy, the bond is broken unevenly, resulting in two different fragments. Homolytic bond dissociation energies are generally higher than heterolytic bond dissociation energies, meaning that homolytic bonds are typically stronger than heterolytic bonds.
Comparison of homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energy
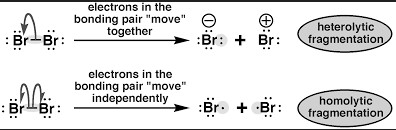
A key concept in understanding chemical reactions is the difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energy. In a homolytic reaction, both atoms that make up a covalent bond share an equal amount of the energy released when the bond breaks. In a heterolytic reaction, one of the atoms takes up the majority of the energy, with the other atom taking up the remaining energy.
In a heterolytic reaction, one of the atoms takes up the majority of the energy, with the other atom taking up the remaining energy. This difference has important implications for understanding how different types of bonds react, and can help us to predict the products of a reaction. By understanding the difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energy, scientists can more accurately calculate the likelihood of a reaction occurring and its products.
Factors affecting the strength of homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energy
The strength of a bond dissociation energy depends on the type of bond being broken. Homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies are two key types of bond dissociation energies, and each is affected by different factors.
Homolytic bond dissociation energy (HBD) is the energy required to break a bond into two fragments that each retain one of the original electrons. Factors that affect the strength of HBD include the atomic size of the atoms involved, the electronegativity of the atoms, the bond order, and the hybridization of the molecules. On the other hand, heterolytic bond dissociation energy (HED) is the energy required to break a bond into two fragments with one fragment retaining both electrons.
Factors that influence the strength of HED include the size of the atoms involved, the electronegativity of the atoms, the bond order, and the presence of a substituent group. As a result, the difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies can be quite significant, and understanding these differences is key to understanding the strength of a bond.
Examples of homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energy
The difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies lies in how the bond energy is distributed between the two reacting molecules. In a homolytic bond dissociation, the energy of the bond is evenly divided between the two molecules, whereas in heterolytic bond dissociation, the energy of the bond is split unequally, with one molecule taking more energy than the other.
Understanding the difference between these two types of bond dissociation energies is essential for understanding how chemical reactions take place in nature.
Benefits of knowing the difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energy
The difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies is an important concept in chemistry. Knowing the difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies can help you better understand chemical reactions and the energy associated with them.
This has important implications for the energy associated with the reaction, as homolytic bond dissociation requires more energy than heterolytic bond dissociation. Understanding this difference can help you better predict the energies associated with different chemical reactions, and can also help you better understand the structure of molecules.
Knowing the difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies can provide you with a deeper understanding of the world of chemistry.
Bottom Line
In conclusion, the difference between homolytic and heterolytic bond dissociation energies lies in the type of bond that is broken when the energy is released. Homolytic bond dissociation energy involves breaking the bond in such a way that both of the atoms hold onto their electrons, whereas heterolytic bond dissociation energy involves one atom taking both electrons from the bond. This difference in electron distribution results in a greater energy release for the heterolytic bond dissociation energy than for the homolytic bond dissociation energy.
This difference in electron distribution results in a greater energy release for the heterolytic bond dissociation energy than for the homolytic bond dissociation energy. This increased energy release makes heterolytic bond dissociation energy a more useful tool for breaking and forming chemical bonds.