Equilibrium is an important concept in the field of chemistry, and understanding the differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium is essential for any student of the subject. In this blog post, we will discuss the differences between these two types of equilibrium and the implications of each.
We will look at the various chemical processes involved in both and explain how they impact our lives. Additionally, we will also discuss the implications of a shift in equilibrium for both types of systems.
Advantages and disadvantages of homogeneous equilibrium
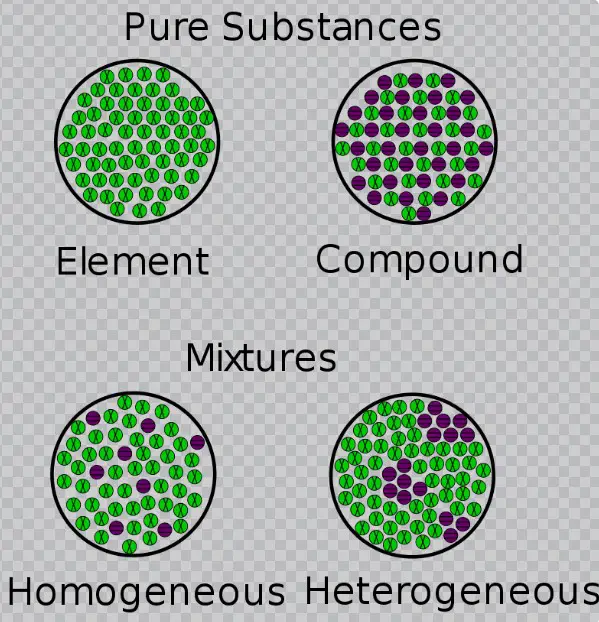
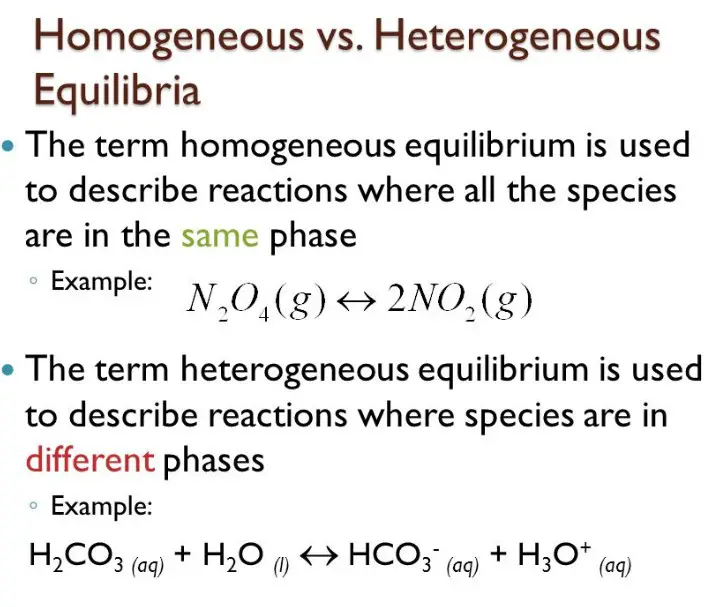
The difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium lies in the distribution of reactants and products. In homogeneous equilibrium, the reactants and products are in the same phase, often in a single solution, whereas in heterogeneous equilibrium, the reactants and products are in different phases, such as a solid and a gas. As a result, homogeneous equilibrium tends to be simpler and easier to understand than heterogeneous equilibrium.
The advantages of homogeneous equilibrium include its ease of understanding, and the fact that it is often faster and more efficient than heterogeneous equilibrium. Additionally, homogeneous equilibrium is often better able to reach thermodynamic equilibrium than heterogeneous equilibrium.
On the other hand, there are also some disadvantages associated with homogeneous equilibrium. Most notably, homogeneous equilibrium can lead to equilibrium constants that are highly dependent on the concentration of reactants and products, making it difficult to predict the outcome of the reaction. Additionally, the reaction may be difficult to control.
Additionally, the reaction may be difficult to control. Finally, homogeneous equilibrium does not always lead to maximum yields of products.
Advantages and disadvantages of heterogeneous equilibrium
In chemistry, homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium are two distinct forms of chemical equilibrium. Homogeneous equilibrium occurs when all the reactants and products of a reaction exist in the same phase, while heterogeneous equilibrium occurs when the reactants and products exist in different phases. Both have their advantages and disadvantages, making them useful in different situations.
The main difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium lies in the fact that in heterogeneous equilibrium, there is an additional energy barrier, called the “interfacial energy”, that must be overcome in order for the reactants to reach equilibrium. This can be beneficial, as it can slow down the reaction and allow for more precise control.
On the other hand, it can also be a disadvantage, as it can slow down the reaction too much, making it difficult to achieve the desired reaction rate. In addition, heterogeneous equilibrium is typically more complicated than homogeneous equilibrium, making it harder to analyze.
Examples of homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium
When it comes to chemical reactions, the concept of equilibrium is important. Equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction. Homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium are two different types of equilibrium.
Homogeneous equilibrium occurs when all the reactants and products involved are in the same phase, such as a gas or liquid. Heterogeneous equilibrium, on the other hand, involves more than one phase, such as a gas and a solid.
The key difference between the two is that in heterogeneous equilibrium, the reactants and products are not in the same phase. This means that they interact differently, resulting in different chemical properties. Understanding the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium is essential for studying and predicting chemical reactions.
Understanding the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium is essential for studying and predicting chemical reactions.
Resources
The difference between homogenous and heterogeneous equilibrium can have a significant effect on how a system functions. Homogeneous equilibrium occurs when the components of a system are all the same, while heterogeneous equilibrium occurs when the components of a system are different. In homogeneous equilibrium, the same reaction will occur in any environment, while in heterogeneous equilibrium, the reaction will depend on the environment.
For example, a homogeneous equilibrium could exist in a solution where the concentration of the reactants and products remain the same regardless of the environment, while a heterogeneous equilibrium could exist in a solution where the reaction only occurs in a specific environment. Understanding the differences between these two states of equilibrium can help us better understand how different systems and reactions work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibria are two different types of chemical equilibria. Homogeneous equilibria involve only one type of species, while heterogeneous equilibria involve two or more types of species.
Homogeneous equilibria involve the reaction of two or more reactants to form products in the same phase, while heterogeneous equilibria involve the reaction of two or more reactants to form products in different phases. Homogeneous equilibria are more common in nature and occur more quickly than heterogeneous equilibria.