Equilibrium constants and rate constants are two important concepts in chemistry that have a major impact on chemical reactions. In this blog post, we’ll explore the difference between equilibrium constants and rate constants, and how they interact to influence a chemical reaction.
We’ll look at what each constant measures, how they are related, and how understanding the difference can help us better understand chemical reactions.
Physical explanation of equilibrium constant and rate constant

Equilibrium constant and rate constant are two of the most important concepts in chemical kinetics. While both are related to equilibrium, they have very different meanings and implications. The equilibrium constant (K) is a measure of the relative concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium.
It is calculated by taking the ratio of the product concentrations divided by the reactant concentrations, raised to the power of their respective stoichiometric coefficients. On the other hand, the rate constant (k) is a measure of how quickly a chemical reaction reaches equilibrium.
It is calculated by taking the rate of reaction (measured in moles/liter/second) and dividing it by the concentrations of the reactants. The most important difference between equilibrium constant and rate constant is that the former is determined only at equilibrium, while the latter is determined throughout the entire reaction process.
Chemical considerations for equilibrium constant and rate constant
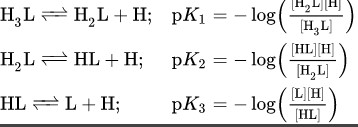
When it comes to chemical reactions, it is important to understand the difference between an equilibrium constant and a rate constant. Both are related to the thermodynamics and kinetics of a reaction, but the equilibrium constant focuses on the position of the reaction at equilibrium, while the rate constant looks at the speed of the reaction. In other words, the equilibrium constant is a measure of the tendency of a reaction to reach equilibrium, while the rate constant tells us how fast the reaction is taking place.
In other words, the equilibrium constant is a measure of the tendency of a reaction to reach equilibrium, while the rate constant tells us how fast the reaction is taking place.
Calculation of equilibrium constant and rate constant
The equilibrium constant and the rate constant are two important concepts in chemical kinetics. They are closely related, but there is an important distinction between them. The equilibrium constant is a measure of the ratio of concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium, while the rate constant is an expression of the rate of the reaction at a given temperature.
In other words, the equilibrium constant describes the balance between the reactants and products, whereas the rate constant describes the speed with which the reaction proceeds.
Examples of equilibrium constant and rate constant
The difference between an equilibrium constant and a rate constant is one of the most confusing topics in chemistry. An equilibrium constant is a measure of the distribution of products and reactants in a chemical reaction at equilibrium, while a rate constant measures the speed at which a reaction occurs. The equilibrium constant is determined by the concentrations of the reactants and products, whereas the rate constant is determined by the activation energy of the reaction.
The equilibrium constant is determined by the concentrations of the reactants and products, whereas the rate constant is determined by the activation energy of the reaction. An example of an equilibrium constant is Kc, which is the concentration of products divided by the concentration of reactants at equilibrium. An example of a rate constant is k, which is the speed at which a reaction occurs and is determined by the activation energy of the reaction.
In summary, the equilibrium constant is a measure of the distribution of products and reactants in a chemical reaction at equilibrium, while the rate constant is the speed at which a reaction occurs and is determined by the activation energy of the reaction.
Applications of equilibrium constant and rate constant
The concept of equilibrium constant and rate constant are integral parts of chemical kinetics. While both involve a numerical value that relates to the rate of a chemical reaction, they each have distinct differences and applications.
The equilibrium constant is a fixed value that represents the ratio of products to reactants at a given temperature, and it is used to determine the rate at which a reaction will proceed. The rate constant, on the other hand, is a variable that relates to the speed at which a reaction occurs. It is largely dependent on the temperature and can be used to predict the rate of a reaction at different temperatures.
In conclusion, the equilibrium constant and rate constant are two different concepts that are used to measure the rate of chemical reactions.
Final Touch
In conclusion, the difference between an equilibrium constant and a rate constant is that an equilibrium constant is a measure of the relative concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium, while a rate constant is a measure of the speed at which a reaction occurs. The value of an equilibrium constant does not change with time, while the value of a rate constant does. Both constants are important measures of a chemical reaction and can be used to better understand the behavior of a system.

