Equalization and neutralization are two fundamental processes widely employed across various industries, each serving distinct purposes and applications. While often mentioned in the same breath due to their importance in maintaining balance and stability, they cater to different needs. From enhancing audio quality in the music industry to treating wastewater before discharge, understanding these processes is crucial for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
The difference between equalization and neutralization primarily lies in their applications and objectives. Equalization is a process used to adjust the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal, commonly applied in audio processing to enhance sound quality. On the other hand, neutralization refers to a chemical reaction where an acid and a base react to form water and a salt, extensively used in wastewater treatment to balance pH levels.
Both processes play pivotal roles in their respective fields. Equalization allows for the fine-tuning of audio outputs to meet desired specifications, significantly improving user experience in multimedia applications. Neutralization, meanwhile, is essential for environmental management, ensuring that industrial effluents meet regulatory standards before release, thus protecting aquatic life and maintaining ecosystem health.
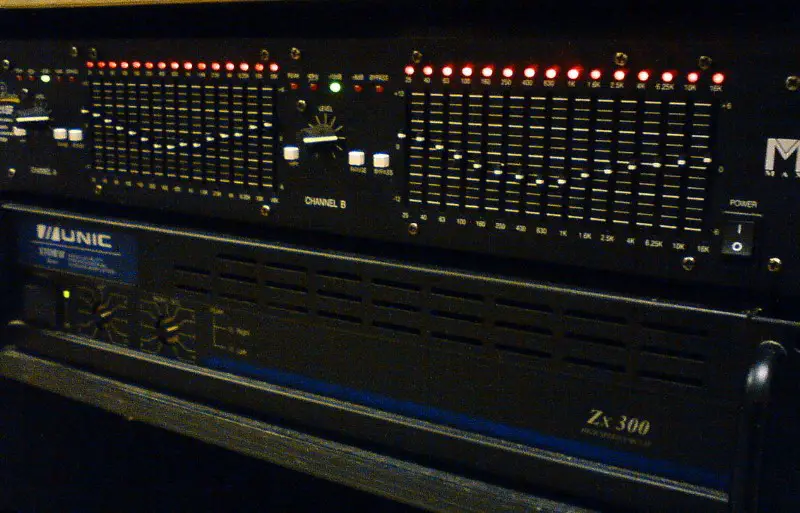
Equalization Explained
Definition and Purpose
Equalization is a crucial technique in audio processing and telecommunications. It involves adjusting the balance of frequency components within an electronic signal. The primary purpose of equalization is to enhance sound quality, ensuring that audio outputs are clear, balanced, and in harmony with the listener’s preferences or the requirements of a specific environment.
Applications and Examples
- Music Production: Adjusting tracks to highlight or minimize certain instruments.
- Live Performances: Tailoring sound to fit the acoustics of a venue.
- Broadcasting: Ensuring clear voice transmission without background noise.
Core Principles
Key Components
The key components of equalization include:
- Filters: High-pass, low-pass, band-pass, and notch filters.
- Equalizers: Devices or software that apply these filters to an audio signal.
Process Overview
- Identifying Frequencies: Determining which frequencies need adjustment.
- Applying Filters: Using filters to enhance or suppress these frequencies.
- Adjusting Levels: Fine-tuning the signal to achieve the desired sound quality.
Techniques and Methods
Audio Engineering
- Graphic Equalizer: Allows adjustment of multiple frequency bands via sliders.
- Parametric Equalizer: Provides more precise control over frequency, bandwidth, and gain.
Water Treatment
- pH Adjustment: Using equalization concepts to balance the chemical composition of water.
Neutralization Defined
Basics and Objectives
Neutralization is a chemical process where an acid and a base react to form water and a salt. This reaction is vital for balancing pH levels in various substances, making it essential for both environmental protection and industrial applications.
Common Uses
- Wastewater Treatment: Adjusting pH levels to meet environmental standards.
- Manufacturing Processes: Neutralizing byproducts to ensure worker safety and environmental compliance.
Fundamental Concepts
Chemical Reactions Involved
The fundamental reaction can be summarized as:
Acid+Base→Water+SaltAcid+Base→Water+Salt
Procedure Details
- Measurement: Determining the current pH level of a solution.
- Calculation: Figuring out the necessary quantity of acid or base for neutralization.
- Application: Adding the neutralizing agent to the solution.
Applications
Wastewater Treatment
- pH Neutralization: Ensuring discharged water does not harm aquatic ecosystems.
Acid-Base Neutralization
- Industrial Cleaning: Neutralizing acidic or basic residues from equipment.
Comparative Analysis
Differences in Purpose
- Equalization: Tailored towards enhancing audio quality or balancing chemical compositions in water.
- Neutralization: Focused on achieving a chemical balance, particularly by adjusting pH levels.
Differences in Application
- Equalization is predominantly used in audio engineering and water treatment for quality and balance.
- Neutralization is employed in chemical processes, environmental management, and manufacturing for safety and compliance.
Equalization vs. Neutralization in Water Treatment
Process Comparison
- Equalization in water treatment involves adjusting chemical compositions for balance.
- Neutralization directly targets pH levels to achieve environmental standards.
Outcome and Efficiency
- Equalization: Aims for a balanced chemical composition, improving water quality for various uses.
- Neutralization: Ensures compliance with environmental standards, protecting aquatic life and ecosystems.
In Audio Engineering and Chemistry
Contrasting Techniques
- Audio Engineering: Equalization manipulates sound frequencies for desired outcomes.
- Chemistry: Neutralization involves precise chemical reactions to achieve balance.
Impact and Results
- Audio Engineering: Enhanced sound quality, tailored to listener preferences or requirements.
- Chemistry: Safe, balanced chemical compositions, essential for environmental and industrial safety.
Advantages and Limitations
Benefits of Equalization
Equalization offers numerous benefits, especially in audio engineering and water treatment.
- Improved Sound Quality: In audio engineering, it allows for the precise shaping of sound, ensuring that music and speech are clear and pleasant to the listener. By adjusting frequencies, unwanted noise can be minimized, and desired tones can be highlighted.
- Balanced Chemical Composition: In water treatment, equalization techniques adjust the chemical composition of water, ensuring a balanced ecosystem and preventing harm to aquatic life.
Benefits of Neutralization
Neutralization plays a critical role in maintaining environmental balance and ensuring safety in various industrial processes.
- Environmental Protection: By neutralizing acidic or basic wastewater, it prevents harmful impacts on aquatic ecosystems and complies with environmental regulations.
- Safety in Industrial Processes: Neutralization ensures that the byproducts of manufacturing processes are safe for disposal or further use, reducing the risk of chemical accidents.
Challenges and Considerations
Equalization Difficulties
Despite its benefits, equalization comes with its own set of challenges.
- Complexity in Audio Engineering: Achieving the perfect sound balance requires skill and experience, as incorrect settings can lead to distorted or unnatural sound.
- Chemical Balance in Water Treatment: Maintaining the right chemical balance through equalization is crucial, as any imbalance can adversely affect water quality and aquatic life.
Neutralization Challenges
Neutralization also faces challenges, particularly in handling complex chemical reactions and ensuring environmental compliance.
- Accurate pH Adjustment: Achieving the exact pH level needed for safe disposal or further processing requires precise calculations and monitoring.
- Handling of Reaction Byproducts: Some neutralization reactions produce byproducts that require further treatment before disposal.
Real-World Implications
Environmental Impact
Both equalization and neutralization have significant environmental impacts.
- Equalization in Water Treatment: Helps maintain the natural balance of water bodies, ensuring that discharged water does not disturb aquatic ecosystems.
- Neutralization: By safely neutralizing acids and bases, it prevents potential environmental hazards, contributing to the health and safety of ecosystems.
Industrial and Commercial Significance
- Equalization: In the commercial domain, especially in audio production and broadcasting, equalization is essential for delivering high-quality sound. It directly impacts consumer satisfaction and engagement.
- Neutralization: Industrially, it’s crucial for meeting environmental standards and ensuring the safety of chemical processes, directly affecting operational costs and regulatory compliance.
Case Studies
Success Stories in Water Treatment
One notable success story involves a wastewater treatment plant that implemented advanced equalization techniques to manage seasonal variations in wastewater composition. By using automated systems to adjust the chemical balance of the incoming water, the plant was able to consistently meet discharge regulations, significantly reducing the impact on the local river ecosystem. This approach not only ensured compliance with environmental laws but also improved the efficiency of the treatment process, leading to cost savings and enhanced community relations.
Breakthroughs in Audio Quality Improvement
In the realm of audio engineering, a groundbreaking case involved the development of a new equalization technology that allowed sound engineers to isolate and adjust frequencies with unprecedented precision. This technology was applied in the remastering of historical music recordings, restoring them to a level of clarity and depth never before heard. The project not only preserved cultural heritage but also set new standards for audio quality in the music industry. It demonstrated how innovative equalization techniques could unlock new potentials in sound, enhancing the listening experience for audiences worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is equalization?
Equalization is a technique used in audio processing and telecommunications to adjust the balance of frequency components within an electronic signal. By manipulating various frequencies, it enhances the overall sound quality and clarity, making it a vital tool in music production, broadcasting, and live performances to ensure the audio output matches the intended auditory experience.
How does neutralization work?
Neutralization is a chemical process where acids and bases react to form water and a salt. This reaction is crucial in various industries, especially in wastewater treatment, where it is used to adjust the pH levels of effluent to safe levels. By carefully adding a base to an acidic solution or vice versa, neutralization ensures that the discharged water is neither too acidic nor too alkaline, safeguarding aquatic life and maintaining the health of the ecosystem.
Why is equalization important in audio engineering?
Equalization is essential in audio engineering because it allows sound engineers to mold audio signals in a way that fits the intended context and user experience. By selectively boosting or cutting frequencies, engineers can eliminate undesirable sounds, emphasize vocals or specific instruments, and adapt recordings to different listening environments, thereby greatly enhancing the quality and impact of the audio.
What are the environmental impacts of neutralization?
The environmental impacts of neutralization are predominantly positive, as it plays a crucial role in pollution control. By neutralizing acidic or basic wastewater before it is discharged into water bodies, this process helps prevent harm to aquatic organisms, protects the integrity of ecosystems, and ensures compliance with environmental regulations. It effectively mitigates the adverse effects of industrial effluents on nature.
Conclusion
Equalization and neutralization, despite serving different purposes, are indispensable processes in their respective domains. Each facilitates a form of balance, whether it’s in the harmonious distribution of sound frequencies for an enriched audio experience or the neutralization of pH levels to protect the environment. Their significance cannot be overstated, as they contribute to advancements in technology and environmental conservation.
Understanding the intricacies and applications of equalization and neutralization provides insight into their critical roles across various industries. As we continue to push the boundaries of technology and strive for environmental sustainability, these processes will remain at the forefront, ensuring quality and compliance. Their contribution to enhancing our daily lives and protecting our planet highlights the importance of mastering these fundamental principles.

