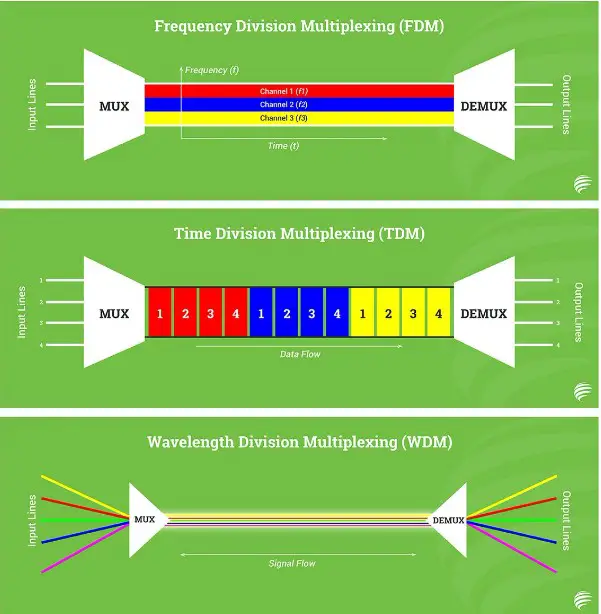
As technology advances, the speed and capacity demands of telecommunications networks increase. To meet these demands, different multiplexing techniques have been developed, such as FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing), TDM (Time Division Multiplexing), and WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing).
In this blog, we will discuss the differences between these three multiplexing techniques, and why they are important for telecommunications networks.
Overview of fdm
FDM, or Frequency Division Multiplexing, is a type of multiplexing technology used in telecommunications networks to increase the capacity of a given line by dividing it into multiple channels. This allows multiple users to access the same line, each with their own frequency.
FDM is different from TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) and WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) in that it divides a single line into multiple frequencies, allowing multiple signals to be transmitted simultaneously. Whereas TDM divides a line into multiple time slots, and WDM divides a line into multiple wavelengths. All three technologies are used in modern communications networks to increase capacity and allow multiple users to access the same line.
Overview of tdm
Telecommunications networks rely on different technologies to transmit data, such as Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM), Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) and Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM). Each of these technologies have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, and which one is best for a particular application depends on the specific requirements of the network. FDM divides the available frequency range into multiple channels, each of which can carry a separate signal.
FDM divides the available frequency range into multiple channels, each of which can carry a separate signal. TDM divides the available time into slots, each of which can be used for a different signal. WDM divides the available range of light wavelengths into channels, each of which can carry a different signal.
All three technologies are used to increase the capacity of a telecommunications network by allowing multiple signals to be sent over the same physical connection.
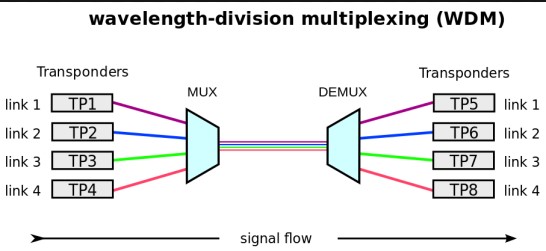
Overview of wdm
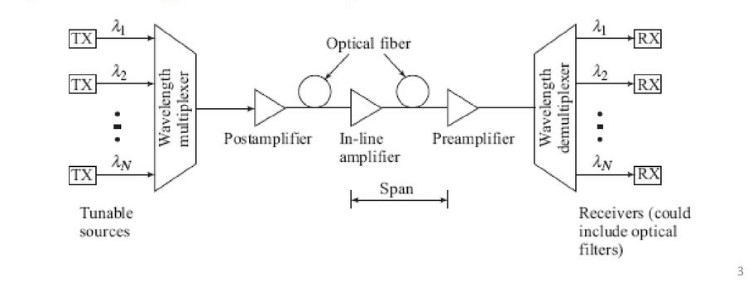
WDM (Wavelength-Division Multiplexing) is a method of combining multiple signals into one, allowing for the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals over a single medium. It is different from FDM (Frequency-Division Multiplexing) and TDM (Time-Division Multiplexing) in that it uses different wavelengths, or colors of light, to carry different signals.
This allows for more efficient use of the transmission medium, as multiple signals can be sent over the same fiber, rather than taking up multiple fibers. WDM also allows for faster transmission speeds, as the light signals are not limited by time delays like in TDM. With WDM, the wavelength of each signal can be precisely set and adjusted to ensure that no interference occurs between signals, resulting in higher quality transmissions.
Key differences between fdm, tdm and wdm
FDM, TDM and WDM are all communication networks that are used to transmit data over long distances. Each of them has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different types of applications.
FDM stands for Frequency Division Multiplexing, which divides the frequency spectrum of a channel into multiple sub-channels to transmit multiple signals simultaneously. TDM stands for Time Division Multiplexing, which divides the transmission time into multiple frames in order to send multiple signals simultaneously. Finally, WDM stands for Wavelength Division Multiplexing, which uses multiple wavelengths of light to send multiple signals at the same time.
Each of these technologies has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different types of applications. FDM is suitable for applications that require low bandwidth and low cost.
TDM, on the other hand, is more suitable for applications that require higher bandwidth. It is also more efficient than FDM, allowing multiple signals to be sent at the same time.
Finally, WDM is the most expensive of the three technologies, but is the most efficient and can support the highest bandwidths. Overall, the choice of technology will depend on the specific application. FDM is suitable for low cost, low bandwidth applications, while TDM and WDM are better suited for applications that require higher bandwidth and faster speeds.
Advantages and disadvantages of fdm, tdm and wdm
From the perspective of data transmission, there are three main transmission techniques: Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM), Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), and Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM). Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, and understanding the differences between them can help businesses select the best option for their networking needs. FDM takes multiple signals and combines them onto a single transmission medium, such as a copper cable or fiber optic cable.
FDM takes multiple signals and combines them onto a single transmission medium, such as a copper cable or fiber optic cable. TDM divides a single data stream into multiple streams, each of which is sent over a different channel. Finally, WDM multiplexes multiple optical signals onto a single strand of fiber optic cable, allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth.
In terms of advantages, FDM is the most economical method, since it requires minimal equipment and is easy to set up. TDM is more efficient, since it allows for more simultaneous users on the same line, while WDM is the most efficient, since it allows for a greater capacity of data to be sent over the same transmission medium.
All three methods offer unique advantages and disadvantages, and businesses must consider their individual requirements when selecting the best option.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FDM, TDM and WDM are three different technologies used in telecommunication networks for the purpose of data transmission. FDM is Frequency-Division Multiplexing, which splits a broad band of frequencies into multiple narrow bands and allows simultaneous transmission of multiple signals.
WDM is Wavelength-Division Multiplexing, which uses multiple wavelengths of light to transmit data over a fiber optic cable. Each technology has its own advantages and disadvantages, and which one is best suited for a particular application depends on the network design and requirements.