The human body is a complex network of structures and systems, each with distinct functions and characteristics. Among these are lesser-known but crucial elements like the frenulum and fourchette, which, despite their small size, play significant roles in our anatomy. These parts are not commonly discussed outside of medical circles, yet they are integral to the health and functioning of related systems.
The frenulum is a small fold of tissue that secures or restricts the motion of a mobile organ in the body. For example, the frenulum under the tongue helps in speech and swallowing. The fourchette, on the other hand, refers specifically to a fold of tissue located at the posterior part of the vulva, playing a role in the structural integrity of this area. While both structures serve as connective tissue, their functions and locations significantly differ, highlighting the diversity of human anatomy.
Insight into these anatomical features is not just academically interesting but also essential for understanding certain medical conditions and their treatments. Exploring their anatomy, issues, and significance can help in recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate medical attention for related health issues.
Frenulum Defined
Location and Function
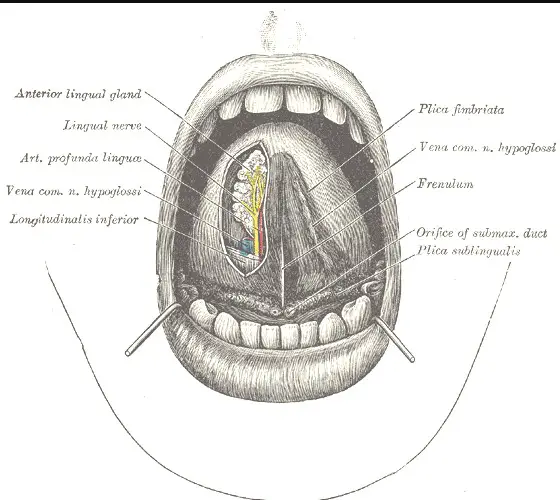
The frenulum is a small fold of tissue that primarily serves to restrict or secure the motion of an organ or part it is connected to. It is most famously known as the frenulum linguae, often simply referred to as the “tongue-tie,” found beneath the human tongue. This frenulum helps in anchoring the tongue to the mouth floor, playing a critical role in speech and swallowing.
However, frenula (plural for frenulum) are not limited to the oral cavity. They are also found in other parts of the body such as the lips, where they help in connecting the lips to the gum and controlling their movements. Additionally, the frenulum is present in the genital area, connecting various parts and ensuring they maintain their position, significantly affecting the function and physical comfort during activities like intercourse.
Variations Across the Body
The structure and sensitivity of frenula can vary widely. In the mouth, the frenulum’s sensitivity is vital for speech and eating, making any anomalies like an overly tight frenulum (ankyloglossia) potentially problematic. In contrast, the penile frenulum plays a role in sexual activity, where its elasticity can affect comfort and functionality.
Fourchette Defined
Specific Anatomy and Location
The fourchette is a less commonly discussed structure found in female anatomy. This fold of skin is located at the vaginal vestibule, where the labia minora meet at the back. Often described as forming the lower border of the vaginal orifice, the fourchette can be a focal point for issues related to physical trauma, such as during childbirth.
Role in Human Body
In terms of function, the fourchette provides structural support and flexibility to the vulva, accommodating changes that occur during intercourse and childbirth. It also plays a protective role, helping to guard the vaginal and urethral openings against infections and physical damage.
Comparative Anatomy
Structural Differences
When comparing the frenulum and the fourchette, one notices distinct differences in structure and location. The frenulum, as a connecting tissue, appears in various body parts as either thin and elastic or relatively robust, depending on its role. For instance, the frenulum in the mouth is much thinner and more elastic compared to the one in the genital area.
The fourchette, on the other hand, exists only within the female anatomy and is characterized by its unique placement and function related to the reproductive system. It’s typically composed of softer, more pliable tissue, which is necessary for its role in accommodating the physical demands placed on it.
Functional Distinctions
Functionally, the frenulum and fourchette serve different purposes despite both being types of connective tissue. The frenulum’s primary role is to provide stability and mobility to the organs it connects, crucial for functions such as speaking, eating, and sexual activity. The fourchette is more about structural integrity and protection within the female genital anatomy, adapting to physical stresses such as those encountered during sexual activities and childbirth.
Significance in Health
Medical Relevance of the Frenulum
Health issues related to the frenulum can range from minor to severe, impacting daily activities and quality of life. Conditions such as tongue-tie in infants can affect feeding, speech, and later, eating habits. In adults, an overly tight penile frenulum can lead to discomfort or pain during sexual activities, sometimes requiring surgical intervention.
Medical Relevance of the Fourchette
Similarly, the fourchette can be implicated in various health issues, primarily related to physical trauma and recovery post-injury. Damage to the fourchette, such as tearing during childbirth, requires careful management to prevent infection and promote healing. Understanding its importance can lead to better preventive measures during physical activities and more informed treatment options post-injury.
Common Issues
Issues Related to the Frenulum
The frenulum can be prone to several medical conditions that may impact daily functioning and comfort. Ankyloglossia, commonly known as tongue-tie, is one of the most well-known conditions where the frenulum under the tongue is too short and tight, causing difficulties in speech, eating, and, in infants, breastfeeding. Similarly, a tight frenulum in the genital area can lead to discomfort or pain during sexual activities, and in severe cases, can tear during intercourse.
Another issue is frenulum breve in males, where the frenulum of the penis is too short, causing pain during erections or sexual activity. This condition can sometimes lead to the frenulum tearing, which is not only painful but can also lead to subsequent scar formation and further restrictions in the tissue’s natural elasticity.
Issues Related to the Fourchette
The fourchette is susceptible to physical damage primarily through mechanical stress. During childbirth, sexual activity, or due to certain medical conditions like lichen sclerosus, the fourchette can tear or become irritated. Such injuries can lead to pain, bleeding, and sometimes, an increased risk of infection if not properly managed. Chronic irritation in this area can also lead to scarring, which may permanently affect its elasticity and function.
Medical Treatments
Treatments for Frenulum-Related Conditions
The approach to treating issues with the frenulum largely depends on the severity and location of the condition:
- Surgical intervention is often recommended for tongue-tie, especially when it significantly impacts feeding in infants or speech in older children and adults. This procedure, known as a frenulotomy, involves a simple cut to release the tight frenulum and is usually a quick and straightforward procedure with minimal complications.
- For issues with the penile frenulum, treatment may involve a frenuloplasty, a surgical procedure that aims to increase the length of the frenulum through a small incision. This surgery helps relieve the tension and allows for normal movement without discomfort.
Treatments for Fourchette-Related Conditions
Treatment options for issues involving the fourchette are typically conservative and focus on managing symptoms and facilitating healing:
- Immediate care for tears involves cleaning the area and, in some cases, suturing if the tear is significant. It’s crucial to maintain hygiene and monitor for signs of infection during the healing process.
- For chronic conditions or recurrent issues, a topical steroid cream may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and aid in healing. In severe cases, surgical intervention might be necessary to correct anatomical changes resulting from scarring.
Preventive Care
Tips for Maintaining Frenulum Health
Maintaining the health of the frenulum involves several straightforward steps:
- Regular check-ups are essential, especially for infants, to ensure that conditions like tongue-tie are diagnosed and treated early.
- Good hygiene is crucial, particularly for the oral and genital frenula, to prevent infections and complications.
- Being mindful of symptoms such as pain, restricted movement, or discomfort during normal activities can help catch potential issues early.
Tips for Maintaining Fourchette Health
The fourchette can be cared for with simple, preventive measures:
- Gentle care during activities that put stress on the area, including sexual activity and childbirth, can prevent tears and irritation.
- Proper hygiene is crucial for preventing infections, especially if there is any damage or injury to the area.
- Consulting a healthcare provider for persistent issues or discomfort is important as it might indicate an underlying condition that needs medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a frenulum?
A frenulum is a connective tissue primarily found at various joints of the body, such as under the tongue, lips, or the head of a penis. It helps in stabilizing the motion of the organ it’s attached to, ensuring proper function and mobility.
Where is the fourchette located?
The fourchette is situated at the back of the vaginal opening, forming a small fold where the labia minora meet. This anatomical structure plays a critical role in the support and structural configuration of the female genitalia.
How do issues with the frenulum affect health?
Problems with a frenulum, like frenulum breve or ankyloglossia (tongue-tie), can impair functions such as speech, swallowing, and, in some cases, sexual activity. Treatment often involves simple surgical procedures to relieve the restriction.
Can the fourchette be damaged?
Yes, the fourchette can be damaged, typically through activities that put pressure on the area, such as childbirth or certain physical activities. Tears or fissures in this area can be painful but are usually treatable with proper medical care.
Conclusion
Understanding the frenulum and fourchette provides more than just anatomical knowledge; it offers insights into how intricate and interconnected human body structures are. Each small part, often overlooked, holds its unique importance and function that can significantly impact an individual’s health and quality of life.
Recognizing and addressing issues related to these structures can lead to better health outcomes and a deeper appreciation for the body’s complexity. This awareness is crucial not only for medical professionals but also for individuals to understand their bodies better and foster proactive health management.