The concept of transition series in chemistry can be intimidating to those just starting out in the field. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the differences between the first, second, and third transition series. We’ll discuss the location of each series on the periodic table, the number of electrons found in each series, and the characteristics of the elements in each series.
By the end of this post, you’ll have a better understanding of the transition series and how they differ from one another.
Overview of the first transition series
The first transition series is made up of elements from the fourth period of the periodic table and includes elements with atomic numbers 21 to 30. This series consists of titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and zinc.
In general, the first transition series elements are more reactive than others in the same period. They are also more electronegative, have higher melting points, and form more stable compounds.
Furthermore, the first transition series elements are more likely to form colored compounds than their counterparts in the second and third transition series. This is because they have more unpaired electrons which can absorb visible light, resulting in the colored compounds.
Overview of the second transition series
The second transition series of elements is a group of elements that form part of the periodic table. It is composed of elements with atomic numbers from 21 to 30, and includes titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, and zinc. These elements have a particular order that is based on their atomic number, with titanium being the lightest and zinc the heaviest.
These elements have a particular order that is based on their atomic number, with titanium being the lightest and zinc the heaviest. Compared to the first transition series, the second transition series is characterized by having higher atomic numbers and having elements that become increasingly electronegative. Additionally, the second transition series has a greater number of elements with higher oxidation states, making them more reactive.
This makes them ideal for industrial applications, such as in the production of steel and alloys. Finally, the third transition series is composed of elements with atomic numbers from 39 to 48, and includes yttrium, zirconium, niobium, molybdenum, technetium, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, and cadmium. These elements are known for their ability to form strong bonds and their high melting points, making them useful for a variety of applications.
Overview of the third transition series
The Third Transition Series, also known as the Lanthanide Series, is a group of elements in the periodic table that, when compared to the First and Second Transition Series, have a few key differences. For starters, the Third Transition Series has a much higher atomic number, ranging from 57 to 71, and they also have a wider range of electron configurations. Additionally, they often show several oxidation states, making them highly reactive in comparison to the First and Second Transition Series.
They are also much softer and have a lower melting point than their counterparts. All of these characteristics make the Third Transition Series a unique and important part of the periodic table.
Differences between the first, second, and third transition series
The first, second, and third transition series are unique in their own ways. In the first transition series, the elements have the lowest energy level and the highest atomic number. In the second transition series, the elements have the highest energy level and the lowest atomic number.
Finally, in the third transition series, the elements have an intermediate energy level and an intermediate atomic number. A key difference between the three series is that the first series has the most reactive elements, while the second series has the least reactive elements, and the third series has elements with reactivity in between the other two series.
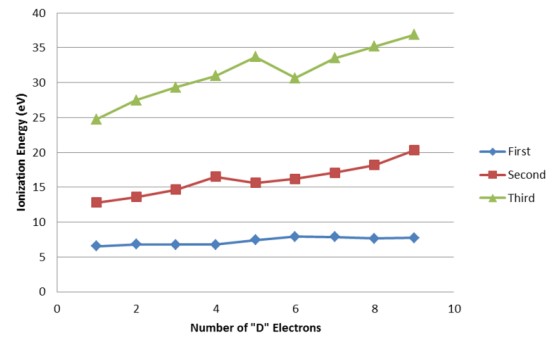
Additionally, the elements in the first series have the highest ionization energies, while the elements in the third series have the lowest ionization energies, and the elements in the second series have ionization energies in between the other two series.
Practical applications of the three transition series
The three transition series are a classification of elements that is based on the number of electrons in the outermost shell of the atom. This number determines the element’s properties and chemical behavior. The first transition series consists of elements with four electrons in the outermost shell, the second transition series has five, and the third transition series has six.
The first transition series consists of elements with four electrons in the outermost shell, the second transition series has five, and the third transition series has six. The differences between the three transition series are significant when it comes to practical applications. By understanding the differences, chemists and other scientists can more accurately predict the behavior of different elements and compounds.
For instance, elements from the first transition series are often used in applications such as gas turbines, catalysts, and rocket fuels. Elements from the second transition series are often used in applications such as medical imaging and sensors, while elements from the third transition series are often used in applications such as lasers and X-ray tubes. Knowing and understanding the differences between the three transition series is an important part of using them in practical applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the first, second, and third transition series elements have a variety of differences. The first transition series elements are generally characterized by their metallic properties, such as malleability and ductility. The second transition series elements, on the other hand, are characterized by their non-metallic properties, such as higher electronegativity and higher ionization energies.
Lastly, the third transition series elements are characterized by their higher nuclear charge and larger atomic size. All of these differences make the transition series elements unique and essential components of the periodic table.